N8N Discord Workflow Template – Turn Your Server Into An Automated Powerhouse
Imagine your Discord server running smoothly in the background, messages handled, questions answered, and updates shared, while you stay focused on the work that really moves you or your business forward. That is the promise of automation with n8n and a well designed Discord workflow.
This guide walks you through that journey. You will start from the common pain points of manual Discord management, shift into a more empowered automation mindset, then use a practical n8n Discord workflow template to build your own AI powered assistant. Along the way, you will see how each step lays the foundation for more time, more clarity, and more space to grow.
From Manual Discord Management To Scalable Automation
Running an active Discord community can be incredibly rewarding, but it also demands constant attention. Repetitive questions, routine announcements, and basic support can quickly eat up your time and energy. It is easy to feel like you are always reacting instead of leading.
Automation with n8n changes that dynamic. By connecting your Discord server, a custom bot, and OpenAI, you can:
- Respond to messages consistently, even when you are offline
- Automate recurring updates and announcements
- Centralize AI powered assistance inside your existing channels
- Scale your community without scaling your workload
The n8n Discord workflow template you are about to set up is not just a technical tool. It is a starting point for a more focused, intentional way of managing your community and your time.
Adopting An Automation Mindset With n8n
Before you dive into the setup, it helps to approach this template with the right mindset. Think of n8n as your flexible automation studio. Each workflow you build is a small system that saves you time, reduces errors, and frees your attention for higher value work.
This Discord workflow template is your first step toward:
- Delegating repetitive tasks to an AI agent
- Designing clear processes instead of improvising every day
- Experimenting with automation, then refining as you learn
You do not need to build everything at once. Start with a simple, working setup. Then gradually customize the AI behavior, expand to more channels, and introduce smarter logic. Each improvement compounds, and your Discord server becomes more self managing over time.
What You Need Before You Start
To turn this template into a working Discord AI assistant, make sure you have these essentials ready:
Prerequisites
- n8n account to host and run your workflow
- Discord bot created in the Discord Developer Portal
- OpenAI API key to power the AI responses
- Discord server access with permission to add and configure bots
Once you have these in place, you are ready to build a system that works alongside you, not against your time.
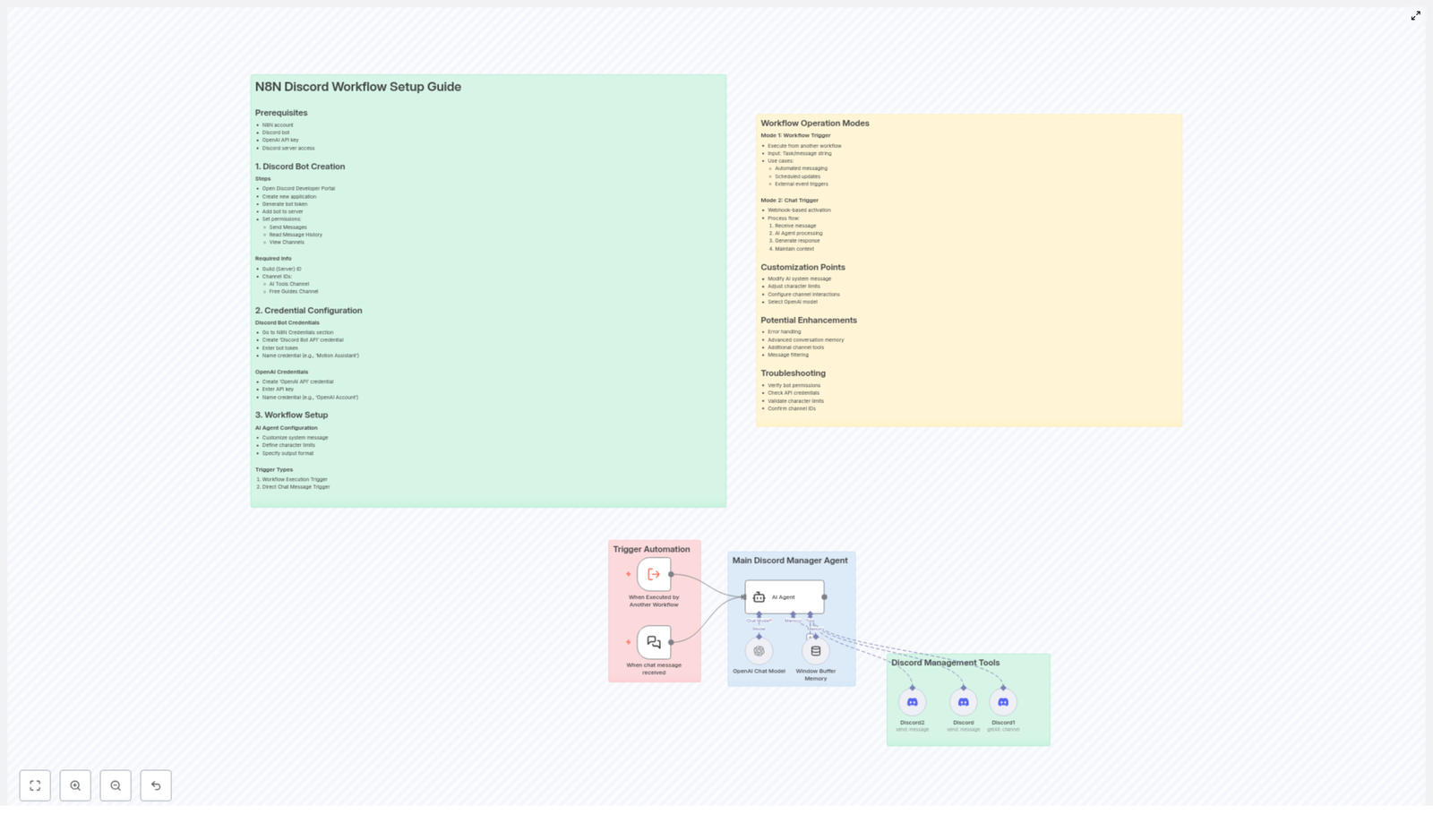
Step 1 – Create And Configure Your Discord Bot
