Music Playlist Mood Tagger with n8n & OpenAI
Imagine a music catalog that effortlessly understands how each track feels. Instead of scrolling endlessly or guessing what fits your mood, your playlists simply adapt. With a bit of automation, that vision is closer than it seems.
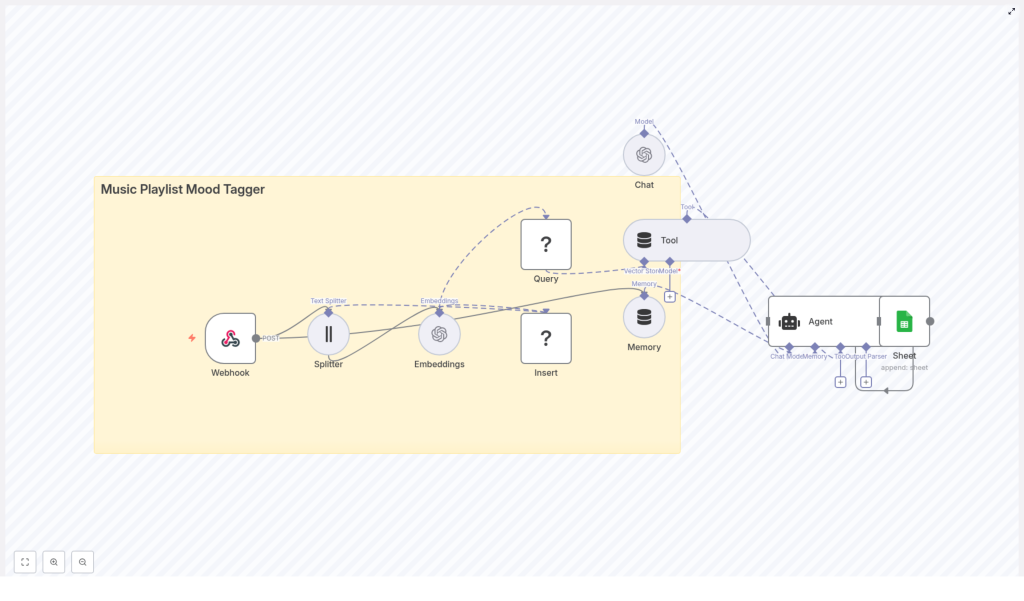
This guide walks you through a Music Playlist Mood Tagger built with n8n, OpenAI embeddings, Redis vector storage, and Google Sheets. You will see how to receive song metadata with a webhook, generate embeddings, store and query them by mood, and log everything for analysis – all without building a full backend.
More importantly, you will see how this workflow can become a stepping stone toward a more automated, focused way of working, where repetitive tagging is handled for you and you can spend your time on higher-value creative or strategic work.
The problem: manual mood tagging slows you down
Building mood-based playlists sounds simple until you try to maintain them at scale. Tagging songs one by one is slow, subjective, and hard to keep consistent across a large catalog. It is easy to fall behind and even easier to lose track of why a track was tagged a certain way.
Mood tagging matters because it shapes the experience your listeners have. Whether they need focus, chill, party, or melancholy vibes, they are really asking for a mood-aligned soundtrack. If you can deliver that reliably, you create deeper engagement and stronger loyalty.
This is where AI and automation step in. By converting lyrics, descriptions, and audio-derived metadata into vector embeddings, you can search and compare songs by mood with far more nuance than manual labels alone.
Mindset shift: from manual tasks to automated systems
Before we dive into the technical steps, it helps to adopt a simple mindset: every repetitive task is an opportunity to build a system that works for you. Instead of thinking “I need to tag these songs,” think “I am going to design a workflow that tags every song from now on.”
n8n is perfect for this shift. It lets you connect tools like OpenAI, Redis, and Google Sheets in a visual way. You do not need a full backend or a large engineering team. You only need the willingness to experiment, iterate, and gradually automate more of your process.
The Music Playlist Mood Tagger you are about to build is not just a one-off solution. It can become a reusable building block in your broader automation strategy for music analytics, recommendations, and content curation.
