Build Your First AI MCP Server with n8n
Imagine letting an AI safely create calendar events for you, generate test data, or clean up text, all while your credentials and logic stay tucked away inside n8n. That is exactly what this n8n MCP server template is built for.
In this guide, we will walk through what the template does, how the pieces connect, when you would want to use it, and how to get it running in your own n8n setup. Think of it as sitting down with a friend who has already wired everything up and is now showing you around.
First things first: what is an MCP server?
Let us start with the basics. MCP stands for Model-Calling-Protocol. An MCP server is basically a safe toolbox that a language model can use.
Instead of giving an AI full access to your accounts or APIs, you expose a small set of controlled tools. Each tool has:
- A clear name
- Structured inputs (parameters)
- Structured outputs (responses)
In n8n, these tools are exposed through MCP Trigger nodes. The AI does not see your API keys, credentials, or internal workflow logic. It only sees a stable interface that it can call.
Using n8n as an MCP server is powerful because you can:
- Visually build and combine tools in workflows
- Add validation and sanitization before anything reaches external services
- Log and audit what the AI is doing
- Extend or change tools without touching the AI model itself
If you have ever wished you could “let the AI do it” without handing it the keys to everything, MCP is exactly that layer of safety and control.
What this n8n MCP template gives you
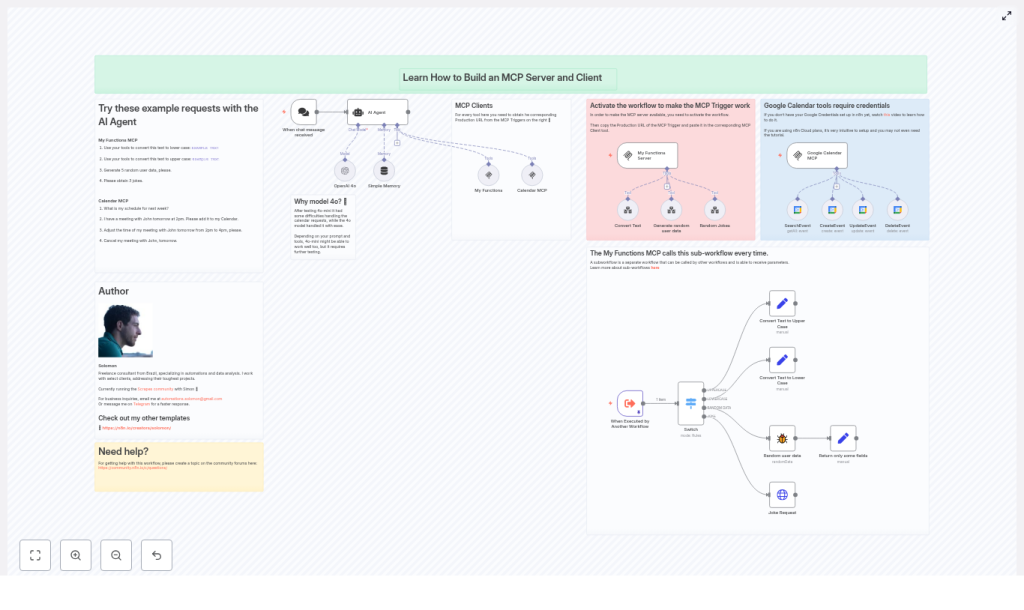
This template is a fully wired example of an MCP server and client setup inside n8n. It is ready to run and includes two main tool groups:
- My Functions MCP – text conversion, random user data, and jokes
- Google Calendar MCP – search, create, update, and delete calendar events
Under the hood, you will find:
- An AI Agent node (OpenAI 4o) that decides which tool to use
- MCP Trigger nodes that expose your tools via production URLs
- MCP Client tools that connect to those MCP endpoints using SSE (server-sent events)
- Sub-workflows for concrete tools, such as:
- Convert text to upper or lower case
- Generate random user data
- Fetch jokes from an external API
- Google Calendar tools for:
- Searching events
- Creating events
- Updating events
- Deleting events
- A Switch node and helper nodes that map incoming MCP requests to the right tool logic
So you end up with a small, focused AI agent that can handle text utilities and calendar management, all routed through n8n.
