Integre sua Clínica com Poli: Automação de Agendamento Inteligente (e Fim das Tarefas Repetitivas)
Imagine esta cena…
Telefone tocando sem parar, WhatsApp explodindo de mensagens, paciente pedindo remarcação em cima da hora, outro perguntando o preço do procedimento, mais um querendo saber se “tem horário amanhã cedinho”. Enquanto isso, alguém na recepção tenta atualizar a agenda, responder com educação, não perder nenhum dado importante e ainda manter o sorriso no rosto.
Se isso parece a rotina da sua clínica, boa notícia: você não precisa mais viver nesse modo “super-herói sobrecarregado”. É aqui que entra o Poli, um agente virtual integrado ao n8n, que assume boa parte desse caos com automação inteligente e um toque bem humano.
O que é o Poli e por que ele é tão útil?
Poli é um agente virtual criado para ser o recepcionista digital da OdontoCompany, atendendo seus pacientes diretamente pelo WhatsApp. Ele não se cansa, não esquece informações e não se irrita quando alguém manda áudio de 3 minutos para remarcar um horário.
Usando um fluxo inteligente no n8n, o Poli cuida de:
- Receber e entender mensagens dos pacientes
- Identificar necessidades, como agendamento ou remarcação
- Consultar e gerenciar a agenda da clínica no Google Calendar
- Confirmar horários disponíveis e registrar consultas
- Enviar mensagens e lembretes personalizados
Em resumo, ele funciona como uma recepção digital sempre disponível, com atendimento acolhedor, organizado e automatizado.
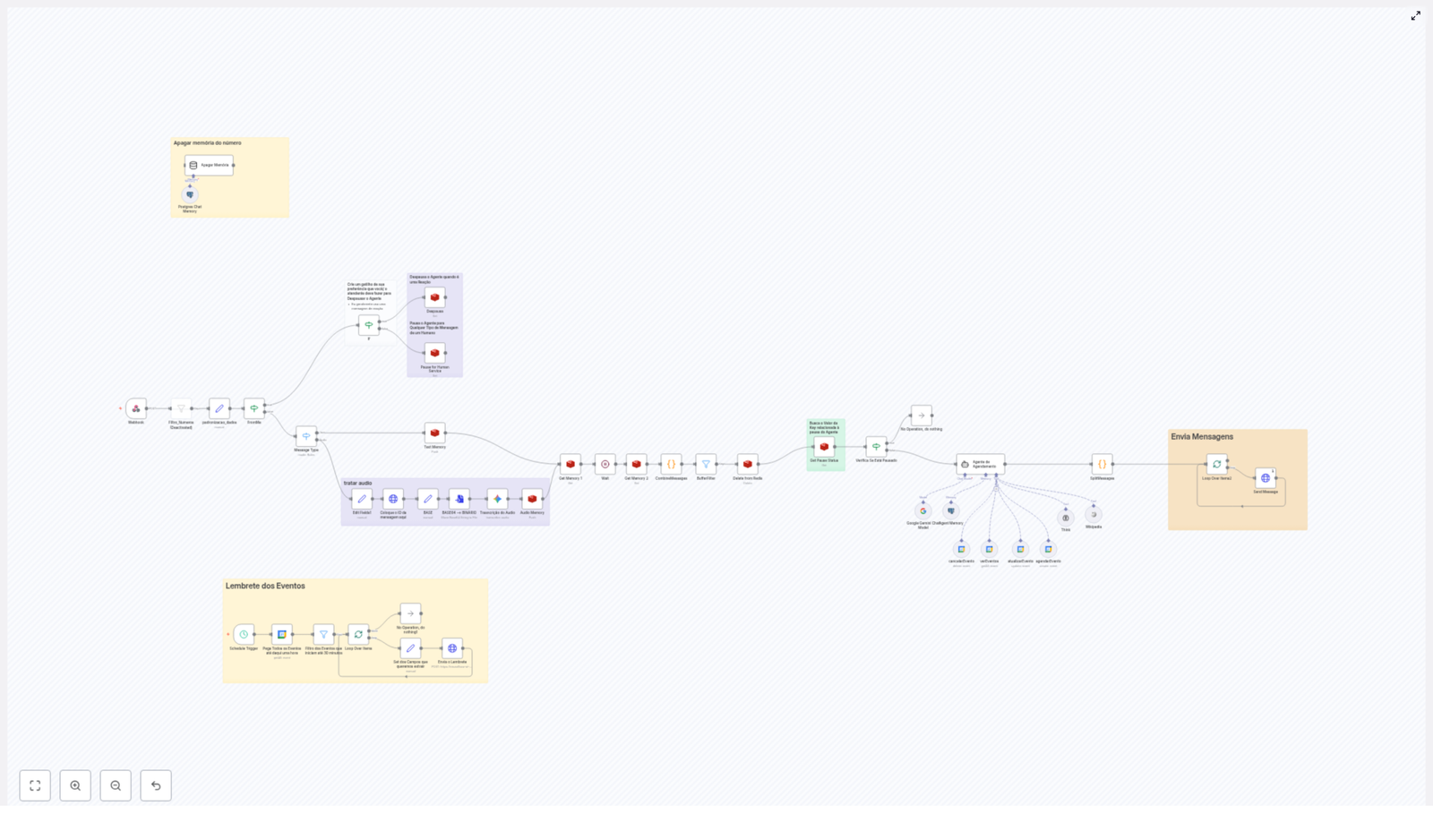
Como o fluxo de automação no n8n funciona por trás dos bastidores
Mesmo com uma pegada leve e amigável, o fluxo do Poli é bem sofisticado. Aqui está o que acontece nos bastidores, etapa por etapa.
1. Webhook: a porta de entrada das mensagens
Tudo começa quando o paciente manda uma mensagem pelo WhatsApp. Essa mensagem chega ao n8n por meio de um webhook, que é o ponto de entrada do fluxo.
Nessa etapa, o fluxo:
- Recebe os dados da mensagem
- Padroniza o número de telefone do paciente
- Organiza o conteúdo da mensagem e outras informações essenciais
