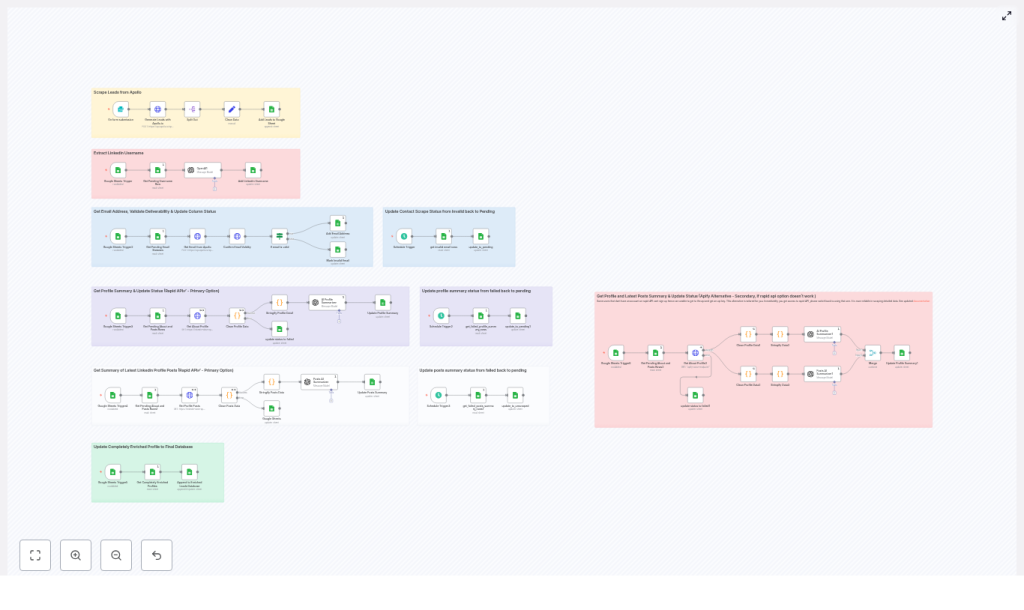
Automate LinkedIn Lead Enrichment with n8n
Looking to turn raw LinkedIn profiles into fully enriched, outreach-ready leads without manual research? This guide walks you through a complete, production-ready n8n workflow that connects Apollo.io, Google Sheets, RapidAPI or Apify, and OpenAI into a single automated pipeline.
By the end, you will understand each stage of the workflow, how the n8n nodes fit together, and how to adapt the template to your own stack.
What you will learn
In this tutorial-style walkthrough, you will learn how to:
- Generate targeted leads from Apollo.io using n8n
- Clean and extract LinkedIn usernames from profile URLs
- Track lead enrichment progress using Google Sheets status columns
- Reveal and validate email addresses before outreach
- Scrape LinkedIn profiles and posts using RapidAPI or Apify
- Summarize profiles and posts with OpenAI for personalized messaging
- Append fully enriched contacts to a final database for sales and marketing
- Handle errors, rate limits, and retries in a robust way
Why automate LinkedIn lead enrichment with n8n?
Manual lead research is slow, inconsistent, and difficult to scale. An automated n8n workflow solves several common problems:
- Faster lead generation at scale – Run searches and enrichment around the clock without manual work.
- Consistent enrichment and tracking – Every lead passes through the same steps with clear status markers.
- Clean, validated contact data – Emails are verified before they ever reach your outreach tools.
- Automatic summarization – Profiles and posts are turned into short summaries for personalized messages.
n8n is ideal for this because it lets you visually chain APIs, add conditions, and maintain state using tools like Google Sheets, all without heavy custom code.
How the n8n workflow is structured
The template is organized into logical stages. In n8n, these often appear as color-coded node groups so you can see the pipeline at a glance. The main stages are:
- Lead generation from Apollo.io
- LinkedIn username extraction
- Lead storage and status tracking in Google Sheets
- Email reveal and validation
- LinkedIn profile and posts scraping (RapidAPI primary, Apify fallback)
- AI-based summarization and enrichment with OpenAI
- Appending fully enriched leads to a final database
- Scheduled retries and status resets for failed items
Next, we will walk through these stages step by step so you can see exactly how the template works and how to adapt it.