The big picture: how the n8n mood tagger workflow works
At a high level, the workflow looks like this:
- A Webhook in n8n receives POST requests with track metadata.
- A Text Splitter breaks long text like lyrics into chunks.
- OpenAI Embeddings convert those chunks into high-dimensional vectors.
- A Redis Vector Store saves those embeddings for fast similarity search.
- Memory and Tool nodes give an Agent access to relevant context.
- An Agent (Chat) turns vector search results into clear mood tags.
- Google Sheets logs each decision for auditing and analytics.
This combination gives you a powerful, scalable mood tagging pipeline that you can extend over time. You are not just tagging tracks, you are building a foundation for smarter playlists, recommendation engines, and editor tools.
Step 1 – Receive track metadata with an n8n Webhook
Start by creating the entry point to your automated system.
In n8n, add a Webhook node and configure it to accept POST requests at a path such as:
/music_playlist_mood_tagger
This webhook will receive JSON payloads that describe each track. For example:
{ "title": "Aurora", "artist": "Example Artist", "lyrics": "A soft and drifting melody that feels like early morning...", "audio_features": {"tempo": 72, "energy": 0.35}
}
You can connect this endpoint to streaming metadata pipelines, ingestion scripts, or even simple manual upload tools. From now on, every track that hits this webhook enters your automated mood tagging flow.
Step 2 – Split long text into manageable chunks
Lyrics and descriptions can be long. To help the embedding model capture context effectively, you will want to break them into smaller, overlapping pieces.
Add a Text Splitter node in n8n and configure it to slice long fields like lyrics or description into chunks. A common starting configuration is:
- Chunk size: 400
- Overlap: 40
This chunking strategy improves embedding quality and supports better contextual retrieval later. You can always tune these values as you test and refine your workflow.
Step 3 – Turn text into embeddings with OpenAI
Now it is time to convert those text chunks into embeddings that capture semantic meaning.
Add an OpenAI Embeddings node and send each chunk from the Text Splitter to this node. Select a model that is optimized for semantic similarity. The node will return a vector for each text chunk.
These vectors are the backbone of your mood tagging system. They allow you to compare songs, lyrics, and descriptions in a high-dimensional space where “similar” moods are close together.
Step 4 – Store embeddings in a Redis vector index
To make your system fast and scalable, you will store the embeddings in a Redis vector index.
Use the Redis Vector Store node and configure it with a dedicated index name, for example:
music_playlist_mood_tagger
Persist each embedding along with rich metadata, such as:
- Track title
- Artist
- Chunk index
- Original text snippet
- A generated track-level ID
Saving this metadata is essential. It allows you to filter, explain, and audit results later. You are not just storing numbers, you are preserving the context behind every embedding.
Step 5 – Query Redis to find similar moods
When you want to predict the mood for a new track, you will repeat part of the process: create an embedding and then search for similar entries in Redis.
For a new track, combine a lyrics snippet with audio features encoded as text, then send this combined text through the OpenAI Embeddings node again. With the resulting embedding, use the Redis Vector Store node in Query mode to search for nearest neighbors in your index.
The query will return the most similar chunks and their metadata. These neighbors form the evidence your Agent will use to infer the track’s mood. This step is where your previous work pays off, since every past track contributes to better tagging for future ones.
Step 6 – Use an Agent to generate mood tags and log results
Now you bring everything together into a clear, actionable output.
Set up an Agent (Chat) node in n8n and connect it with:
- Memory nodes to provide context about recent tracks and interactions.
- Tool nodes that give the Agent access to the Redis vector search results.
The Agent can then read the neighbor metadata, summarize the patterns it sees, and propose one or more mood tags such as Chill, Energetic, Melancholic, or Uplifting, along with confidence scores.
Finally, connect a Google Sheets node to append each outcome. Log fields like:
- Track ID and title
- Suggested mood tags
- Confidence scores
- Key snippets used for the decision
- Timestamps
This log becomes your audit trail, analytics source, and feedback loop for improving the system over time.
Designing a strong prompt for the Agent
The quality of your mood tags depends heavily on the instructions you give the Agent. A clear prompt keeps the output consistent and explainable.