Isso garante que, independentemente de como o paciente escreve ou salva o número, o sistema consegue entender e tratar tudo de forma consistente.
2. Memória com Redis: o cérebro da conversa
Para que o Poli não pareça um robô sem memória, o fluxo usa o Redis para armazenar e recuperar dados da conversa em tempo real.
Com essa memória estruturada, o sistema consegue:
- Manter o histórico do paciente
- Controlar o estado atual da conversa
- Continuar o atendimento de forma coerente, mesmo em interações longas ou pausadas
3. Trilha de mensagens: texto, áudio e tudo no meio do caminho
Nem todo mundo gosta de digitar. Alguns pacientes preferem mandar um áudio de “só um minutinho” que dura uma eternidade. O Poli está preparado para isso.
O fluxo é capaz de:
- Diferenciar mensagens de texto e áudio
- Transcrever automaticamente áudios em texto para facilitar o processamento
Assim, independentemente do formato, o conteúdo é entendido e tratado pelo agente de forma eficiente.
4. Controle de pausa: quando entra o atendimento humano
Nem tudo precisa ser 100% automatizado. Em alguns casos, é melhor que um humano assuma a conversa, por exemplo em situações mais sensíveis ou específicas.
Por isso, o fluxo conta com um controle inteligente de pausa:
- Permite pausar o Poli quando necessário
- Evita que conversas paralelas se misturem
- Garante que o atendimento humano e o automático convivam sem bagunça
5. Agente de agendamento: o coração da automação
Esta é a parte que faz os olhos da equipe brilharem. O agente de agendamento usa Language Models (modelos de linguagem) para interpretar o que o paciente quer e agir em cima disso.
Ele é responsável por:
- Entender comandos de forma natural, como “quero marcar uma limpeza” ou “posso remarcar meu horário de amanhã?”
- Coletar dados importantes como nome, preferência de horário e tipo de procedimento
- Consultar o Google Calendar em busca de horários disponíveis
- Aplicar regras rígidas para evitar erros de agendamento
- Executar agendamentos e remarcações automaticamente
Em outras palavras, o Poli entende o que o paciente quer, verifica a agenda e já resolve, sem precisar interromper ninguém da equipe.
