Automate Emelia Reply Notifications with an n8n Workflow
Overview
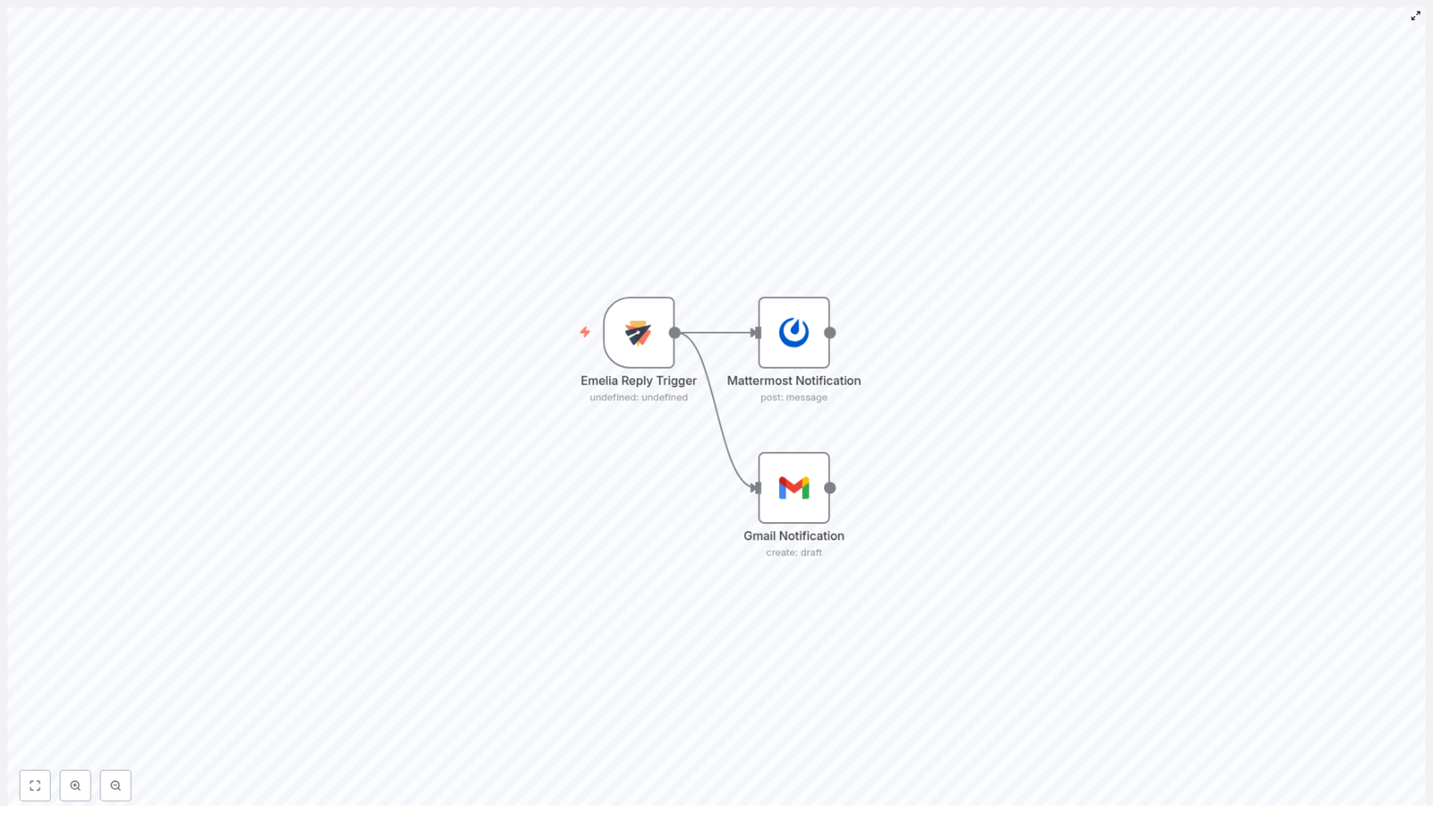
This guide describes a ready-to-use n8n workflow template that automatically sends notifications whenever a contact replies to an Emelia email campaign. The workflow connects Emelia with Mattermost and Gmail so that your team receives real-time alerts in chat and by email without manual monitoring of campaign replies.
The automation is built around an Emelia reply webhook trigger and two notification nodes, and is suitable for teams that already use Emelia for outbound campaigns and want reliable, low-latency reply tracking.
Architecture & Data Flow
At a high level, the workflow follows this event-driven pattern:
- Emelia Reply Trigger (Webhook)
- Listens for
repliedevents from a specific Emelia campaign. - Receives reply metadata, including contact details such as first name and company.
- Listens for
- Mattermost Notification
- Posts a formatted message into a predefined Mattermost channel.
- Uses dynamic fields from the trigger payload to personalize the message.
- Gmail Notification
- Sends an email notification to an administrator or shared inbox.
- Includes reply information so the email team can follow up quickly.
Once deployed, the workflow runs continuously in n8n. No polling is required, since Emelia pushes reply events directly to the n8n webhook URL.
Prerequisites
- An active Emelia account with at least one email campaign configured.
- An n8n instance (self-hosted or cloud) with access to the public internet.
- A Mattermost workspace and channel where notifications will be posted.
- A Gmail account (or Google Workspace account) for sending admin notifications.
