Build an NDA Risk Detector with n8n & LangChain
Every NDA you review is a promise to protect your business, your ideas, and your relationships. Yet buried in those pages can be clauses that quietly introduce risk, slow down deals, or demand extra legal back-and-forth. If you have ever felt the weight of repetitive contract review, this guide is for you.
In this article, you will walk through a journey: from the frustration of manual NDA review, to a new mindset about automation, and finally to a practical, ready-to-use n8n NDA Risk Detector workflow template. By the end, you will see how a single workflow can become a stepping stone to a more automated, focused way of working.
The problem: hidden risks and lost time
NDAs and contracts are full of details that matter. Overbroad confidentiality, harsh indemnity clauses, one-sided change terms, long durations, and unclear data handling can all create real exposure. Manually scanning every document for these issues is:
- Slow and repetitive
- Mentally draining, especially at scale
- Hard to track and audit over time
As your volume of NDAs grows, so does the risk that something slips through. You want to protect the business, but you also want your team free to focus on strategy and high-value work, not endless copy-paste and clause hunting.
The shift: seeing automation as an ally
Instead of treating each NDA as a brand new manual task, imagine having an automated assistant that:
- Scans every NDA that comes in
- Highlights risky clauses for your review
- Remembers similar clauses from past documents
- Logs decisions so you build a living knowledge base over time
This is where n8n, LangChain-compatible components, and modern language models come together. You are not replacing legal judgment. You are building a system that does the repetitive searching and surfacing, so you can bring your expertise to the right clauses at the right time.
The NDA Risk Detector workflow template is a concrete way to start that transformation. It is a small, focused automation that can unlock big time savings and lay the groundwork for more advanced contract workflows later.
The vision: what this NDA Risk Detector can do for you
Using this n8n workflow, you can:
- Accelerate NDA review by automatically flagging potential risks
- Create a searchable memory of clauses using embeddings and a Redis vector store
- Build an auditable trail in Google Sheets for every NDA processed
The result is a more consistent, scalable, and traceable way to handle NDAs. Instead of starting from zero with each new document, you tap into a growing base of knowledge and automation that works for you in the background.
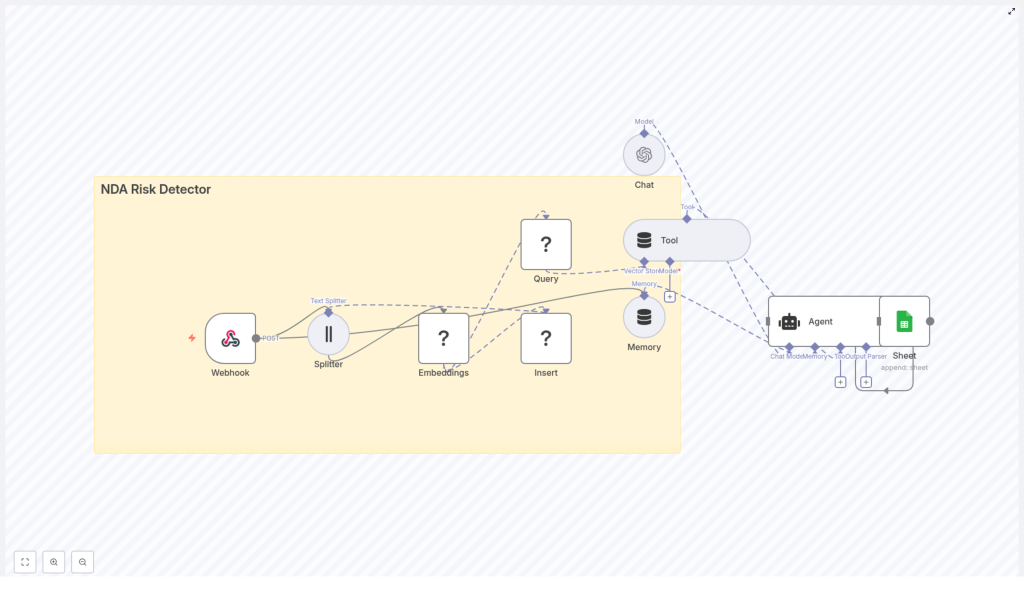
Architecture at a glance: how the workflow fits together
Before we dive into the steps, it helps to see the big picture. The NDA Risk Detector uses the following components inside n8n:
- Webhook – Receives NDA text or file content via POST
- Text Splitter – Breaks the NDA into smaller, overlapping chunks
- Embeddings – Converts those chunks into vector embeddings using Hugging Face or OpenAI
- Redis Vector Store – Indexes the embeddings and powers vector search
- Query / Tool – Exposes Redis search as a tool that the language agent can call
- Memory – Maintains short-term context for multi-step reasoning
- Chat / Agent – Uses an LLM to assess risk and generate structured results
- Google Sheets – Logs outputs for auditing and follow-up
Each piece is simple on its own. Combined, they create a powerful, reusable workflow that can grow with your needs.
