Automate Notion API Updates with n8n & RAG
Every growing team reaches a point where manual tracking simply cannot keep up. Notion pages multiply, updates fly in from every direction, and important changes quietly slip through the cracks. If you have ever felt that you are spending more time monitoring Notion than actually acting on what matters, you are not alone.
This is exactly where automation can become a turning point. In this guide, you will walk through an n8n workflow template that transforms raw Notion API updates into structured insights using vector embeddings, Supabase, and a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) agent. You will see how each step fits together, not just as a technical setup, but as a practical system that frees your time and amplifies your focus.
By the end, you will have a working automation that processes Notion changes, enriches them with semantic embeddings, and creates useful outputs like logs, alerts, and synthesized summaries. More importantly, you will have a repeatable pattern you can adapt, extend, and build on as your automation journey continues.
The challenge: Notion is powerful, but noisy
Notion has become a central hub for docs, tasks, and knowledge across many teams. Yet as usage grows, so does the noise. Updates, comments, and edits arrive constantly. Manually reviewing every change is not sustainable, and relying on memory or ad-hoc checks risks missed insights and delayed reactions.
Automating Notion API updates with n8n helps you:
- Extract and normalize content from Notion so it is ready for downstream processing
- Index updates in a vector store for semantic search and intelligent augmentation
- Use a RAG agent to generate summaries, suggestions, or next actions from raw changes
- Log outcomes in Google Sheets and alert teammates in Slack when something needs attention
Instead of chasing updates, you can design a system that brings the right information to you, at the right time, in a format you can act on immediately.
From possibility to practice: a new mindset for automation
Before diving into nodes and configuration, it helps to adopt a different mindset. Automation is not about replacing your judgment. It is about creating space for it. Each workflow you build in n8n is a small investment that pays you back with every run.
This Notion API workflow template is one of those investments. It is a concrete example of how you can:
- Turn unstructured updates into structured, searchable knowledge
- Let an LLM handle the heavy lifting of summarization and reasoning
- Create a traceable audit trail in Google Sheets
- Get real-time awareness through Slack alerts when something goes wrong
Think of this template as a starting point, not a finished destination. You can import it, run it as-is, then gradually tweak prompts, add branches, and integrate more tools as your confidence grows.
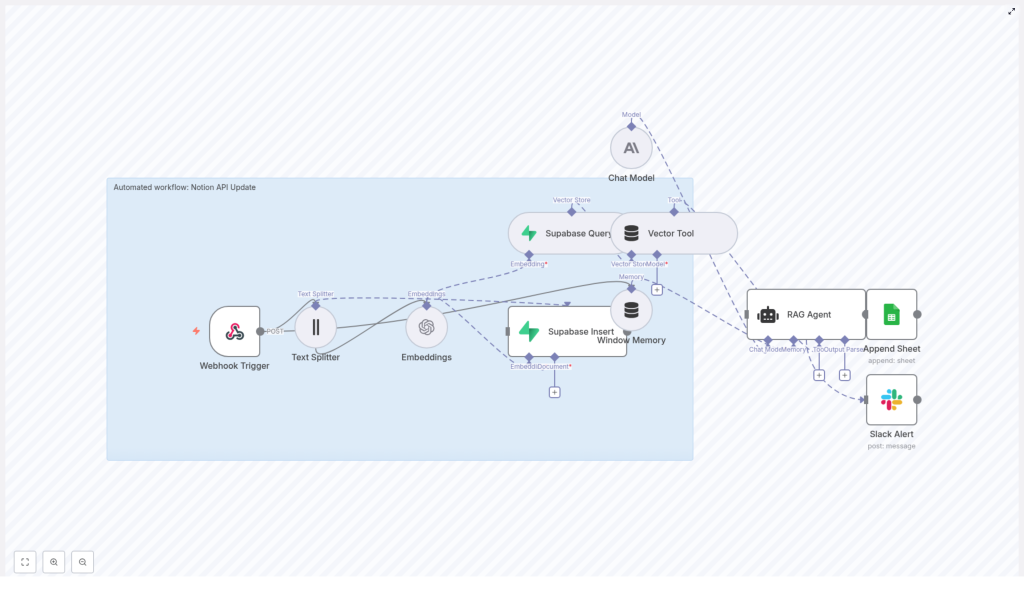
High-level architecture: how the workflow fits together
To understand the power of this template, it helps to see the full picture. The n8n workflow connects your tools into a single flow that listens to Notion updates, enriches them with context, and produces meaningful outputs.