Your Discord bot is the visible face of your automation. It is how your community interacts with the AI powered workflows you define in n8n. Setting it up is straightforward, and once done, you rarely need to touch it again.
Create The Bot In Discord
- Open the Discord Developer Portal
- Create a new application for your bot
- Generate a bot token that n8n will use to connect
- Add the bot to your server using the OAuth2 URL
Set The Right Permissions
To function correctly, your bot needs access to specific Discord permissions. At minimum, enable:
- Send Messages
- Read Message History
- View Channels
These give your workflow the ability to read incoming messages, generate AI responses, and post them back into the correct channels.
Gather Key IDs For Your Workflow
n8n will need to know exactly where to listen and respond inside your server. Make sure you have:
- Guild (Server) ID
- Channel IDs such as:
- AI tools or assistant channel
- Free guides or resources channel
With your bot ready, you can now connect Discord and OpenAI directly into your n8n environment.
Step 2 – Connect Your Credentials In n8n
Credentials are the secure bridge between n8n and your external services. Setting them up correctly ensures your workflow runs reliably and safely.
Discord Bot Credentials
- In n8n, go to the Credentials section
- Create a new credential of type “Discord Bot API”
- Paste in your Discord bot token
- Give it a clear name, for example “Motion Assistant”
This tells n8n which bot to use when sending or reading messages from your server.
OpenAI API Credentials
- In the same Credentials area, create a new “OpenAI API” credential
- Enter your OpenAI API key
- Name it something recognizable, such as “OpenAI Account”
With both credentials configured, your workflow can now act as a bridge between Discord and OpenAI, turning raw messages into helpful, AI powered responses.
Step 3 – Shape Your AI Agent Inside The Workflow
This is where your automation starts to feel personal. You are not just wiring tools together, you are designing the behavior of your Discord AI assistant.
AI Agent Configuration
- Customize the system message to match your Discord management style. You can instruct the AI to behave like a helpful moderator, a friendly tutor, or a concise assistant.
- Define character limits so responses stay readable inside Discord. A typical setting is a maximum of 1800 characters per message.
- Specify text formatting that fits Discord, such as code blocks, bold, italics, or structured bullet points, so answers look clean and professional.
These small choices add up. They help your bot feel aligned with your brand, your tone, and your community values.
Step 4 – Choose How Your Workflow Gets Triggered
The same n8n Discord workflow template can support different ways of working, depending on how you want to interact with it. You can trigger it from other workflows, or directly from chat messages.