Design choices that shape the workflow
Chunking: giving the model the right context
The first key choice is how to split your NDA into chunks. A good chunking strategy helps your vector store return relevant matches and gives the agent enough context to reason about each clause.
In this template, you use a character-based or sentence-based Text Splitter with settings such as:
chunkSize: 400chunkOverlap: 40
The overlap preserves context across boundaries, so important phrases that span two chunks are still understood when the vector store is queried. You can tune these values as you learn more about your own contracts.
Embeddings model: balancing cost and quality
The embeddings step turns NDA text into vectors that capture semantic meaning. You can choose:
- Hugging Face embeddings for an on-premise-friendly, flexible option
- OpenAI embeddings for high quality on many semantic tasks
Whichever you select, keep the embeddings normalized and consistent across your documents. This ensures that similar clauses end up close together in vector space, which improves the quality of search results.
Vector store: Redis as your contract memory
Redis makes an excellent vector store for this use case. It is fast, scalable, and well supported. In this workflow, you:
- Create a Redis vector index, for example
nda_risk_detector - Insert each chunk’s embedding along with metadata like document name, chunk index, and original text
Later, when the agent needs to evaluate a clause, it can query this index to find similar clauses from other NDAs and use them as evidence.
Agent and tools: letting the model reason with context
The real power appears when the LLM agent can call tools. In this case, you:
- Expose the Redis query node as a Tool inside n8n
- Give the agent a prompt that instructs it to:
- Call the vector store tool to fetch similar clauses
- Evaluate the NDA text against risk categories such as confidentiality scope, duration, indemnity, exclusivity, termination, and data handling
- Return a structured risk summary and clear recommendations
This pattern lets the model combine its language understanding with your stored knowledge, which is a powerful foundation for many future workflows beyond NDAs.
Step-by-step: building the NDA Risk Detector in n8n
Now let us turn this architecture into a concrete, working workflow. You can follow these steps directly or use the template as a starting point and adapt it to your environment.
1. Webhook input: your automation entry point
Start with a Webhook node configured for POST. Give it a path such as /nda_risk_detector. This webhook will accept:
- Raw NDA text in the request body
- Or an uploaded file that you convert to plain text in n8n before processing
This single endpoint can be called from many places: email processors, upload portals, internal tools, or even other workflows. It is the door through which every NDA enters your automated review pipeline.
2. Text Splitter: breaking NDAs into chunks
Next, add a Text Splitter node. Configure it with settings such as:
chunkSize: 400chunkOverlap: 40
The splitter will take your NDA text and output a list of overlapping chunks. Aim to preserve sentence boundaries where possible so that each chunk reads coherently. This improves both the embeddings and the agent’s understanding.
3. Embeddings: turning text into vectors
Connect the splitter to an Embeddings node, using either Hugging Face or OpenAI. For each chunk:
- Generate the embedding vector
- Attach metadata such as:
- Document name or ID
- Chunk index
- The original text snippet
These vectors are the core of your semantic search capability. Once stored, they let you compare new clauses to your existing corpus of NDAs.
4. Insert into Redis: building your vector index
Now add a Redis node configured as a vector store. Set it to:
- Mode: insert
- Index name: for example
nda_risk_detector
Insert each embedding vector along with its metadata. Over time, this index becomes a rich memory of the clauses you have processed, which you can reuse across many workflows and analyses.
5. Query / Tool: connecting Redis to the agent
To let the agent leverage this memory, add a Query node that searches your Redis index. This node should:
- Accept a query vector or text, depending on your configuration
- Return the most similar chunks, along with similarity scores and metadata
Expose this query node as a Tool in your agent configuration. This way, the LLM can programmatically call it when it needs supporting evidence or examples.
6. Memory and Agent: orchestrating the risk analysis
With the tool ready, set up your Agent node using a chat-capable LLM such as OpenAI or a compatible model. Attach a Memory buffer that keeps a short context window so the agent can remember earlier decisions and queries during a session.
Configure the agent so that it:
- Receives the NDA chunks and any relevant context
- Calls the Redis tool when it needs similar clauses
- Evaluates the text against your chosen risk categories
- Produces a structured summary, including risk scores and recommendations
This is where your workflow begins to feel like a true assistant rather than just a pipeline. The agent is using tools, memory, and your data to reason about each NDA.
7. Logging to Google Sheets: building an audit trail
Finally, connect the agent output to a Google Sheets node. Configure it to append a new row for each NDA with fields such as:
- Risk category or categories
- Severity (for example low, medium, high)
- Identified clauses or chunk references
- Recommendations or next steps
- Timestamp and document identifier
This gives you a living audit log that anyone on your team can review. Over time, this sheet becomes a powerful dataset for improving your prompts, training classifiers, or tracking trends in contract risk.
Prompting the agent for consistent results
A clear, stable prompt is essential if you want reliable output. Here is an example structure you can adapt:
System: You are a contract risk analyst. Use the vector store tool to fetch related clauses, then evaluate the NDA chunk for risks.
User: Evaluate the following NDA text and return a JSON with: {"risk_score": 0-100, "risk_categories": [...], "evidence": [matching_chunks], "recommendation": "..."}
Tool instructions: When uncertain, call the vector store tool to fetch similar clauses and supporting text.
The agent should always return machine-readable JSON. That makes it easy for n8n to log, route, or trigger follow-up actions based on the results. As you gain experience, you can refine the JSON schema and prompt wording to match your internal processes.
Testing, tuning, and growing your workflow
Once the workflow is in place, the next phase is experimentation. This is where you turn a template into a tailored, high-value tool for your team.
- Test with real examples: Run both known safe NDAs and known risky ones through the webhook. Check whether the risk scores and categories align with your expectations.
- Tune your retrieval settings: Adjust chunk size, chunk overlap, and the number of retrieved neighbors (k) to improve precision and recall.
- Refine the prompt and thresholds: Review false positives and false negatives. Update the prompt, risk definitions, or classification thresholds until the output feels trustworthy.
Every small improvement here pays off across every future NDA the system processes. This is the compounding effect of automation in action.
Operational and security considerations
Contracts and NDAs are sensitive by nature. As you automate, keep security and privacy at the center of your design:
- Use HTTPS for webhooks and TLS for Redis connections so data in transit is encrypted.
- Apply strict access controls and rotate API keys for Hugging Face, OpenAI, and Redis regularly.
- Define data retention policies for embeddings and logs. Delete or anonymize old entries when they are no longer needed.
With these practices in place, you can enjoy the benefits of automation without compromising on trust or compliance.
What the workflow produces: sample outputs and next actions
For each NDA processed, the agent can generate a structured summary that includes:
- Risk score from 0 to 100
- Primary risk categories, such as:
- Overbroad confidentiality
- Indemnity
- Data transfer or data handling
- Exclusivity, termination, or duration
- Evidence: the most relevant chunk text and similarity scores from Redis
- Recommended action, for example:
- “Escalate to legal”
- “Request redline on clause X”
- “Low risk – proceed”
You can then trigger follow-up automation based on these results, such as sending alerts, updating a CRM, or kicking off an internal review process.
Extending the workflow: your next automation steps
Once your basic NDA Risk Detector is live, you have a powerful foundation. From here, you can expand in several directions:
- Automated redlines: Use the agent to propose alternative wording for flagged clauses and send suggestions directly to your legal team.
- Supervised classifiers: Train a classifier on labeled clauses to sharpen precision for specific risk categories.
- Ticketing integration: Connect to tools like Jira or Asana so that high-risk NDAs automatically create tasks for legal review.
Each extension builds on the same core pattern: embeddings, vector search, an agent that can call tools, and clear logging. As you grow more comfortable with n8n and LangChain-compatible components, you will find many more workflows that follow this pattern.
From template to transformation
Using n8n with embeddings, a Redis vector store, and an agent that can call tools is more than a clever technical exercise. It is a practical way to reclaim time, reduce manual review work, and create a repeatable, auditable NDA review process.
This NDA Risk Detector template is a small but powerful step toward a more automated, focused workflow. Start with it, learn from it, and then keep building. Every improvement you make to this workflow will quietly multiply your impact across hundreds or thousands of future NDAs.
Call to action: Load the workflow template into your n8n instance, try it on a few real NDAs, and begin tuning chunk sizes, prompts, and thresholds to match your contracts. Treat it as a living system that you can refine over time.
If you