Unlocking Productivity: How One Marketer Mastered MCP Tools for Google and Social Media
The Day Everything Fell Apart
On a Tuesday morning that looked harmless enough, Maya stared at her laptop with a sinking feeling. She was a solo marketer at a fast-growing startup, juggling Google Calendar invites, Gmail follow-ups, LinkedIn posts, and Twitter (X) updates. Her day was supposed to be planned to the minute, yet somehow she had already missed a client call, forgotten to share a document, and left a draft campaign email unsent.
Her tabs told the story: Google Calendar, Google Drive, Gmail, LinkedIn, Twitter, a dozen docs, and a few random tools she was trying to stitch together on her own. Every task required another login, another click, another mental context switch. By noon, she felt less like a marketer and more like a human router, shuffling data between platforms.
That afternoon, after a particularly awkward message from a client asking, “Did we still have a meeting today?”, Maya decided she needed a different approach. Manual work was not just inefficient, it was risky. She could not afford to keep missing details.
That was the moment she discovered an n8n workflow template built around MCP tools, designed to connect Google services and social media through a single AI Agent. It did not just promise automation. It promised sanity.
The Hidden Engine Behind the Chaos
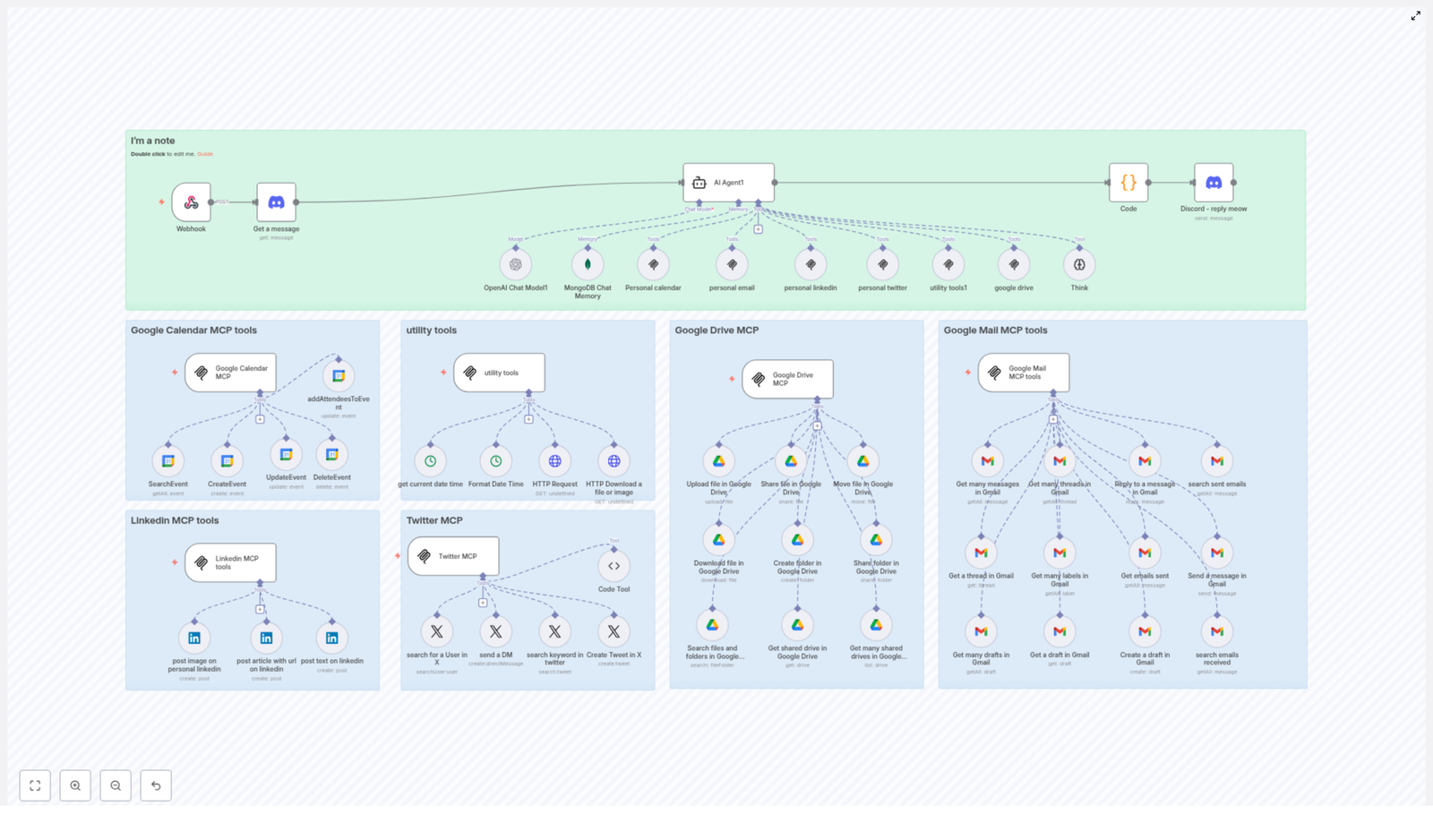
As Maya dug into the template documentation, she realized her problem was not just “too many apps”. It was the lack of a central brain coordinating them. The n8n template introduced her to something she had never used before: an MCP (Multi-Channel Platform) architecture powered by a central AI Agent.