Step-by-step guide to the LinkedIn enrichment workflow
Step 1 – Generate leads from Apollo.io
The workflow begins by calling the Apollo API to search for leads that match your criteria. In n8n, this is usually done with an HTTP Request node configured with your Apollo credentials.
Typical Apollo search filters include:
- Job title or seniority
- Location or region
- Industry or company size
per_pageto control how many leads are returned per request
The response from Apollo typically includes fields such as:
idnamelinkedin_urltitle
In n8n, you then use a combination of nodes to prepare this data:
- HTTP Request (Apollo) – Executes the search and retrieves the leads.
- Split Out – Splits the array of results into individual items so each lead can be processed separately.
- Set – Cleans and reshapes fields, for example keeping only the fields you need.
- Google Sheets (append) – Appends each lead as a new row in a central sheet.
At the end of this step, you have a structured list of leads in Google Sheets, ready for enrichment.
Step 2 – Extract and clean LinkedIn usernames
Most LinkedIn URLs contain a standard prefix and sometimes query parameters. For scraping APIs, you usually need just the username portion.
Typical URLs look like:
https://www.linkedin.com/in/jane-doe-123456/
https://www.linkedin.com/in/john-doe?trk=public_profile
The workflow uses either:
- An OpenAI node with a simple prompt to extract the username, or
- A lightweight Code node (JavaScript) to strip the prefix and remove trailing parameters
The goal is to convert the full URL into a clean username, for example:
https://www.linkedin.com/in/jane-doe-123456/→jane-doe-123456
This cleaned username is then stored back in Google Sheets and used later when calling the LinkedIn scraping APIs.
Step 3 – Store leads in Google Sheets with status tracking
To make the workflow resilient and easy to monitor, each lead is written to a central Google Sheet that includes several status columns. These columns act like a simple state machine for each contact.
Common status columns include:
contacts_scrape_status(for example pending, finished, invalid_email)extract_username_status(for example pending, finished)profile_summary_scrape(for example pending, completed, failed)posts_scrape_status(for example unscraped, scraped, failed)
By updating these fields at each stage, you can:
- Resume the workflow after interruptions
- Identify where leads are getting stuck
- Trigger retries for specific failure states
In n8n, Google Sheets nodes are used to read, update, and append rows as the lead moves through the pipeline.
Step 4 – Reveal and validate email addresses
Once leads are stored, the next goal is to obtain valid email addresses. The workflow checks for rows where contacts_scrape_status = "pending" and processes only those leads.
The typical sequence is:
- Call Apollo person match endpoint using an HTTP Request node to reveal the lead’s email address, where allowed by your Apollo plan and permissions.
- Validate the email using an email validation API such as mails.so or another provider of your choice.
- Check validation result with an If node in n8n to branch based on deliverability.
Based on the validation:
- If the email is deliverable, the Google Sheet is updated with the email and
contacts_scrape_status = "finished". - If the email is invalid or risky, the row is updated with
contacts_scrape_status = "invalid_email".
Marking invalid emails explicitly allows you to schedule retries, use alternate verification services, or send those leads for manual review later.
Step 5 – Fetch LinkedIn profile data and recent posts
With valid emails and usernames in place, the workflow moves on to enrich each contact with LinkedIn profile content and recent posts. This step uses a two-layer approach for scraping.
Primary: RapidAPI LinkedIn data API
The main path uses a LinkedIn data API available through RapidAPI. A typical configuration includes:
- Passing the cleaned LinkedIn username
- Requesting profile details such as headline, summary, experience, and education
- Retrieving recent posts or activities
The response is normalized with n8n nodes so that fields are consistent across leads.
Fallback: Apify-based scraper
If you cannot use RapidAPI or you hit limits, the template includes an alternate path that uses Apify. This path:
- Triggers an Apify actor or task to scrape profile content and posts
- Waits for the run to complete and fetches the results
- Normalizes the payload to match the structure expected by the rest of the workflow
Error handling and retry logic
Scraping can fail for many reasons, such as rate limits or temporary network issues. To handle this cleanly:
- When a scrape fails, the workflow sets
profile_summary_scrape = "failed"orposts_scrape_status = "failed"in Google Sheets. - Scheduled triggers in n8n periodically scan for failed rows and reset them to
"pending"so they can be retried.
This pattern ensures the workflow can run continuously without manual intervention, even if some calls fail on the first attempt.