For details on authentication and available parameters, refer to the official documentation:
Node-by-Node Breakdown
1. Emelia Reply Trigger Node
The Emelia reply trigger is implemented as a webhook endpoint in n8n that is called whenever a contact replies to a specific campaign. This node is responsible for:
- Listening for
repliedevents associated with a configuredcampaignId. - Extracting key fields from the incoming payload, such as:
- Contact first name
- Contact company
- Any additional reply metadata provided by Emelia
- Passing the structured data to downstream nodes in the workflow.
Key Configuration Parameters
- Event Type: Set to a reply-related event, typically
replied. - Campaign Identifier:
campaignIdmust match the campaign in Emelia that you want to monitor.- Only replies from this specific campaign will trigger the workflow.
- Webhook URL:
- Generated by n8n when you create the workflow.
- Configured in Emelia so reply events are sent to this URL.
Behavior & Edge Considerations
- If the
campaignIddoes not match, no trigger will occur for that campaign’s replies. - If Emelia sends a reply event with missing optional fields (for example, company not set), those values may be empty in subsequent nodes. Template your messages to handle missing data gracefully.
- Network or connectivity issues between Emelia and n8n can prevent the webhook from firing. Check your n8n logs and Emelia webhook configuration if no events are received.
2. Mattermost Notification Node
After the trigger fires, the next node posts a real-time notification into a chosen Mattermost channel. This ensures the team can see and act on replies without leaving their chat environment.
Core Responsibilities
- Receive the data payload from the Emelia trigger node.
- Compose a message that includes:
- The contact’s first name.
- The contact’s company.
- Any other relevant reply context available from the trigger.
- Send the message to a specific Mattermost channel using the configured credentials.
Essential Configuration
- Mattermost Credentials:
- Configured in n8n under credentials (for example, personal access token or bot account, depending on how your Mattermost integration is set up).
- Must have permission to post messages to the target channel.
- Channel:
- Set the channel name or ID where notifications should appear.
- Ensure the channel is accessible to the configured Mattermost user or bot.
- Message Template:
- Use n8n expressions to reference fields from the Emelia payload, such as:
{{$json["firstName"]}}{{$json["company"]}}
- Include a short description of the event, for example, that a contact replied to a specific campaign.
- Use n8n expressions to reference fields from the Emelia payload, such as:
Error Handling Notes
- If Mattermost credentials are invalid or permissions are insufficient, the node will fail and the message will not be posted.
- Consider configuring workflow error handling or retries in n8n if you expect transient connectivity issues.
- Message formatting should be robust to missing optional fields. For example, avoid relying on company if it is not always present.
3. Gmail Notification Node
In parallel with the Mattermost alert, the workflow also sends an email notification through Gmail. This is intended for administrators or an email operations team that prefers to track replies directly from their inbox.
Core Responsibilities
- Build an email that summarizes the reply event.
- Include dynamic data from the Emelia trigger, such as:
- Contact name
- Company
- Any other reply details you choose to map
- Send the email to a configured admin address using Gmail credentials.
Essential Configuration
- Gmail Credentials:
- Configured in n8n as a Gmail or Google account connection.
- Must be authorized to send emails from the selected account.
- Recipient Address:
- Set to an admin email, shared inbox, or distribution list that should receive reply alerts.
- Subject and Body Templates:
- Use n8n expressions to insert data from the Emelia trigger, similar to the Mattermost node.
- Example elements to include:
- Campaign identifier
- Contact first name and company
- Short indication that the contact has replied
Behavior & Reliability
- If Gmail rate limits or authentication issues occur, the node may fail and the admin email will not be sent.
- Ensure that the sending account complies with your organization’s email policies to avoid deliverability issues.
- For critical notifications, you can monitor n8n execution logs to confirm that emails are being sent as expected.
Configuration Notes
Connecting Emelia to n8n
- In Emelia, configure the webhook or reply callback URL to point to the webhook URL generated by the Emelia reply trigger node in n8n.
- Ensure the
campaignIdin your n8n workflow matches the campaign configured in Emelia. - Test the connection by sending a test reply to the campaign and verifying that the workflow executes in n8n.
Securing Your Integrations
- Store Emelia, Mattermost, and Gmail credentials securely using n8n’s built-in credentials manager.
- Restrict access to the workflow and credentials to authorized users only.
- Review permission scopes for each integration so that they are limited to what is required for notifications.
Advanced Customization Ideas
The base template focuses on a straightforward, three-node pipeline. You can extend it in n8n to fit more complex operational needs while preserving the original logic.
- Additional Filters
- Add conditional logic to handle replies differently based on contact attributes or campaign segments.
- Enriched Notifications
- Include more fields from the Emelia payload in Mattermost and Gmail messages to give your team more context.
- Multi-channel Routing
- While this template uses Mattermost and Gmail, you can easily add more nodes to push notifications to other systems supported by n8n.
Benefits of This n8n – Emelia Workflow
- Efficiency
- Automates reply tracking and removes the need to manually check Emelia for responses.
- Real-time Team Alerts
- Mattermost notifications keep your team informed the moment a contact replies.
- Centralized Email Communication
- Gmail notifications ensure that important replies are visible in the inboxes your team already uses.
Get Started
To implement this automation in your environment, import and configure the template in your n8n instance, then connect it to your Emelia campaign, Mattermost workspace, and Gmail account.
For in-depth configuration details and credential setup, consult the official documentation:
Once everything is in place, every reply to your Emelia campaign will automatically trigger the workflow, send a Mattermost message, and dispatch a Gmail notification so your team never misses a response.