Build a WhatsApp Chatbot with n8n & LangChain: Turn Your Website Into a Business Encyclopedia
Imagine if every guest question, every routine inquiry, and every “What time is check-out?” could be answered instantly, accurately, and with a friendly tone – without you or your team lifting a finger. That is the promise of this n8n workflow template.
In this guide, you will walk through a reusable n8n workflow that automatically scrapes your business website, turns it into a clean, deduplicated Business Encyclopedia, and powers a reliable WhatsApp AI concierge using LangChain and Google Gemini. It is especially powerful for hotels, restaurants, and service businesses that want a single, trustworthy source of truth for automated guest support.
Think of this template as a stepping stone. Once you set it up, you will not just have a chatbot. You will have the foundation for a more automated, focused way of working, where your time is freed up for the work that actually grows your business.
Keywords: WhatsApp chatbot, n8n workflow, business encyclopedia, LangChain, hotel AI agent, AI concierge, support automation.
The starting point: why traditional chatbots fall short
Most people try a support chatbot once and walk away disappointed. The answers feel generic, wrong, or outdated. Behind the scenes, there are two core problems:
- The bot hallucinates or “makes things up” instead of admitting it does not know.
- The information it relies on is scattered, stale, or not clearly connected to your real website content.
When a guest is asking about check-in times, parking, or cancellation policies, “close enough” is not good enough. You need a system that respects your information, stays within the facts, and gracefully escalates to a human when needed.
This is where the n8n WhatsApp chatbot template comes in. It is designed to be:
- Grounded in your actual website content.
- Defensive against hallucinations and guesswork.
- Reusable and easy to adapt to different businesses and use cases.
Instead of starting from scratch, you start from a workflow that has already solved the hardest parts for you.
Shifting your mindset: from answering questions to building a knowledge asset
Before we dive into nodes and triggers, it helps to reframe what you are really building.
You are not just creating a WhatsApp chatbot. You are creating a Business Encyclopedia – a structured, traceable, always-available knowledge base that your AI agent can safely rely on. Once this exists, you can plug it into WhatsApp, your website, internal tools, or any other channel you choose.
This mindset shift matters because:
- You stop treating support as a series of one-off answers and start treating it as a repeatable system.
- You gain a single source of truth that your team and your AI can both trust.
- You open the door to more automation over time, without losing control over accuracy.
The template you are about to explore is the bridge between that mindset and a concrete, working implementation in n8n.
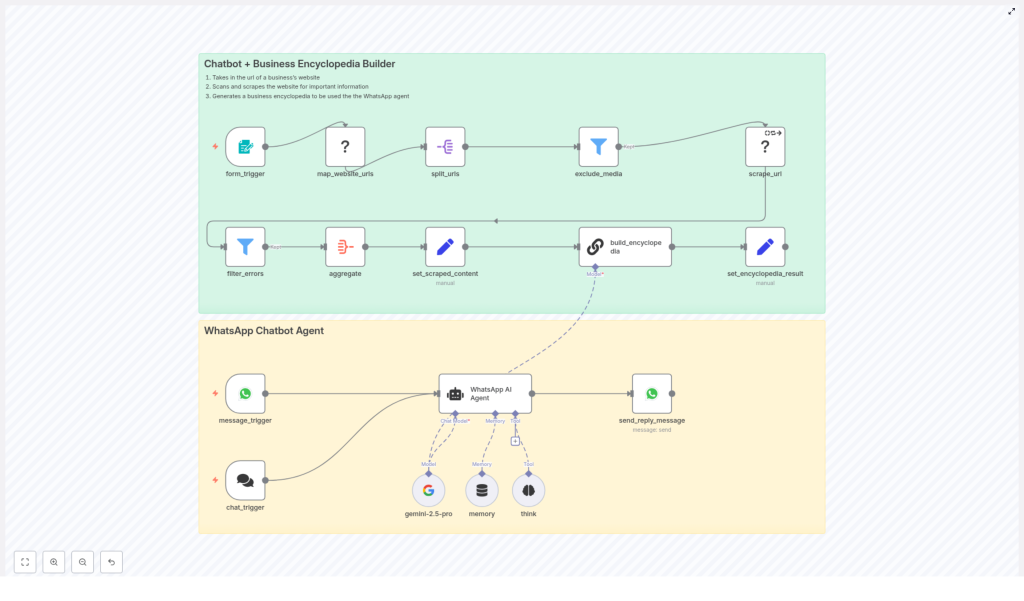
The big picture: how the n8n WhatsApp chatbot workflow works
At a high level, this n8n workflow template has two main layers working together:
- Scrape & Build Encyclopedia (green layer) – turns your website into a structured Business Encyclopedia.