Here is a sample instruction you can adapt inside your Agent node:
Given the following nearest-neighbor metadata and audio features, propose up to 3 mood tags with short justification and a confidence score (0-100). Prioritize emotional descriptors (energetic, calm, melancholic, uplifting, romantic, aggressive, relaxing).
Make sure the Agent receives both the source text snippets and the encoded audio features. This combination helps it capture not just lyrical content but also sonic character, leading to more accurate and transparent mood tags.
Best practices to get reliable mood tagging
To turn this workflow into a robust system, keep these recommendations in mind:
- Normalize audio features: Convert numeric audio data into readable text like “tempo: 72, energy: low” so embeddings reflect both lyrics and sound.
- Refine chunking: Adjust chunk size and overlap to balance completeness with context. Larger chunks capture more meaning, but too large can dilute focus.
- Store rich metadata: Always save track-level IDs, timestamps, and original text in Redis so you can trace back how each mood tag was generated.
- Respect rate limits: When processing large catalogs, batch embedding requests and implement backoff logic to stay within API limits.
- Protect privacy: Do not send personally identifiable information to third-party APIs without proper consent and policies.
Scaling your mood tagging system
As your catalog grows, your workflow should be ready to grow with it. Redis vector indexes are designed to be fast and cost-effective at scale, and n8n lets you orchestrate more complex pipelines over time.
To scale further, you can:
- Shard Redis or use a managed Redis offering with larger memory and vector index support.
- Cache frequent queries in n8n memory or a CDN when appropriate.
- Adopt asynchronous ingestion pipelines, so bulk imports do not block your webhook.
Each of these steps moves you from a helpful tool to a production-grade mood tagging platform that can support real-world workloads.
Troubleshooting and improving accuracy
As you experiment, you may run into issues. That is a normal part of building any automation. Use problems as signals for where to improve your system.
- Empty query results: Confirm that embeddings are being inserted correctly and that the index name used for inserts matches the one used for queries.
- Mood predictions feel off: Combine lyrics with audio features in your embedding text. Relying only on lyrics can miss important sonic mood cues.
- API errors: Monitor OpenAI responses and add retry logic or error handling nodes in n8n so temporary issues do not break your pipeline.
Security and governance for your workflow
Even for creative use cases like music, security and governance matter.
Protect your n8n Webhook with a secret token or an IP allowlist to prevent unauthorized ingestion. Store sensitive credentials like OpenAI keys, Redis passwords, and Google Sheets tokens in environment variables inside n8n, not in plain text within nodes.
If your logs contain source text or user-related data, restrict access according to your privacy policies and regulatory requirements.
Real-world ways to extend this template
Once you have the core mood tagger running, you can expand it in many directions. Here are some practical extensions:
- Dynamic playlist creation: Automatically build and refresh mood-specific playlists based on user preferences and similarity queries.
- Hybrid recommendation engines: Combine mood vectors with collaborative filtering or user behavior data to power richer recommendations.
- Editor review tools: Give music supervisors or curators a dashboard where they can review suggested moods, accept them, or make adjustments that feed back into your system.
Each extension builds on the same foundation you just created. Every improvement you make to this workflow can ripple across your entire music experience.
From template to transformation: your next steps
This Music Playlist Mood Tagger is more than a clever trick. It is a practical, extensible way to bring semantic mood tagging into your catalog using n8n, OpenAI embeddings, and Redis. By storing original snippets and metadata, you keep the system explainable. By using vector search, you keep it fast and scalable.
The real value comes when you treat this template as a starting point, not a finished product. You can:
- Tune chunk sizes and overlap for your specific genre mix.
- Refine the Agent prompt to match your brand voice or tagging taxonomy.
- Add extra logging, dashboards, or approval steps for human review.
Every small iteration turns your workflow into a stronger ally in your day-to-day work, freeing you from repetitive tagging and giving you more time to focus on strategy, creativity, and growth.
Action step: Import the provided n8n workflow template, connect your OpenAI, Redis, and Google Sheets credentials, and start by POSTing a small batch of tracks. Review the mood tags, adjust your prompt or chunking strategy, and run another batch. Let experimentation guide you toward a setup that truly fits your catalog and your goals.