n8n AI Conversation Workflow: A Story Of One Marketer And A Smarter Chatbot
By the time the third support ticket hit her inbox before 9 a.m., Lina knew something had to change.
She was the solo marketer at a fast-growing SaaS startup. Her job should have been focused on campaigns and growth, yet every day she was dragged into the same problem: their “AI chatbot” was unreliable, hard to tweak, and impossible to debug. Conversations disappeared, answers were inconsistent, and nobody could explain why.
Then the CEO asked the question she had been dreading:
“Can we trust this AI assistant to handle real customer conversations?”
Lina did not have a good answer. Not yet.
The Pain: A Chatbot You Cannot Trust
Their existing setup was a patchwork of scripts and a hosted AI tool. If responses looked weird, no one knew whether it was the prompt, the model, or an API hiccup. There was no proper logging, no clear error handling, and no way to iterate quickly.
- Prompts were scattered across different tools.
- API keys were buried in code and hard to rotate.
- Conversation history was not stored in a structured way.
- When the model failed, customers saw awkward error messages or nothing at all.
Lina needed something different: a transparent, reliable way to orchestrate AI conversations that her team could actually understand and improve. She was comfortable with tools like Zapier and Make, so a visual automation tool felt natural. That is when she discovered n8n.
Discovery: Why n8n Was The Missing Piece
Lina stumbled onto an n8n AI conversation workflow template while searching for “n8n GPT chat automation with logging.” The promise sounded almost too good to be true:
- Drag-and-drop workflow design instead of opaque code
- Nodes for data preparation, conditional logic, and HTTP APIs
- Easy integration with language models like GPT-5 preview
- Built-in debugging, logging, and error handling
It was exactly what she needed: a way to build a reliable AI conversation workflow that her team could see, tweak, and trust.
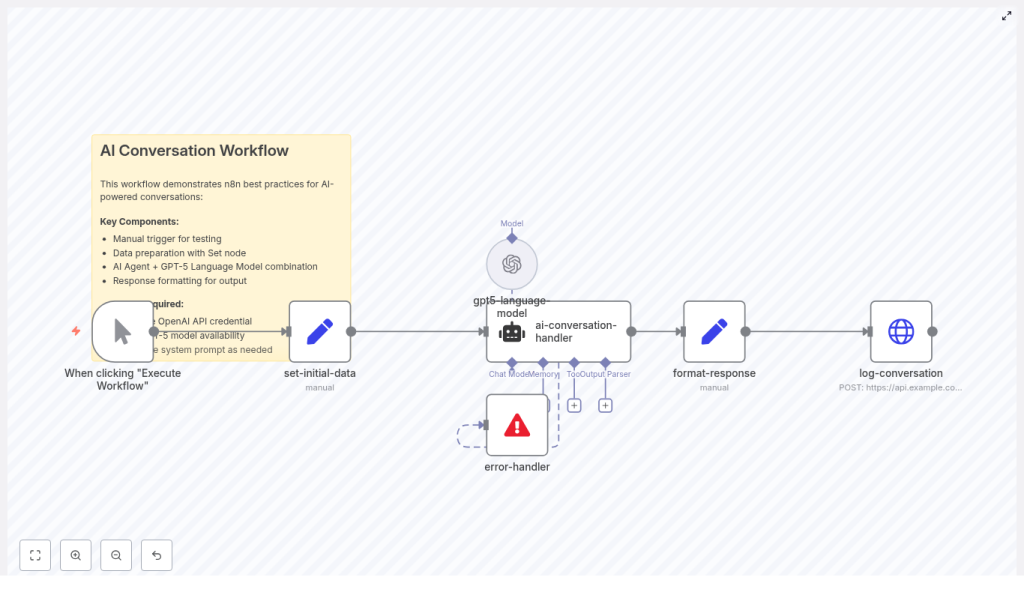
So she imported the template into n8n and started to explore the nodes that would soon become the backbone of their customer assistant:
- Manual Trigger for testing conversations
- Set node (set-initial-data) to prepare system prompt, user message, and context
- AI Agent node (ai-conversation-handler) to orchestrate logic and memory
- Language Model node (gpt5-language-model) to connect to GPT-5 preview
- Set node (format-response) to clean and enrich the answer
- HTTP Request (log-conversation) to store the full transcript
- Error handler to avoid silent failures
- Sticky note as inline documentation
For the first time, Lina could see the entire AI conversation pipeline laid out in front of her, step by step.