Main Trigger Types In The Template
- Workflow Execution Trigger
Use this when you want to call the Discord AI workflow from another n8n workflow. You pass in a task or message string, and the template handles the AI processing and Discord response. - Chat Message Trigger
Use this when you want users to interact with the bot directly in Discord. A webhook receives the incoming chat message, then sends it into the workflow for AI processing.
Both modes unlock different possibilities. One supports behind the scenes automation, the other supports live, conversational interaction in your server.
How The Workflow Operates In Practice
Once your triggers are in place, the workflow can run in two primary modes. Each mode serves a different style of automation and can be expanded as your needs grow.
Mode 1 – Workflow Trigger For Automated Tasks
- Another n8n workflow executes this Discord workflow and sends it a task or message string.
- The AI agent processes the input, generates a response, and posts it to the relevant Discord channel.
- This is ideal for:
- Automated messaging and announcements
- Scheduled updates or reminders
- Notifications triggered by external events or tools
In this mode, your Discord bot becomes part of a larger automation system, reacting to events across your entire stack.
Mode 2 – Chat Trigger For Direct Conversations
- A webhook receives an incoming message from your Discord channel.
- The AI agent analyzes the message and generates a tailored response.
- The workflow uses buffer memory to maintain conversational context, so replies feel like part of an ongoing dialog, not isolated answers.
This mode turns your Discord bot into a live AI assistant inside your community, available at any time and able to remember context across multiple turns.
Customize The Template To Match Your Vision
The real power of n8n is that nothing is fixed. This template is a starting point, and you are encouraged to adapt it so it fits your unique use case, audience, and growth plans.
Key Customization Options
- AI system message Adjust the tone, role, and priorities of your assistant so it reflects how you want your community managed.
- Message length limits Fine tune the maximum character count per message to match your channel style and keep conversations concise.
- Multi channel behavior Configure how the workflow interacts with multiple Discord channels, for example one for tools, one for guides, and others for support or announcements.
- OpenAI model choice Select the OpenAI model that best fits your needs, such as a suitable GPT 4 variant for higher quality responses.
Each adjustment brings your automation closer to the ideal assistant you have in mind.
Grow Your Automation With Enhancements
Once your basic workflow is running, you can gradually enhance it to handle more complex scenarios. Think of this as leveling up your automation skills over time.
Potential Enhancements To Explore
- Error handling Add nodes that detect and manage failures gracefully, so your community experience stays smooth even if an external API has issues.
- Richer conversation memory Extend the buffer memory logic to support longer, multi turn dialogs, especially for deeper support or mentoring conversations.
- More channel specific tools Create specialized flows for different Discord channels, such as FAQ handling, content recommendations, or onboarding guidance.
- Filtering and moderation Introduce message filters or moderation steps to maintain quality, safety, and alignment with your community guidelines.
Each enhancement you add increases the value of your automation and reduces the manual work you need to do every day.
Troubleshooting So Your Workflow Stays Reliable
As you experiment and iterate, you may run into small issues. A quick checklist can help you diagnose most problems fast and keep your automation dependable.
- Check bot permissions Confirm your Discord bot has the correct permissions to view channels, read message history, and send messages.
- Verify API credentials Make sure your Discord and OpenAI credentials in n8n are accurate and still active.
- Validate character limits If messages appear cut off, review your configured character limits to avoid unintended truncation.
- Confirm IDs Double check that all channel IDs and the guild (server) ID used in the workflow match your actual Discord setup.
With these checks in place, your workflow can run smoothly in the background while you focus on strategy, creation, and connection.
Your Next Step – Turn This Template Into Your Own Automation System
You now have a clear path from manual Discord management to a more automated, scalable, and focused way of running your community. The n8n Discord workflow template is your practical tool for making that shift real.
Start simple. Set up your bot, connect your credentials, choose your trigger mode, and let the AI handle a small part of your workload. Then iterate. Refine the system message, expand to more channels, and explore new automations that support your goals.
Each improvement gives you back time and mental space, and each workflow you build with n8n becomes another building block in a more intentional, automated workday.
Ready to experience intelligent Discord automation in your own server?
Set up the template, experiment boldly, and keep evolving your automation. Your future workflows – and your future time freedom – start here.