Build an NDA Risk Detector with n8n & LangChain: Turn Manual Reviews Into Scalable Automation
From Manual NDA Reviews To Focused, Strategic Work
Reviewing NDAs is important work, but it can also be repetitive, draining, and slow. Legal teams, product leaders, and procurement specialists often spend hours scanning for risky clauses, trying not to miss anything, and copying notes into spreadsheets for tracking.
That time could be spent on deeper analysis, strategic negotiations, or building better processes. Automation will not replace your judgment, but it can protect your attention, surface risks faster, and give you the clarity to focus on what truly matters.
This is where an automated NDA Risk Detector built with n8n and LangChain comes in. Instead of reading every clause from scratch, you can:
- Send NDA text into a webhook
- Automatically break it into meaningful chunks
- Index it in a Redis vector store with Hugging Face embeddings
- Let an OpenAI-powered agent analyze risk levels and reasons
- Log everything neatly into Google Sheets for tracking and audits
The result is not just a workflow. It is a repeatable system that helps you scale your review process, reduce human error, and reclaim hours every week.
Shifting Your Mindset: Automation As Your Co-pilot
Before we dive into nodes and prompts, it helps to see this template as more than a one-off tool. It is a stepping stone toward a more automated, focused way of working.
With this NDA Risk Detector you can:
- Transform unstructured legal text into structured, searchable data
- Build a consistent risk scoring rubric instead of ad-hoc judgments
- Experiment, tweak, and improve your prompts and thresholds over time
- Use the same pattern later for other contracts, policies, or internal documents
Think of it as your first building block in a larger automation ecosystem. Once you get this running, it becomes easier to imagine and implement the next workflow, and the next.
Why This NDA Risk Detector Approach Works
The power of this n8n template lies in how it combines modern AI techniques with practical automation:
- Scalable: Vector embeddings + Redis enable fast semantic search across individual clause fragments, even as your volume grows.
- Transparent: Chunking text and storing metadata makes it easy to trace which exact clause triggered a risk flag.
- Automated: A webhook-driven workflow captures NDAs, runs analysis, and logs results into Google Sheets without manual copying or pasting.
Instead of treating every NDA as a new problem, you create a reusable pipeline that works the same way every time.
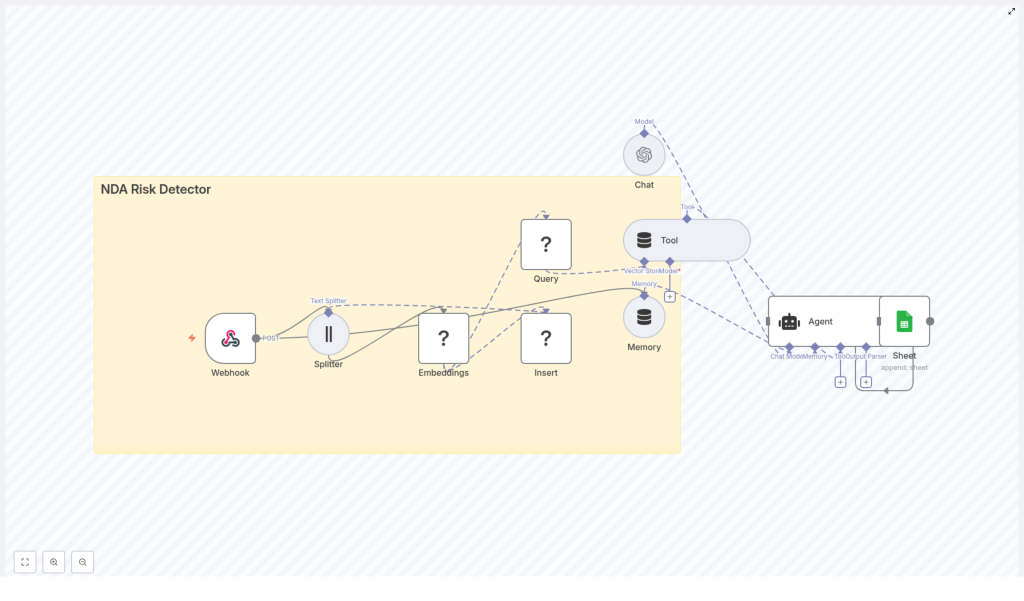
High-Level Architecture: How The Workflow Fits Together
The NDA Risk Detector template weaves together several n8n and LangChain components into one coherent automation:
- Webhook – Accepts NDA text via POST requests.