Rising Action: Building The Conversation Flow In n8n
Starting Small: Triggering And Shaping The First Conversation
Lina began in the safest place possible: a Manual Trigger. No live users, no risk. Just her, the workflow, and a single test message.
Right after the trigger, the template used a Set node named set-initial-data. This node prepared a structured payload for the AI agent:
{ "systemPrompt": "You are Max, a friendly assistant.", "userInput": "Hello! How are you doing today?", "context": "This is a friendly AI assistant conversation"
}
She quickly realized how powerful this simple pattern was. The systemPrompt defined the assistant’s role and tone, the userInput captured the latest message, and the context provided any surrounding information.
By keeping the system prompt concise and explicit, Lina could control how the model behaved without rewriting code. If she wanted a more professional tone or a brand-specific voice, she could change it in one place.
The Brain: Configuring The AI Agent Node
The next part of the story unfolded in the ai-conversation-handler node. This was where the “agent” logic lived. It did more than just call a model. It was responsible for:
- Assembling the full prompt from system prompt, context, and user input
- Managing short-term memory or conversation history
- Applying output parsing rules so responses followed a predictable format
Lina configured the node to expect structured output when needed, such as JSON for downstream actions. If the model needed to return tags, actions, or specific fields, she defined a clear schema.
Instead of a black box chatbot, she now had an AI agent layer that she could reason about. It felt like upgrading from a magic trick to a real, maintainable system.
The Voice: Connecting GPT-5 In The Language Model Node
Next came the gpt5-language-model node. This node was wired to the actual large language model, in her case GPT-5 preview via an OpenAI credential.
She double-checked a few critical details:
- Model name availability, such as
gpt-5-preview - API key and secret stored securely in n8n credentials, not hard-coded in nodes
- Generation settings like temperature and max tokens
For their customer assistant, Lina chose a temperature in the 0.4 – 0.8 range. Lower values felt too robotic, higher ones too unpredictable. Settling in the middle gave them helpful but still consistent responses.
With one node, she could swap models, adjust creativity, and stay within cost and rate limits, all without touching application code.
Turning Point: From Raw Output To Production-Ready Responses
The first time Lina clicked “Execute Workflow,” the model responded politely. It was a good start, but the raw output alone was not enough. She needed structure, traceability, and logs.
Shaping The Answer: The format-response Node
The template’s format-response Set node became her favorite part. It took the model’s reply and enriched it with metadata that would matter in production.
The node performed three key tasks:
- Normalized text by stripping extra whitespace
- Added metadata such as timestamp, conversationId, and userId
- Prepared structured JSON for downstream systems
The template included assignments like:
response: {{ $json.output }}
timestamp: {{ new Date().toISOString() }}
conversationId: conv_{{ Math.random().toString(36).substr(2,9) }}
Suddenly every response had a unique conversationId and a precise timestamp. That meant Lina could track entire chat sessions, correlate them with users, and debug specific interactions.
Making Conversations Traceable: Logging With HTTP Request
Before n8n, conversations disappeared into the hosted chatbot tool. Now, with the log-conversation HTTP Request node, Lina could send a POST request containing the full response payload to their own API.
This opened up several possibilities:
- Store transcripts in their database for analysis and compliance
- Send analytics events to their monitoring stack
- Trigger follow-up workflows, such as billing events or support tickets
She made sure their logging endpoint supported idempotency and could handle retries if the workflow restarted. That way, they would not accidentally duplicate logs when recovering from failures.
Facing Reality: Error Handling And Failures
The real turning point came when Lina simulated an outage by using an invalid API key. Previously, that kind of error would have surfaced as a cryptic message or an empty chat bubble. In the new n8n workflow, an error-handler node caught the failure.
She configured it with a few best practices:
- Return a user-friendly fallback message if generation failed
- Log detailed error context to a separate error stream
- Implement exponential backoff for transient API errors
Now, instead of “Something went wrong,” customers would see a helpful fallback, and the team would have a clear record of what had happened.
The chatbot was no longer fragile. It was resilient.
Leveling Up: From Prototype To Production Workflow
With a working workflow in place, Lina started to think about production-readiness. She knew that once the CEO saw the new assistant in action, usage would spike. That meant she had to address security, cost, prompts, and observability.
Keeping Secrets Safe: Security And Credentials
First, she cleaned up how credentials were handled:
- All API keys moved into n8n credentials or environment variables
- No secrets hard-coded in Set nodes or HTTP requests
- Logging endpoints restricted and protected
- Any stored transcripts encrypted at rest where possible
This gave her peace of mind and made audits easier. If they needed to rotate keys, they could do it in one place.