- WhatsApp Chatbot Agent (yellow layer) – uses that encyclopedia to answer real user questions via WhatsApp.
Both layers are designed to be reusable and extensible, so you can improve them as your business evolves.
Layer 1: Scrape & Build Encyclopedia (green layer)
This layer is responsible for transforming your website into a clean, deduplicated knowledge base. It includes:
- Form trigger – Receives the website URL that you want to process.
- map_website_urls – Crawls the site to discover pages and sitemap entries.
- split_urls & exclude_media – Breaks the discovered URLs into scrape tasks and filters out media or irrelevant endpoints.
- scrape_url – Downloads each page’s content and metadata.
- aggregate → set_scraped_content – Combines all scraped content into a single payload.
- build_encyclopedia – Uses a LangChain chain with an LLM to synthesize a deduplicated, traceable Business Encyclopedia.
- set_encyclopedia_result – Stores the final encyclopedia so the chatbot can use it later.
Layer 2: WhatsApp Chatbot Agent (yellow layer)
This layer connects your Business Encyclopedia to real conversations on WhatsApp:
- message_trigger / chat_trigger – Listens for incoming WhatsApp messages or chat events.
- WhatsApp AI Agent – A LangChain agent that reads from the Business Encyclopedia and crafts responses.
- gemini-2.5-pro – The LLM model node (Google Gemini) used in the template to generate answers.
- memory (optional) – Short-term buffer to keep context for each WhatsApp user, so conversations feel more natural.
- send_reply_message – Sends the final answer back to the user’s WhatsApp number.
Together, these layers let you move from a static website to a living, conversational AI concierge that is grounded in your real content.
Design principles: accuracy, integrity, and trust
This workflow is built with a very specific philosophy: the AI should never be more confident than your data. That is why the following constraints are baked into the design:
- Single source of truth: All answers must be sourced from the Business Encyclopedia. The agent does not rely on external web search or unrelated knowledge bases as primary sources.
- No invention: If a detail is missing from the encyclopedia, the agent is instructed not to make it up. Instead, it clearly states that the information is unavailable.
- Human escalation: When the encyclopedia does not contain a requested detail, the agent guides the user to a human contact, such as a front desk phone number or a support email.
- Professional tone: Responses are designed to be friendly, clear, and concierge-style, suitable for hospitality and service businesses.
This approach might feel stricter at first, but it is what builds long-term trust with your guests or customers. They quickly learn that if the bot answers, it is because the answer is actually known.
Diving deeper: what each key node is responsible for
map_website_urls (Firecrawl)
The map_website_urls node explores your site structure using Firecrawl. It looks at pages and sitemaps to figure out what should be scraped.
To get the best results:
- Configure sensible limits to avoid overly aggressive crawling.
- Use sitemap support if your website has a well-maintained sitemap.
- Balance thoroughness with performance, especially for large sites.
scrape_url (Firecrawl)
The scrape_url node is where each page is actually fetched. It pulls down HTML and extracts useful metadata and text (often in markdown format).
For reliability:
- Enable retry logic to handle temporary network issues.
- Set reasonable timeouts so a single slow page does not block the entire workflow.
build_encyclopedia (LangChain chain)
This is your workflow’s “brain” for knowledge synthesis. The build_encyclopedia node runs a deterministic LangChain chain that turns messy, overlapping website content into a clean, structured Support Encyclopedia.
The prompt and logic in this node enforce several important behaviors:
- Stable IDs: Each entry uses a
kebab-caseslug so you can reference it consistently. - Traceability: Every fact is linked back to its source page IDs, so you know where it came from.
- Contradiction reporting: If different pages disagree, the node explicitly flags the contradiction instead of silently picking a side.
- Unknowns are explicit: Missing data is marked as
UNKNOWN, rather than invented.
This is what turns your scraped content into a dependable Business Encyclopedia that the WhatsApp AI agent can trust.
From encyclopedia to conversation: how the WhatsApp flow feels
Once the encyclopedia is built and stored, the yellow layer comes to life. Here is how a typical interaction flows:
Sample conversation: “What time is check-out?”
- message_trigger captures the incoming WhatsApp message and the user’s ID.
- The WhatsApp AI Agent searches the Business Encyclopedia for entries related to Check-In / Check-Out & Front Desk.