How the whole thing fits together
Let us walk through the architecture in plain language so you can see how data flows through the system.
- A user sends a prompt to the AI Agent
For example, via a chat trigger in n8n: “Convert this text to lower case” or “Add a meeting with John tomorrow at 2 pm.” - The AI Agent chooses a tool
The AI Agent node (OpenAI 4o) reads your system prompt and decides whether it needs to call a function, such as one of the MCP tools. - The AI calls an MCP Client tool
When the AI wants to use a tool, it calls the corresponding MCP Client node. This client:- Connects to the MCP Trigger’s SSE endpoint
- Sends a structured request that includes a function name and parameters
- The MCP Trigger runs the right sub-workflow
The MCP Trigger node receives the request and passes it into a sub-workflow (or local nodes) that actually implement the tool logic. - A structured response is sent back to the AI
The sub-workflow returns a clean, predictable response. The MCP Trigger sends that back to the AI Agent through SSE, and the AI uses it to answer the user.
The key idea: your credentials and detailed logic live safely inside n8n. The AI only sees the MCP interface, which you control.
When would you use this template?
This template is ideal if you:
- Want an AI agent that can perform real actions (like managing your calendar) without exposing raw credentials
- Need structured, predictable tool calls instead of free-form prompts
- Prefer a no-code / low-code way to design and update tools
- Plan to grow from simple text utilities to more advanced internal systems or CRMs
You can start with the included tools, then gradually add your own sub-workflows while keeping the same MCP pattern.
Step 1: Activate the MCP Trigger and set the SSE endpoint
Before anything works, the MCP Trigger nodes need to be live and the MCP Client tools need to know where to connect.
- Activate the workflow
Open the template workflow and turn it on. MCP Triggers only expose production endpoints when the workflow is active. - Copy the MCP Trigger production URL
Click an MCP Trigger node, for example:- My Functions Server
- Google Calendar MCP
In n8n, copy the Production URL that appears. This is the SSE endpoint your MCP Client will use.
- Paste the URL into the MCP Client tool
Open the matching MCP Client node, such as:- My Functions
- Calendar MCP
Paste the production URL into the
sseEndpointparameter. That tells the client exactly where to connect for tool calls.
Once this is done for each pair of MCP Trigger and MCP Client, the AI Agent can start calling your tools.
Digging into the tools: what you get out of the box
My Functions MCP: text utilities & simple helpers
The My Functions MCP sub-workflow is a nice starting point because it shows how to handle multiple operations behind a single MCP endpoint. It works like this:
- The MCP request comes in with a function name and a payload.
- A Switch node looks at the function name and routes the request to the right branch.
- Each branch implements one operation and returns a structured response.
The included operations are:
- Convert text to UPPERCASE
- Convert text to lowercase
- Return random user data
- Get jokes
To keep things consistent, the sub-workflow uses Set nodes to format outputs. That way, every MCP response follows a predictable shape, which is exactly what the AI model needs to stay reliable.
Random user data & jokes: working with external APIs
Two of the helper tools are great examples of how to mix internal logic and external APIs inside an MCP tool:
- Generate random user data
This sub-workflow takes a numeric parameter that tells it how many users to generate. It returns simple objects with fields like:firstNamelastNameemail
Perfect for testing, demos, or seeding fake data.
- Get jokes
This tool calls an external jokes API, then cleans up and returns the result in a tidy format that the AI can easily use in responses.
Once you understand these, you can plug in your own APIs or internal services in the same pattern.
Google Calendar MCP tools: let the AI manage your schedule
The template also includes a complete set of Google Calendar actions wired through n8n:
- SearchEvent
- CreateEvent
- UpdateEvent
- DeleteEvent
These nodes are connected to a Google Calendar OAuth credential in n8n. A few important points to keep in mind:
- Set up Google OAuth first
Before you activate the calendar MCP, configure your Google Calendar OAuth credential in n8n and make sure it is authorized for the calendar you want to use. - Parameters are passed through from MCP
Things like limit and time range come from the MCP request and are forwarded to the Google Calendar nodes. The AI can ask “What is my schedule for next week?” and the workflow translates that into concrete parameters. - Sanitize event content
When creating events, use descriptive but safe summaries and descriptions. Avoid dumping raw user prompts directly into your calendar entries.