6. Envio de mensagens: comunicação clara e acolhedora
Depois de processar tudo, o Poli responde o paciente pelo próprio WhatsApp, com mensagens:
- Personalizadas de acordo com o contexto
- Escritas em um tom caloroso, empático e natural
- Claras sobre horários, confirmações e próximos passos
Assim, o atendimento continua humano e próximo, mesmo sendo automatizado.
7. Lembretes automáticos: adeus, esquecimento de consulta
Para reduzir faltas, o fluxo conta com um subfluxo de lembretes automáticos.
Ele:
- Verifica no Google Calendar os eventos que vão acontecer nos próximos minutos
- Envia mensagens pró-ativas lembrando o paciente do compromisso
É como ter alguém na recepção ligando para cada paciente, só que sem ocupar o tempo de ninguém.
Principais benefícios da automação com Poli e n8n
Além de acabar com boa parte das tarefas repetitivas, o fluxo com Poli traz resultados bem práticos para a clínica.
Atendimento realmente humanizado, mesmo sendo digital
- Uso de um tom caloroso e empático nas mensagens
- Comunicação natural, sem parecer um robô engessado
- Possibilidade de personalizar interações de acordo com o perfil do paciente
Gestão de agenda inteligente e confiável
- Antes de confirmar qualquer horário, o sistema checa conflitos para evitar sobreposições
- Os compromissos são criados com descrições claras, facilitando o entendimento da equipe
- O fluxo segue regras rígidas para manter a agenda organizada
Flexibilidade em múltiplos canais e formatos
- Captação de mensagens em diferentes formatos, como texto e áudio
- Adaptação da resposta conforme o canal de comunicação
- Transcrição de áudios para garantir que nada importante se perca
Histórico e padronização dos atendimentos
- Registro detalhado de histórico de conversas e agendamentos
- Facilidade para consultar informações em futuras remarcações
- Padronização dos dados do paciente, o que evita confusão com nomes, telefones e horários
Operação automatizada, escalável e menos cansativa
- Atende vários pacientes ao mesmo tempo sem perder o controle
- Permite pausar e retomar o agente quando a equipe humana precisar intervir
- Libera a recepção para focar em atendimentos mais complexos e presenciais
Como começar a usar o template do Poli no n8n
Se você já está imaginando a paz na recepção, o próximo passo é colocar esse fluxo para rodar. O melhor de tudo é que você não precisa montar tudo do zero, já existe um template pronto no n8n que representa esse fluxo visualmente.
Passo a passo simplificado
- Acesse o template do Poli no n8n usando o link disponível abaixo.
- Importe o fluxo para o seu ambiente n8n.
- Configure:
- O webhook que recebe as mensagens do WhatsApp
- A conexão com o Redis para a memória da conversa
- A integração com o Google Calendar para os agendamentos
- As chaves e credenciais necessárias para os serviços envolvidos
- Ajuste as mensagens, o tom de voz e as regras de agendamento conforme a realidade da sua clínica.
- Teste o fluxo com alguns números de WhatsApp antes de liberar para os pacientes.
Depois disso, é só deixar o Poli trabalhar e acompanhar os resultados.
Conclusão: menos tarefa repetitiva, mais foco no paciente
Integrar o Poli com o n8n transforma o jeito como a OdontoCompany lida com agendamentos, remarcações e comunicação com pacientes. Você ganha um fluxo de trabalho automatizado, visualmente claro dentro do n8n, que combina:
- Inteligência para interpretar pedidos e gerenciar horários
- Empatia na forma de se comunicar com o paciente
- Regras robustas para manter a agenda organizada e confiável
O resultado é uma clínica mais produtiva, pacientes melhor atendidos e uma recepção que finalmente pode respirar.
Quer implementar essa solução na sua clínica ou negócio?
Se você quer reduzir tarefas manuais, organizar melhor os agendamentos e oferecer uma experiência moderna para os pacientes, vale ver o fluxo do Poli em ação.
Entre em contato conosco para uma demonstração personalizada e descubra como levar o atendimento da sua clínica para o próximo nível com n8n e automação inteligente.