At the core of this setup was a webhook interface. Every request from her different channels could be sent into this central AI Agent, which was wired into multiple APIs and tools. It used:
- Discord for communication and quick interactions
- MongoDB for memory, so it could remember context over time
- Google Calendar, Google Drive, and Gmail for her daily operations
- LinkedIn and Twitter tools for social media management
The AI Agent itself relied on powerful models like OpenAI GPT, enriched with memory storage and synchronized with her personal calendars, emails, and social accounts. Instead of Maya manually deciding what to do in each app, she could send one instruction and let the Agent route it to the correct workflow.
She imagined a future where she could simply say, “Schedule a follow-up with this client, attach the proposal, and share a quick LinkedIn update about it,” and the system would know exactly which tools to trigger.
Rising Pressure, Rising Complexity
The next week, things escalated. Maya’s CEO announced a new product webinar. She had to coordinate:
- Calendar invites for internal and external stakeholders
- A shared folder with all presentation assets
- An email campaign for registrations
- LinkedIn posts to promote the event
- Twitter threads to build momentum
In the past, this would have meant late nights and endless copy-pasting. This time, she decided to fully commit to the MCP-driven n8n workflow template.
Turning Point: When the AI Agent Took Over
Maya started by wiring her accounts into the template. The webhook endpoint was already configured inside n8n, so once she connected her Google and social media accounts, the central AI Agent could finally “see” her digital universe.
Step 1: Taming the Calendar Chaos
First, she addressed the most painful part of her workflow: scheduling. The Google Calendar MCP tools in the template gave her a complete toolkit for event management, all driven by the AI Agent.
Behind the scenes, the Agent could call:
- SearchEvent to retrieve events within a specific date range, so it never double-booked her
- CreateEvent to schedule new events with detailed descriptions
- UpdateEvent when a meeting time changed or details needed refinement
- DeleteEvent to remove canceled events from her calendar
- addAttendeesToEvent to add participants without her manually typing every email
For the webinar, she simply provided the date, time, and title to the Agent. The MCP workflow handled the rest, creating the event and inviting stakeholders. When the CEO later asked to move the time, Maya did not open Calendar. She updated it via the Agent, and the workflow automatically adjusted the event.
Step 2: Utility Tools That Quietly Held Everything Together
As she explored further, Maya realized that some of the most powerful pieces of the system were the quiet utility tools that made everything else reliable.
- Get Current Date Time ensured every action used an accurate timestamp for scheduling and logging
- Format Date Time converted her natural language inputs like “next Thursday at 3 PM” into standard ISO format that all tools understood
- HTTP Request & Download allowed the workflow to fetch web resources or download files and images whenever needed
These utilities became the glue. Whenever she triggered a workflow, she knew dates would be correct, formats would be consistent, and external resources could be pulled in automatically.
Step 3: Organizing the Mess in Google Drive
The next bottleneck was file management. Before MCP, Maya would create folders manually, upload decks, and then forget who had access to what. The Google Drive MCP tools in the template changed that completely.
