AI Logo Sheet Extractor to Airtable: Enterprise-Grade Automation with n8n & AI
Transform dense logo collages into a structured, queryable dataset with a fully automated n8n workflow. This guide details a production-ready AI logo sheet extractor that leverages AI vision, LangChain, and Airtable to detect product logos, infer attributes, and map similarity relationships, then upsert everything into Airtable with deterministic logic.
The article is written for automation engineers, solution architects, and operations teams who want a repeatable, low-maintenance workflow rather than a one-off script.
Business context: Why automate logo sheet extraction?
Logo sheets – visual grids or collages of product logos and short labels – show up across market landscapes, vendor matrices, and internal research decks. Manually converting these visuals into a structured tools database is:
- Slow and operationally expensive
- Prone to transcription errors and inconsistent naming
- Difficult to standardize across teams and projects
By connecting an AI-powered logo sheet extractor to Airtable with n8n, you can:
- Convert logo images into structured records automatically
- Generate standardized attributes such as categories and capabilities
- Capture similarity or competitor relationships between tools
- Continuously enrich an Airtable dataset using idempotent upserts
The result is a living database of tools that can feed analytics, market research, and internal knowledge systems.
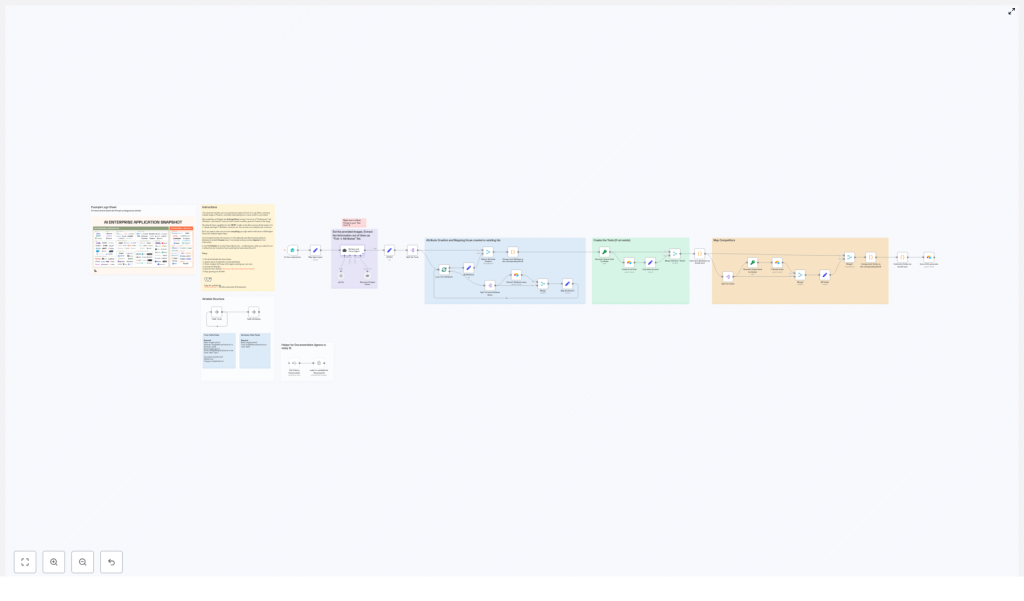
High-level workflow architecture
The n8n implementation follows a clear, modular pipeline:
- Form-based ingestion – A public n8n form receives the logo sheet image and optional context prompt.
- AI vision and parsing – A LangChain-based agent with image support analyzes the sheet, detects tools, and returns a structured JSON payload.
- Schema validation – A structured output parser enforces a predictable JSON schema.
- Attribute management – Attributes are normalized and upserted into an Airtable Attributes table.
- Tool upsert with hashing – Tools are created or updated in the Tools table using deterministic hashes as unique keys.
- Similarity mapping – Similar tools are resolved to Airtable record IDs and linked to form competitor relationships.
This design separates vision, parsing, and persistence concerns, which makes the workflow easier to debug, scale, and extend.
Airtable data model required for the workflow
Before building the n8n workflow, configure Airtable with a minimal schema that supports attributes, tools, and similarity links.
Tools table (core fields)
- Name – Single line text, the tool or product name.
- Attributes – Linked records to the Attributes table, multiple values allowed.
- Hash – Single line text, deterministic key derived from the tool name used for idempotent upserts.