Controlling Costs And Rate Limits
Next, Lina tackled cost and performance. Language models are powerful, but they are not free. She monitored token usage and set reasonable maxTokens values in the language model node.
To stay within budget and respect rate limits, she considered:
- Caching common responses for FAQs
- Using a smaller or cheaper model for simple queries
- Adding a rate limiter or queue in front of high-volume workflows
With n8n, these adjustments were simple configuration changes, not full rewrites.
Prompt Engineering And Memory: Giving The Assistant A Real Personality
As the workflow matured, Lina focused on the assistant’s voice and memory. She refined the prompt pattern used in the Set node so that “Max” felt on-brand and consistent.
One robust pattern she adopted looked like this:
System: You are Max, a friendly assistant who responds with humor and emojis.
Context: {{ context }}
User: {{ userInput }}
Instruction: Provide a friendly, helpful answer. Keep it concise and add one emoji.
She kept system prompts short and explicit, and when they needed persistent memory, she added a database step that stored summarized context. Before each call to the model, she could load relevant history into the Set node, or even use semantic search over embeddings to retrieve longer-term context.
Suddenly, Max felt less like a toy and more like a helpful team member.
Observability: Seeing The Whole Conversation Landscape
To avoid surprises in production, Lina instrumented the workflow with observability in mind. Using the metadata she had already added, such as conversationId, userId, and timestamp, she emitted logs and metrics that answered key questions:
- What is the success rate of AI responses?
- How long do responses take?
- How many tokens are used per conversation?
With this data, she could detect regressions quickly and prove to her team that the AI assistant was performing as expected.
Troubles, Tweaks, And Extensions
As usage grew, a few issues surfaced, but they were now straightforward to fix inside n8n.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- If the agent returned unexpected formats, she tightened the output schema in the ai-conversation-handler node and added an explicit output parser.
- When responses felt slow, she checked network latency, model token limits, and considered using streaming where supported.
- If they hit rate limits, she added a rate limiter node and queued requests to smooth traffic spikes.
Each problem had a visible place in the workflow where it could be addressed. No more hunting through obscure logs in a hosted chatbot tool.
Extending The Workflow Beyond Simple Chat
Once the core AI conversation workflow was stable, Lina started to dream bigger. The same n8n template could evolve into a powerful automation hub:
- Integrate embeddings and vector databases for knowledge retrieval
- Add multi-turn memory using a database or Redis
- Use conditional nodes to escalate complex issues to human agents
- Support multimedia inputs like attachments or images with pre-processing steps
What began as a simple chat automation now looked like the foundation for a scalable, multi-user AI support system.
Resolution: A Reliable AI Conversation Workflow In Production
A few weeks later, Lina sat in a product review meeting. The CEO shared his screen and opened a conversation with Max, the AI assistant now powered by the n8n AI conversation workflow.
Max answered clearly, with the right tone, and even a touch of humor. When someone asked, “What happens if the model fails?” Lina calmly explained the error handler, the logging, and the fallback messages. When another teammate asked about costs, she showed the token usage metrics and rate limit safeguards.
The room went quiet for a second, then the CEO smiled.
“Let’s roll it out to all users.”
Lina had not just fixed a chatbot. She had built a transparent, auditable, and scalable AI conversation system using n8n.
Next Steps: Make This Story Yours
n8n turned out to be the orchestration layer Lina needed to turn a fragile chatbot into a production-ready AI conversation workflow. The template she started from showed her how to:
- Prepare structured data and prompts with Set nodes
- Configure an AI agent node that manages logic and memory
- Connect a language model like GPT-5 preview securely
- Format, enrich, and log every response
- Handle errors gracefully and monitor behavior in production
You can follow the same path. Import the template, connect your model, and start running test conversations. Then iterate on prompts, add memory and retrieval, and layer in observability until your AI assistant is something your team can trust.
Call to action: Import the template into n8n, configure your OpenAI or third-party credentials, and run a few test conversations today. Once it works, export the workflow JSON, store it in your repo, and treat it like any other critical part of your infrastructure.
If you would like help, you can:
- Get a ready-to-import n8n workflow JSON adapted to your models and endpoints
- Craft system prompts tailored to your brand voice and audience
- Design an architecture for scaling multi-user AI conversation workloads
Reply with which option you want to start with, and the next chapter of your AI automation story can begin.