Step 6 – Summarize and enrich with OpenAI
Raw profile text and post content is often too long or unstructured for sales outreach. The template uses OpenAI to turn this information into concise, personalized summaries.
Two OpenAI nodes are typically used:
- Profile Summarizer Takes structured profile data (headline, about section, experience) and produces a short summary designed for cold outreach. Example outcome: a 2 to 3 sentence description of the person’s role, background, and interests.
- Posts Summarizer Takes recent LinkedIn posts and summarizes key themes, tone, and topics in a brief paragraph.
The outputs from these nodes are then written back to Google Sheets, for example:
about_linkedin_profile– the profile summaryrecent_posts_summary– the posts summary
At the same time, the status columns are updated, for example:
profile_summary_scrape = "completed"posts_scrape_status = "scraped"
These summaries are now ready to be used in personalized email copy or outreach sequences.
Step 7 – Append fully enriched leads to a final database
Once a lead has:
- A validated email address
- A LinkedIn profile summary
- A recent posts summary
the workflow treats it as fully enriched and moves it into a dedicated “Enriched Leads” database.
In the template, this final database is another Google Sheet, but you can later swap this out for a CRM or data warehouse.
Typical logic at this stage:
- Use a Google Sheets node to append or update the lead in the Enriched Leads sheet.
- Match records by email address to avoid duplicates.
- Optionally, mark the original row as archived or synced.
This gives your sales or marketing team a single, clean source of truth for outreach-ready contacts.
Operational tips and best practices
Managing API keys, rate limits, and quotas
- Store all API keys (Apollo, RapidAPI, Apify, OpenAI, email validation) in n8n credentials, not in plain text fields.
- Rotate keys periodically and restrict them to the minimum permissions required.
- Implement rate limit handling and backoff strategies, especially for scraping and AI APIs.
- Request only the fields you need from each API to reduce payload size and costs.
Building resilience and observability
- Rely on status columns in Google Sheets to track the state of each lead and make the process resumable.
- Use
executeOnceand scheduled triggers to control how often different parts of the pipeline run. - Log failures in a dedicated sheet or monitoring tool so you can spot patterns and fix root causes.
- Send alerts (for example via email or Slack) when error rates spike or you hit quota limits.
Privacy, compliance, and terms of service
- Review and comply with the Terms of Service for LinkedIn, Apollo, RapidAPI, Apify, and any other providers you use.
- Ensure you have a lawful basis for storing and processing personal data under regulations like GDPR or CCPA.
- Mask, encrypt, or tokenize sensitive data at rest if required by your internal policies.
Common pitfalls and how to troubleshoot them
- Missing or malformed LinkedIn URLs Add validation steps before username extraction. For example, check that the URL contains
"linkedin.com/in/"and normalize trailing slashes or parameters. - High rate of undeliverable emails Use a robust email validation provider and consider a fallback service. You can also route invalid emails to a separate sheet for manual review.
- Rate-limited scraping endpoints Introduce queues or delays between requests, run scraping batches on a schedule, and use status columns to spread the load over time.
Scaling your LinkedIn enrichment system
As your volume grows, you may want to extend the template beyond Google Sheets and a single n8n instance.
- Move to a database Store enriched leads in a database such as Postgres, BigQuery, or another data warehouse for better performance and analytics.
- Distribute workload If a single n8n instance becomes a bottleneck, consider distributed workers or a message queue such as RabbitMQ or AWS SQS to spread tasks.
- Add analytics Track metrics like enrichment success rate, email deliverability, and conversion rate from enriched leads to opportunities.
Recap and next steps
This n8n workflow template gives you a complete, end-to-end LinkedIn lead enrichment system powered by Apollo.io, Google Sheets, RapidAPI or Apify, and OpenAI. It is designed to be:
- Resumable – Status columns and retries keep the pipeline running even when individual steps fail.
- Observable – You can see exactly where each lead is in the process.
- Extensible – You can plug in new enrichment sources, scoring logic, or CRM sync steps as you grow.
To get started:
- Provision and configure API keys for Apollo, scraping providers, OpenAI, and email validation.
- Import the n8n template and connect your credentials.
- Run the workflow on a small batch of leads to test each stage.
- Monitor errors, adjust rate limits, and refine prompts or filters as needed.
Call to action: If you want a ready-to-import n8n workflow or help adapting this pipeline to your stack (CRM integration, outreach tools, or data warehousing), reach out for a tailored implementation plan.