- Similar – Linked records to the same Tools table, multiple values allowed to represent competitors or adjacent tools.
- Optional fields – Description, Website, Category (multi-select) or any other enrichment fields you plan to populate later.
Attributes table (core fields)
- Name – Single line text, canonical attribute label such as a category or capability.
- Tools – Linked records back to the Tools table to maintain a many-to-many relationship.
This schema is intentionally minimal and supports both automated ingestion and later manual curation.
Key n8n components and their responsibilities
The workflow relies on a set of n8n nodes that each handle a specific responsibility. Structuring the flow this way improves maintainability and observability.
- Form Trigger
- Exposes a public form endpoint for users to upload a logo sheet image.
- Accepts an optional free-text prompt that provides context to the AI agent.
- Mapping / Pre-processing node
- Normalizes the form payload.
- Maps the uploaded image and user-provided prompt into the expected input format for the AI agent node.
- LangChain Agent (Retrieve and Parser)
- Uses an LLM with image capabilities to inspect the logo sheet.
- Detects logos and surrounding text, infers product names and attributes.
- Outputs a JSON array with tools, attributes, and suggested similar tools.
- Structured Output Parser
- Validates that the model output conforms to the defined JSON schema.
- Prevents malformed responses from breaking downstream Airtable operations.
- Split / Loop nodes
- Iterate over the list of tools and attributes.
- Allow independent creation, normalization, and linking logic for attributes and tools.
- Airtable nodes
- Upsert attributes into the Attributes table, avoiding duplicates.
- Upsert tools into the Tools table and maintain links to attributes and similar tools.
- Crypto node (MD5 or similar hash)
- Generates deterministic hash values from normalized tool names.
- Provides a stable unique identifier to support repeat-safe upserts.
AI agent contract: prompt design and output schema
The reliability of this workflow depends heavily on a strict contract between the n8n workflow and the AI agent. The agent must return a predictable JSON structure.
Expected JSON output structure
[ { "name": "ToolName", "attributes": ["category", "feature"], "similar": ["OtherTool", "AnotherTool"] }
]
Each object in the array represents a single tool detected in the logo sheet:
name– Canonical tool or product name.attributes– Short, categorical labels that describe the tool.similar– Names of tools that are similar or competitive.
Prompting recommendations
- In the system message, clearly instruct the agent to:
- Return only tools it can identify with high confidence.
- Provide attributes as short, categorical phrases such as “Browser Infrastructure”, “Agentic Application”, “Storage Tool”.
- Output strictly valid JSON that matches the defined schema.
- If the sheet contains small or dense logos, request:
- A confidence flag per item, or
- Bounding box metadata if supported, for later visual review.
- Expose an optional user prompt field in the form for additional context, for example:
- “This sheet compares enterprise AI infrastructure providers.”
- “These are tools used by data engineering teams.”
Being explicit with the agent instructions and providing an example JSON snippet significantly reduces hallucination and improves output consistency.
Detailed implementation in n8n
1. Configure the ingestion form
Start with a Form Trigger node in n8n:
- Add an upload field for the logo sheet image.
- Add an optional text field for user-provided context.
- Set a clear webhook path such as
/form/logo-sheet-feederto make integrations and documentation easier.
The form becomes the primary entry point for analysts, marketers, or internal stakeholders to submit new sheets for processing.
2. Set up and tune the AI vision agent
Use a LangChain-based node connected to OpenAI or another LLM with image understanding capabilities:
- Enable binary image passthrough (for example,
passthroughBinaryImages) so the node receives the raw image data. - In the system prompt, describe the task:
- Identify tools from the logo sheet, including nearby labels.
- Infer attributes and similar tools where possible.
- Return only the JSON structure defined earlier.
- Optionally, inject the user prompt from the form as additional context.
At this stage, the output is a raw JSON-like structure that still needs validation.
3. Enforce a strict JSON schema
Connect the AI node to a Structured Output Parser:
- Define the expected fields and their types:
nameas stringattributesas array of stringssimilaras array of strings
- Reject or sanitize malformed responses before they reach Airtable operations.
This step is critical for workflow stability, particularly under high volume or when model behavior changes.
4. Create and normalize attributes in Airtable
Next, handle attributes as a separate loop:
- Use a Split or Item Lists node to iterate over each tool’s
attributesarray. - Normalize attribute strings (for example, trim whitespace, standardize casing) before upserting.