Through the AI Agent, she could now:
- Upload File directly into a specific folder or the root directory
- Share File/Folder with read-only permissions via email, so stakeholders saw the latest version without her worrying about edits
- Move File to reorganize assets as the project evolved
- Create Folder for each new campaign or event
- Search Files and Folders by name when she could not remember where something lived
- Retrieve Shared Drives to access and list shared drives across the team
For the webinar, the workflow automatically created a dedicated folder, uploaded the slides and promo images, and shared them with the team. Instead of hunting for links, Maya had a single source of truth that the Agent could reference whenever she needed to attach or share a file.
Step 4: Finally Getting Ahead of Email
Gmail was where Maya felt most overwhelmed. Important leads were buried under newsletters, and follow-ups slipped through the cracks. The Google Mail MCP tools in the n8n template gave her a way to bring structure back to her inbox.
The Agent could now:
- Get Many Messages to fetch recent emails and surface what mattered
- Get Many Threads to manage entire conversations instead of isolated messages
- Reply to a Message directly within a thread, without her opening Gmail
- Search Sent Emails using criteria like recipient or subject line
- Create and Send Drafts so she could have the Agent prepare emails for approval before sending
- Manage Labels and Drafts to organize her inbox and keep track of pending replies
For webinar registrations, the workflow automatically drafted thank-you emails and follow-up reminders. Maya reviewed and approved them, but she no longer had to copy and paste the same message dozens of times.
Step 5: Making Social Media Work While She Slept
With the operational chaos under control, Maya turned to what she actually enjoyed: building an audience. The MCP tools for LinkedIn and Twitter (X) were already wired into the same n8n template, ready for the AI Agent to command.
LinkedIn MCP Tools in Action
For LinkedIn, the workflow allowed her to:
- Create text posts that announced the webinar and shared insights
- Post images directly to her profile to increase engagement
- Share articles with embedded URLs to drive traffic and visibility
She fed the Agent a short brief about the webinar topic. The workflow generated and scheduled a series of posts, each tailored to a different angle: thought leadership, product value, and behind-the-scenes preparation.
Twitter (X) MCP Tools for Real-Time Reach
On Twitter (X), the MCP toolkit helped her:
- Search for users by username to identify relevant partners and influencers
- Send Direct Messages to invite key contacts to the webinar
- Search keywords across tweets to monitor conversations around her topic
- Post tweets instantly to share updates and reminders
Instead of manually tweeting in between meetings, Maya let the workflow handle posting and monitoring. The AI Agent could search for relevant discussions and help her craft timely responses or follow-ups.
The Result: From Frantic Juggling to Focused Strategy
By the time the webinar went live, Maya noticed something she had not felt in months: calm. The calendar was accurate, everyone had the right link, assets were in one place, emails were queued, and social media was already seeding interest.
What changed was not just automation. It was the presence of a central AI Agent, orchestrating MCP tools across Google services and social platforms. Instead of her brain acting as the integration layer, the n8n workflow template did the work:
- Webhook requests came in from various channels
- The AI Agent interpreted her commands using GPT and stored context in MongoDB
- Google Calendar, Drive, Gmail, LinkedIn, and Twitter tools executed the right actions
- Utility tools ensured dates, formats, and external resources stayed consistent
Her productivity was no longer limited by how many tabs she could keep open. She could finally focus on strategy, creativity, and relationships, while the MCP-driven automation handled the repetitive coordination.
Where You Fit Into This Story
If you recognize yourself in Maya’s struggle, you do not need to rebuild this system from scratch. The n8n workflow template that transformed her day is designed to give you the same integrated MCP experience, connecting your Google tools and social media accounts through a single AI Agent.
With it, you can:
- Centralize scheduling, file management, email, and social media
- Automate repetitive tasks across Google Calendar, Drive, and Gmail
- Maintain an active presence on LinkedIn and Twitter without constant manual posting
- Rely on utility tools to keep your data clean, consistent, and reliable
The difference between barely keeping up and confidently scaling your work often comes down to how well your tools talk to each other. MCP tools inside n8n give you that unified layer, powered by an AI Agent that understands your intent and executes across platforms.
Start Your Own Automation Chapter
You do not have to wait for the next missed meeting or forgotten email to make a change. The same MCP-driven n8n template that helped Maya can be adapted to your workflow, your stack, and your priorities.
Explore the template, connect your accounts, and let the AI Agent become the central nervous system of your digital workday. Once you see your calendar, inbox, files, and social channels moving in sync, you will not want to go back.