- Splitter – Breaks long documents into smaller chunks based on character length and overlap.
- Embeddings – Uses Hugging Face (or similar) to convert each chunk into semantic vectors.
- Redis Vector Store – Stores embeddings in an index named
nda_risk_detector. - Query + Tool – Retrieves the most relevant clause chunks for the risk analysis.
- Memory – Maintains short-term context for multi-step or conversational analysis.
- Chat/Agent (OpenAI) – Classifies risk, explains why, and assigns a score.
- Google Sheets – Logs every result into a spreadsheet for auditing and tracking.
Once configured, you can send any NDA into this pipeline and receive structured risk insights in return.
Step 1: Webhook Intake – Opening The Door To Automation
Your journey starts with a simple entry point: an n8n Webhook node. This is how NDAs enter your automated review system.
Create a webhook with the path /nda_risk_detector. The workflow expects a JSON payload similar to:
{ "document_id": "nda_1234", "text": "Full NDA text goes here...", "submitter": "alice@example.com", "company": "Acme Inc"
}
You can add more metadata later, but this basic structure gives your workflow what it needs to identify, process, and log each document.
Step 2: Splitting The Text Into Meaningful Clauses
Long legal documents are difficult to analyze as a single block. To make the AI more effective, you use a Splitter node to break the NDA into manageable chunks that roughly match clause-level sections.
Recommended starting settings from the template:
- chunkSize: 400 characters
- chunkOverlap: 40 characters
These values help preserve context without making each chunk too large. For legal language, aim for chunks in the range of 200 to 800 characters so that individual clauses stay intact.
This is one of the key places to experiment. If the detector misses context or breaks sentences awkwardly, adjust the chunk size or overlap and test again.
Step 3: Creating Embeddings & Storing Them In Redis
Next, you convert each chunk into a vector representation that captures its meaning. This is handled by the Embeddings node.
Use the Hugging Face embeddings node (or OpenAI embeddings if you prefer). Configure your API credentials in n8n so the workflow can call the embedding service. For each chunk:
- An embedding is created
- The resulting vector is inserted into Redis using the index name
nda_risk_detector
Store helpful metadata alongside each vector, such as:
document_idchunk_indexchunk_textsubmitter
This metadata is what allows you to trace any risk flag back to the exact clause and document later.
Step 4: Querying The Vector Store & Exposing It As A Tool
Once the NDA is indexed, the workflow uses a Query node to search the Redis vector index for the most relevant chunks during analysis.
The Tool node then exposes this vector store to the AI agent. This lets the agent:
- Retrieve specific clause fragments that matter for risk evaluation
- See surrounding context instead of isolated sentences
- Ground its responses in the actual NDA text
This combination of embeddings, Redis, and tools is what makes the system scalable and context aware.
Step 5: Memory & Chat – Letting The Agent Analyze Risk
To support multi-step analysis or follow-up questions, attach a short windowed memory to the agent. This helps it keep track of recent context across requests.
Then use the OpenAI Chat node to run the core risk analysis agent. The agent receives:
- The retrieved clause chunks from the vector store
- A carefully designed prompt that explains risk categories and the output format
This is where your workflow turns raw text into structured insight.
Designing The Prompt: Clear Instructions, Consistent Output
A strong prompt is essential for reliable automation. Here is a simplified version of a prompt you can use to classify NDA risk:
Analyze the following NDA clauses. For each clause, do two things:
1) Assign a risk level: Low, Medium, or High.
2) Provide a short reason (1-2 sentences) and suggest a remediation (if any).
Return JSON with: document_id, clause_index, clause_text, risk_level, risk_score (0-100), reason, recommendation.
Here are the retrieved clause fragments:
---
{{retrieved_clauses}}
---
Ask the agent to return well-structured JSON. This makes it far easier to log results into Google Sheets and to build additional automations on top of this workflow later.
Using A Clear Risk Scoring Rubric
To keep your analysis consistent, define a simple rubric that the agent follows. For example:
- High (70-100): Broad confidentiality exceptions, one-sided IP assignment, indefinite or very long obligations, or asymmetric penalties.
- Medium (35-69): Unclear definitions, vague timeframes, or mutual clauses that are ambiguous or incomplete.
- Low (0-34): Standard confidentiality terms, reasonable durations, balanced and mutual protections.
This rubric gives you a shared language for risk and makes your automation more predictable.
Logging Results To Google Sheets For Visibility & Growth
Once the agent has evaluated each clause, you want those results to be easy to review, filter, and share. Configure a Google Sheets node to append rows to a sheet, for example called “Log”.
Recommended columns include:
- Timestamp
- Document ID
- Submitter
- Clause Index
- Risk Level
- Risk Score
- Reason
- Recommendation
Over time, this sheet becomes a valuable dataset. You can use it to spot patterns, refine your prompts, and improve your contract templates or negotiation playbooks.
Example Agent Output
To visualize how the agent responds, here is a sample JSON output for a single clause:
{ "document_id": "nda_1234", "results": [ { "clause_index": 3, "clause_text": "Recipient may disclose information to affiliates without notice.", "risk_level": "High", "risk_score": 85, "reason": "Permits broad onward disclosure to affiliates without restrictions.", "recommendation": "Limit affiliate disclosures; require notification and binding obligations." } ]
}
This structure is ideal for automation. Each field can be logged, filtered, or used to trigger follow-up workflows.
Deployment & Testing: Turning Your Workflow Into A Reliable System
Once your nodes are connected and credentials are configured, it is time to test and refine. A few practical steps:
- Run integration tests with several sample NDAs and confirm that rows are correctly appended to your Google Sheets log.
- Review chunk overlap behavior and ensure clauses are not split mid-sentence in ways that change the meaning.
- Validate that the agent reliably returns strict JSON. Add a lightweight parser node to catch malformed JSON and fail gracefully.
Think of this phase as training your automation. Every test helps you tune the system for accuracy and reliability.
Security & Compliance For Sensitive NDA Data
Because NDAs often contain confidential and personal information, it is important to treat security as a core part of your design, not an afterthought. Consider:
- Encrypting data at rest in Redis and using HTTPS for all endpoints.
- Using scoped service accounts, rotating API keys regularly, and following least-privilege principles.
- Masking or redacting PII that is not necessary for risk analysis before storing it.
- Restricting access to the Google Sheet and enabling audit logging for accountability.
With these measures, you can enjoy the benefits of automation while respecting privacy and compliance requirements.
Continuous Improvement: Tuning & Extending Your Detector
One of the most empowering aspects of this n8n template is that it is not fixed. You can keep improving it as your needs evolve.
- Increase precision by building a labeled dataset of clauses and training a classifier on top of your embeddings.
- Use multi-model pipelines such as combining OpenAI for reasoning with a smaller local model for fast classification.
- Store provenance metadata so each flagged item maps back to the original source text, chunk index, and version.
- Rate-limit webhook intake and queue large documents for asynchronous processing to keep performance stable.
Each improvement turns your NDA Risk Detector into a more powerful, specialized tool that fits your team and your workflows.
Troubleshooting: Common Issues & Simple Fixes
As you experiment, you might encounter a few common challenges. Here are some quick diagnostics:
- No or poor results: Increase
chunkSizeor adjustchunkOverlapso clauses remain intact and context is preserved. - Agent returns freeform text: Tighten your prompt, clearly require JSON output, and validate the structure before logging.
- Redis index errors: Double-check that your index name is exactly
nda_risk_detectorand verify that your Redis vector plugin is correctly configured.
Each fix brings you closer to a stable, production-ready workflow.
From Template To Transformation: Your Next Steps
This NDA Risk Detector is more than a demo. It is a practical, extensible baseline for automated contract screening that combines:
- n8n automation
- LangChain primitives like splitter, embeddings, and vector store
- An OpenAI agent that delivers structured risk analysis
- Google Sheets logging for transparency and audits
By putting these pieces together, you turn a time-consuming manual process into a reusable system that works for you, not the other way around.
Start Automating Your NDA Reviews Today
Try it now: Import the workflow into n8n, connect your Hugging Face, Redis, OpenAI, and Google Sheets credentials, and send an NDA to the /nda_risk_detector webhook path. Then open your “Log” sheet and watch the analysis appear.
From there, you can customize the prompt, refine the scoring rubric, add a UI to review flagged clauses, or build downstream automations that notify stakeholders when high-risk clauses are detected.
Call to action: Import the template, run a few real-world tests, and note what you would like to improve. Share your feedback with your team or community, and keep iterating. Each small change is a step toward a more automated, focused, and scalable workflow.