- If the encyclopedia contains the check-out time (for example, 12:00 PM), the agent replies with a friendly, clear message, optionally including a citation or escalation contact.
- If the encyclopedia does not contain that detail, the agent responds with something like:
“I do not have that specific detail in our hotel encyclopedia. Please contact reception at +39 089875733 or booking@leagavipositano.com.”
The result is a chatbot that feels both capable and honest. It saves you time on routine questions and gracefully hands off edge cases to your team.
Best practices: launching your n8n WhatsApp chatbot with confidence
To get the most out of this template and keep it stable in production, keep these best practices in mind.
Responsible crawling and updating
- Respect robots.txt: Configure Firecrawl to honor
robots.txtand any crawl-delay directives. - Rate-limit crawls: Use limits and delays to avoid overloading your website server.
- Schedule rebuilds: Plan periodic encyclopedia rebuilds (daily, weekly, or monthly) depending on how often your site changes.
Keep the model focused
- Restrict model access: In production, do not allow the agent to browse the open web or tap into unrelated knowledge bases.
- Enforce citations: Ensure prompts require the agent to base answers explicitly on encyclopedia entries.
Maintain a human safety net
- Include escalation paths: Keep phone numbers, emails, or front desk contacts in the encyclopedia so the bot can redirect users when needed.
- Log interactions: Store user queries and agent responses for auditing, improvement, and safety checks.
Security, privacy, and compliance: building trust into your automation
As you scale automation, trust becomes your most important asset. This workflow touches both website content and user messages, so consider the following:
- Secure storage: Store scraped website content and the generated encyclopedia in encrypted storage where possible.
- Data minimization: Avoid storing personal data from user messages unless it is necessary and aligned with your policies.
- Regional compliance: Follow rules like GDPR when processing or transferring user data, and provide a way to purge user-specific logs upon request.
Getting these foundations right makes it easier to expand your automation later without running into compliance headaches.
Troubleshooting: sharpening your workflow over time
Part of the power of n8n is that you can iterate quickly. If something does not behave as expected, you can adjust and improve. Here are some common issues and what to check:
- Pages missing from the encyclopedia: Review your map_website_urls node settings, sitemap coverage, and crawl limits.
- Inconsistent answers: Inspect the build_encyclopedia node output for flagged contradictions or ambiguous data.
- Hallucinated responses: Tighten the agent prompt to require exact-match citations from the encyclopedia, and disable any open-domain or fallback knowledge sources.
Each improvement you make is an investment in a more reliable, scalable support system.
Use cases: where this template creates real leverage
Although this workflow is demonstrated with hospitality in mind, it is flexible enough to support many scenarios where accurate, repeatable answers matter.
- Hotel and hospitality AI concierge: Answer questions about check-in, check-out, amenities, spa hours, restaurant times, and local recommendations.
- Local business support: Provide instant information about menus, opening hours, parking, policies, or event details.
- Enterprise knowledge layer: Give customer support teams a reliable first-line AI that handles common questions before escalating to human agents.
Each use case starts with the same foundation: your website, turned into a Business Encyclopedia, accessed through a WhatsApp chatbot built on n8n and LangChain.
Your next step: turn this template into your automated concierge
You do not need to build everything from scratch. The template is ready for you to adapt and extend.
How to get started
- Export the n8n workflow template.
- Connect your web crawling credentials (for example, Firecrawl) so the workflow can map and scrape your site.
- Set your model credentials for Google Gemini or an equivalent LLM compatible with LangChain.
- Configure your WhatsApp provider so the message_trigger and send_reply_message nodes can send and receive real messages.
- Start with a sandbox website or a staging version of your site to validate scraping and encyclopedia synthesis.
Once you see your first successful conversation, you will have proof that your website can power a real-time, always-on, AI-driven concierge.
Keep iterating and expanding
After the initial setup, consider:
- Adding booking links or reservation flows directly from the chatbot.
- Enabling multi-language support so guests can interact in their preferred language.
- Enhancing traceability with richer citations or logs for internal review.
If you want support tailoring this flow to your business, you can reach out for guidance, custom integrations, or a walkthrough of the template.
Start today: clone the workflow, run a test scrape, and watch your WhatsApp AI Agent deliver reliable, source-backed answers that free up your time and elevate your guest experience.
Author: The Recap AI – Practical templates and guides for building reliable AI-driven support. For consultancy and custom integrations, reply on WhatsApp or email our team.