- Use an Airtable node to:
- Check if an attribute with the same name already exists.
- Create it if missing.
- Return the attribute record ID for downstream linking.
The goal is to maintain a single canonical record for each attribute label and avoid unnecessary duplication.
5. Upsert tools with deterministic hashing
For each tool detected by the agent:
- Normalize the tool name, for example:
- Trim whitespace.
- Convert to lowercase.
- Use a Crypto node to compute an MD5 (or similar) hash of the normalized name.
- Use an Airtable node to:
- Upsert into the Tools table based on the Hash field.
- Attach the corresponding attribute record IDs from the previous step.
- Store the Airtable record ID for later similarity mapping.
This deterministic upsert strategy ensures that reprocessing the same or updated logo sheets does not create duplicate tool entries.
6. Map and persist similar tools
Once all tools exist in Airtable, handle similarity relationships:
- Iterate through each tool’s
similararray. - For each similar tool name:
- Normalize the name and compute its hash using the same logic as above.
- Upsert the similar tool into the Tools table if it does not already exist.
- Retrieve its Airtable record ID.
- Update the primary tool’s Similar field with the collected record IDs.
This two-pass approach – first creating tools, then resolving similar relationships – ensures that all referenced tools have valid IDs before linking.
Operational best practices
Handling low-confidence detections
- Ask the agent to include a confidence indicator for each tool when possible.
- Route low-confidence items to a manual review queue or a separate Airtable view.
- Consider re-running problematic sheets with a refined prompt or at higher resolution.
Name and attribute canonicalization
- Normalize tool names before hashing to avoid duplicates based on trivial differences such as case or spacing.
- Optionally implement additional normalization rules for common variants, for example:
- “OpenAI” vs “Open AI”.
- For attributes, maintain a manual alias or mapping table in Airtable if you frequently see variants like “Agentic Application” vs “Agentic-App”.
Prompt engineering and stability
- Keep system prompts strict and specific about required output format.
- Include an explicit example of the JSON array to guide the model.
- Periodically review outputs and adjust the prompt to reduce hallucinations or drift.
Rate limiting, performance, and cost control
- Be mindful of model costs for large or frequent logo sheets.
- Batch processing where possible or use smaller, cheaper models for first-pass extraction.
- Use n8n’s built-in rate limiting or queuing mechanisms if you expect high throughput.
Privacy considerations
- Restrict uploads to logo sheets and public branding assets.
- Avoid using this workflow for images that contain sensitive personal data or confidential information.
Troubleshooting common issues
Logos are missing or merged
Small, low-contrast, or overlapping logos can be difficult for the model to detect reliably.
- Increase image resolution before upload.
- Crop large sheets into multiple smaller segments and process them separately.
- Consider adding bounding box extraction and a review UI for high-value use cases.
Duplicate or inconsistent attributes
Attribute duplication often stems from minor text variations.
- Strengthen normalization logic in n8n before upserting attributes.
- Maintain a manual alias table in Airtable to merge similar labels.
- Periodically audit the Attributes table and consolidate near-duplicates.
Incorrect or missing similarity links
- Verify that the similarity mapping step runs only after all tools are created.
- Ensure that you are using the same hashing and normalization logic for both primary and similar tool names.
- Inspect the agent prompt if it frequently suggests irrelevant or nonsensical similar tools.
Extensions and advanced enhancements
- Bounding box and visual review Add bounding box data to the agent output and build a simple review UI that overlays detected tools on the original sheet.
- OCR integration Integrate OCR to capture small labels or fine print near logos, which can significantly improve name disambiguation.
- Embeddings for semantic similarity Use embeddings to compute similarity between descriptions or attributes and suggest competitors beyond what appears on a single sheet.
- Scheduled re-processing Set up a scheduled n8n job to re-run older sheets after you improve prompts or switch to a more capable model.
Real-world applications
- Market research teams Automatically extract vendor landscapes from industry cheat sheets and analyst reports.
- Content and marketing teams Build and maintain tool directories from conference slides, webinars, and partner decks.
- Product and strategy teams Track competitor presence across presentations, events, and external publications.
Conclusion: From static logo sheets to a dynamic tools database
By combining n8n, AI vision, and Airtable, you can convert static logo collages into a living, structured dataset with minimal manual effort. With careful prompt design, deterministic hashing, and attribute canonicalization, this AI logo sheet extractor becomes a robust and repeatable part of your automation stack.