Once this is set up, your AI can search your calendar, add meetings, adjust times, or cancel events, all through the MCP layer.
Trying it out: example prompts to test your MCP server
After activating the workflow and wiring up the SSE endpoints, you can start chatting with the AI Agent and watch the tools in action. Here are some prompts you can try:
- Convert this text to lower case:
EXAMPLE TeXt - Convert this text to upper case:
example TeXt - Generate 5 random user data
- Please obtain 3 jokes
- What is my schedule for next week?
- I have a meeting with John tomorrow at 2pm. Please add it to my Calendar.
- Adjust the time of my meeting with John tomorrow from 2pm to 4pm, please.
- Cancel my meeting with John, tomorrow.
Behind the scenes, each of these prompts triggers the same pattern:
- The AI chooses a tool based on your request.
- The MCP Client sends a structured function call.
- The MCP Trigger runs the matching sub-workflow.
- The response is formatted by Switch and Set nodes and returned to the AI.
This consistent structure is what makes MCP-based automation so reliable.
Staying safe: best practices & security tips
Because MCP endpoints can be exposed over the internet, it is worth taking a bit of time to lock things down. Here are some practices you should follow:
- Protect MCP Triggers with authentication
If your n8n instance is publicly reachable, do not leave MCP Triggers wide open. Use API keys, tokens, or a reverse proxy with access control. - Validate all incoming parameters
Treat every input from the AI as untrusted. In your sub-workflows, add checks for required fields, types, and ranges before calling external services. - Expose only what is needed
Keep your toolset minimal. Only give the AI the actions it truly needs, especially for sensitive systems like CRMs or internal APIs. - Log calls for auditing
Store metadata about MCP calls in a database or secure log inside n8n. This helps you debug, monitor usage, and meet compliance requirements if needed. - Keep credentials inside n8n
For third-party services like Google Calendar, always use n8n’s credentials system. Never embed secrets in MCP responses or expose them to the AI.
Common issues and how to fix them
MCP Client cannot connect
If your MCP Client tool is failing to connect, check the following:
- Is the workflow with the MCP Trigger active?
- Did you paste the correct Production URL into the
sseEndpointfield? - Can the environment where the client runs reach your n8n instance, or is a firewall or network rule blocking it?
Calendar operations are failing
When Google Calendar actions do not work as expected, verify:
- Your Google OAuth credential is configured and authorized correctly.
- The Google Calendar node can pass its own test in n8n.
- The event IDs you use for update or delete operations are valid and belong to the connected calendar.
The AI behaves in unexpected ways
If the AI is not calling tools correctly, or is returning oddly structured data, focus on the system prompt and examples:
- Refine the AI Agent’s system message to clearly describe:
- Which tools exist
- When to use each tool
- The exact structure for function calls and responses
- Use the template’s example requests as a base and tweak them to match your use case.
Growing your MCP server: ideas for extensions
Once the basic template is running smoothly, you can start turning it into your own AI-powered automation hub. Some ideas:
- Add rate limiting or quotas per client to prevent abuse.
- Build richer sub-workflows for:
- CRM operations
- Email automation
- Internal tools and databases
- Return more complex structured objects that the AI can combine in multi-step plans.
- Use memory nodes to keep conversation context and let the AI remember previous actions.
The pattern stays the same: MCP Trigger at the front, sub-workflows inside n8n, and an AI Agent that calls tools when needed.
Wrapping up: why this template makes your life easier
This n8n template gives you a practical, secure starting point for building an MCP server and clients. You get:
- Safe, controlled AI access to tools like Google Calendar
- Simple text utilities and helper functions ready to use
- A clear, extensible pattern for adding your own tools
- Full control over validation, logging, and security
Instead of wiring everything from scratch, you can focus on what you want the AI to do, not how to glue all the pieces together.
Next steps: try it in your own n8n instance
Ready to see it in action?
Here is a quick checklist: