Build a Visa Requirement Checker with n8n
Ever found yourself endlessly scrolling government websites trying to figure out if you actually need a visa for your next trip? You are not alone. In this guide, we will walk through how to build a Visa Requirement Checker in n8n that can answer those questions automatically, using embeddings, a vector store, and a conversational AI agent.
We will look at what the template does, when it is useful, and how each part of the workflow fits together. By the end, you will know how to connect a webhook, text splitter, Cohere embeddings, a Weaviate vector store, an Anthropic-powered agent, and Google Sheets logging into one smooth, automated experience.
What this n8n Visa Requirement Checker actually does
At a high level, this workflow takes in details about a traveler and their question, looks up the right visa rules in a vector database, and then uses an LLM to respond in clear, natural language. It is like having a smart assistant that has read all the visa policy docs and can pull out the relevant bits on demand.
Here is what the template helps you automate:
- Receive visa questions through a simple webhook API
- Split and embed long policy documents for semantic search
- Store those embeddings in Weaviate for fast, accurate retrieval
- Use an Anthropic-powered agent to craft a human-friendly answer
- Keep a short-term memory of the conversation for follow-up questions
- Log every interaction to Google Sheets for audits and analytics
Why build a Visa Requirement Checker with n8n?
Visa rules are notoriously complex. They change often and depend on things like:
- Citizenship and residency
- Destination country
- Length of stay
- Purpose of travel (tourism, business, study, etc.)
- Previous travel history or special cases
Trying to keep up manually is painful. With an automated visa checker, you can:
- Deliver up-to-date answers quickly through a webhook endpoint
- Use vector search to match nuanced, context-heavy guidance
- Log every query and response in Google Sheets for review or analytics
- Scale to more users and more languages without multiplying manual work
If you are building a travel app, chatbot, or internal tool for a travel team, this n8n template can become a core part of your user experience.
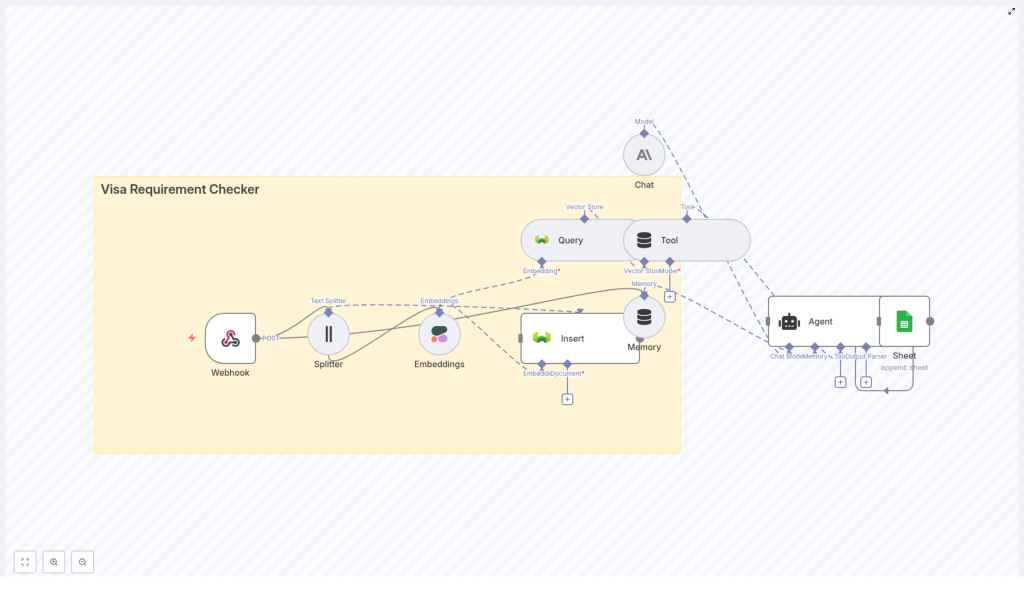
How the workflow is structured
Let us zoom out before we go step by step. The workflow is made up of a few key building blocks in n8n:
- Webhook – Receives incoming POST requests with traveler details and their question.
- Text Splitter – Breaks large visa policy documents into smaller chunks.
- Cohere Embeddings – Turns each chunk into a vector representation for semantic search.
- Weaviate Insert – Stores embeddings plus metadata in a vector database.
- Weaviate Query – Finds the most relevant chunks when a user asks a question.
- Tool & Agent – An Anthropic-based agent uses those chunks as context to write the final answer.
- Memory – Keeps short-term conversation context for follow-up questions.
- Google Sheets – Logs questions and answers for audits and metrics.
You can think of it in two phases:
- Ingestion – Split policy documents, embed them, and store them in Weaviate.
- Runtime – When a user asks a question, query Weaviate, pass results to the agent, and log the interaction.
Step-by-step: Node-by-node walkthrough
1. Webhook: your public entry point
Everything starts with a Webhook node in n8n. This exposes a POST endpoint, for example:
/visa_requirement_checkerYour frontend, chatbot, or any client can send a JSON payload like this:
{ "citizenship": "India", "destination": "United Kingdom", "purpose": "tourism", "stay_days": 10, "question": "Do I need a visa?"
}Some good practices at this stage:
- Validate the incoming fields before processing
- Add rate limiting so a single client cannot overwhelm your workflow
- Require an API key or HMAC signature to prevent unauthorized access
2. Text Splitter: preparing your policy documents
Visa policies tend to be long and full of edge cases. To make them usable for embeddings and vector search, you run them through a Text Splitter node.
This node divides large documents into overlapping chunks, for example:
chunkSize = 400chunkOverlap = 40
The overlap helps preserve context between chunks, while the size keeps each chunk within token limits for the embedding model. This balance is important so your semantic search remains accurate and cost effective.
3. Cohere Embeddings: turning text into vectors
Next, you feed each chunk into a Cohere Embeddings node. This converts the text into numerical vectors that capture semantic meaning.
When configuring this node, you will:
- Pick a Cohere embeddings model that fits your quality and budget needs
- Generate embeddings for each chunk created by the text splitter
- Attach metadata such as:
sourcecountryeffective_datedocument_id
That metadata becomes very handy later when you want to trace a specific answer back to its original policy document.
4. Insert into Weaviate: building your vector store
With embeddings in hand, you use the Insert (Weaviate) node to store them in your vector database. This is where your knowledge base actually lives.
Recommended setup tips:
- Use a dedicated class or index name such as
visa_requirement_checkerto keep things organized - Store both the vector and the metadata so you can filter by:
- Country or region
- Visa type
- Effective date
- Leverage Weaviate’s hybrid filters to narrow down results based on structured fields
This ingestion step usually runs when you add or update policy documents, not necessarily on every user query.
5. Query & tool integration: finding relevant guidance
When a traveler asks a question, the workflow moves into retrieval mode. The Weaviate Query node searches your vector store and returns the most relevant chunks.
Typical behavior at runtime:
- The workflow takes the user’s question and any relevant metadata (citizenship, destination, purpose, etc.)
- It queries Weaviate for the top-k best matching chunks
- Those chunks are then passed into the agent as a tool or context source
This tool integration lets the LLM selectively use the retrieved pieces of information instead of guessing from scratch, which significantly reduces hallucinations.
6. Agent (Anthropic Chat): composing the answer
Now comes the conversational part. The Agent (Anthropic Chat) node runs an LLM in chat mode. It receives three key ingredients:
- The user’s original question
- The context retrieved from Weaviate
- Short-term memory from previous turns in the session
You control the behavior of the agent by carefully designing the prompt. Helpful instructions include:
- Use only the retrieved sources for factual claims
- Clearly indicate uncertainty and suggest official verification if needed
- Return both:
- Structured data (like visa type, required documents, links)
- A plain-language explanation that users can easily understand
This combination lets you serve answers that are both machine readable and user friendly.
7. Memory & Google Sheets logging: keeping context and records
Visa questions often come in follow-up form, such as “What about multiple entry?” or “What if I stay two days longer?” To handle this gracefully, the workflow uses a short-window Memory component.
This memory keeps the recent conversation history so the agent can respond in context without re-asking the user for all details every time.
At the same time, a Google Sheets node logs each interaction. Typical data you might store:
- Timestamp
- Traveler details (ideally anonymized)
- User question
- Agent response
- Any confidence or metadata fields you include
These logs are useful for audits, quality checks, analytics, and improving your prompts or retrieval strategy over time.
Prompt design and safety: keeping answers reliable
Since you are dealing with important travel decisions, safety and accuracy matter a lot. A few prompt and design guidelines help keep your system responsible:
- Ask the agent to cite the
document_idor source link for each factual statement. - Instruct the model that if it does not find strong context, it should respond with a safe fallback such as:
"I could not find authoritative guidance, please consult the embassy or official government website." - Be careful with personally identifiable information:
- Avoid logging raw PII where possible
- If you must store it, consider encryption or other safeguards
Deployment tips for your n8n visa checker
Once the workflow is working in your development environment, you will want to harden it for production. Here are some things to keep in mind:
- Store all sensitive credentials as environment variables:
- Cohere API key
- Weaviate credentials
- Anthropic API key
- Google Sheets credentials
- Set up monitoring and alerts for:
- Workflow errors
- Unusual traffic spikes
- Failed vector store queries
- Schedule periodic re-indexing so your vector store reflects the latest visa policies
- Define data retention rules to comply with privacy regulations in your region
Testing and validation: does it really work?
Before you rely on the system for real users, it is worth investing in structured testing. Some ideas:
- Test across a wide range of nationalities and destinations
- Cover different purposes of travel like tourism, business, study, and transit
- Include tricky edge cases:
- Multiple-entry visas
- Airport transit and layovers
- Diplomatic or official passports
- Maintain a small, human-reviewed test set with:
- Sample questions
- Expected answers
- Notes on acceptable variations
This helps you evaluate both the retrieval quality (are the right documents being found?) and the final agent response (is it accurate, clear, and safe?).
Sample webhook flow: putting it all together
To summarize the full journey of a single request, here is what happens when a client hits your webhook:
- The client sends a POST request to
/visa_requirement_checkerwith traveler details and a question. - The Webhook node receives the request and triggers the workflow.
- For ingestion flows, documents go through the Text Splitter and Embeddings nodes, then get inserted into Weaviate.
- For runtime queries, the workflow calls the Weaviate Query node to retrieve the top-k relevant chunks.
- The Agent node uses those chunks, along with conversation memory, to generate a structured answer and a natural-language explanation.
- The workflow logs the query and response to Google Sheets.
- The final answer is returned to the client via the webhook response.
Common pitfalls to avoid
There are a few easy mistakes that can cause problems later. Watch out for:
- No document versioning – If you do not track versions or effective dates, you may end up serving outdated guidance.
- Letting the model answer without retrieved context – This increases the risk of hallucinations and incorrect advice.
- Storing raw PII unprotected – Keeping sensitive data in plain text in your sheet or index is a security and compliance risk.
Extensions and improvements once you are live
After the basic workflow is stable, you can start to get more ambitious. Some useful enhancements:
- Automatically ingest updates by scraping official government websites or consuming their APIs, then trigger re-embedding when content changes.
- Support multiple languages by:
- Using language-specific embeddings, or
- Translating queries before vector lookup and translating answers back.
- Expose friendly endpoints for:
- Chatbots on your website
- Slack or internal tools
- WhatsApp or other messaging platforms
- Include a confidence score and direct links to official consular or immigration pages so users can double check details.
When should you use this template?
This Visa Requirement Checker template is ideal if you:
- Run a travel platform and want smarter, automated visa guidance
- Need an internal tool for support agents to quickly answer visa questions
- Are experimenting with LLMs plus vector search in n8n and want a real-world use case
- Care about traceability and want to know exactly which document each answer came from
If that sounds like you, this workflow gives you a solid, practical starting point without having to glue all the pieces together from scratch.
Wrap-up and next steps
The n8n Visa Requirement Checker showcases how automation, embeddings, and conversational AI can work together to deliver accurate, explainable visa guidance at scale. You start with a small, curated set of policy documents, refine your prompts and retrieval filters, and then gradually grow the system as your needs expand.
If you would like a ready-to-use starter template or help connecting your preferred vector store and LLM, feel free to contact us or subscribe to our newsletter for detailed templates and code snippets.