The workflow includes these core components:
- Webhook Trigger – Receives HTTP POST events from Notion or a middleware service.
- Text Splitter – Breaks long Notion content into manageable chunks.
- Embeddings (OpenAI) – Generates vector embeddings using
text-embedding-3-small. - Supabase Insert & Query – Stores embeddings and retrieves relevant context from a vector index.
- Window Memory – Maintains recent conversational context for the RAG agent.
- Vector Tool – Exposes vector search as a tool the RAG agent can call.
- Chat Model (Anthropic) – Provides the LLM reasoning engine.
- RAG Agent – Orchestrates retrieval, reasoning, and final responses.
- Append Sheet – Logs structured results to Google Sheets.
- Slack Alert – Sends error notifications if something breaks.
This combination gives you a robust pattern: ingest, enrich, retrieve, reason, and record. Once you understand the pattern, you can reuse it for many other workflows, not just Notion.
Step 1: Capture Notion events with a Webhook Trigger
Your journey starts with the entry point: an n8n Webhook node. Configure it to accept HTTP POST requests. This webhook will receive update events from Notion or any intermediary service you use to forward Notion changes.
In practice, you will:
- Create a Webhook node in n8n and set the HTTP method to POST
- Copy the webhook URL that n8n generates
- Configure your Notion integration or middleware to send change events to that URL
This node is your automated gatekeeper. Every new Notion update passes through here, ready to be processed without you lifting a finger.
Step 2: Split long Notion content into usable chunks
Notion pages and blocks can contain long-form text. Feeding very long content directly into an embedding model can hurt performance and retrieval quality. The solution is to split content into smaller, meaningful pieces.
Use the Text Splitter node in n8n with a character-based strategy, for example:
chunkSize = 400chunkOverlap = 40
This configuration keeps each chunk within the embedding model context limits and preserves enough overlap so that ideas are not cut off mid-thought. You end up with multiple coherent text chunks that can each be embedded and searched later.
Step 3: Create embeddings for each chunk
Next, you turn raw text into a format that a vector database can understand. Use the Embeddings node with OpenAI’s text-embedding-3-small model (or another supported provider) to generate embeddings for every chunk produced by the Text Splitter.
For each chunk, store:
- The embedding vector
- Key metadata such as Notion page ID, block ID, and timestamp
This metadata is crucial. It lets you trace any search result or summary back to the exact piece of original Notion content, which is essential for audits and follow-up actions.
Step 4: Persist and retrieve knowledge with Supabase
With embeddings generated, you need a place to store and query them. Supabase serves as the vector store in this workflow template.
Insert embeddings into Supabase
Use the Supabase Insert node to write embedding documents into a dedicated index or table, for example:
notion_api_update
Each record typically includes the embedding vector, the text chunk, and its metadata. Over time, this becomes a rich, searchable history of your Notion workspace changes.
Query Supabase for relevant context
Use the Supabase Query node to perform semantic searches. Given a query or an incoming event, this node returns the most relevant chunks from your index. These results become the context that powers your RAG agent’s reasoning.
At this point, you have transformed your Notion updates into a living knowledge base that you can query and build on.
Step 5: Add memory and tools for deeper reasoning
To make your RAG agent truly useful, it needs both short-term memory and access to tools that can retrieve information on demand.
Window Memory
The Window Memory node stores recent conversational context or previous messages. This allows your agent to maintain continuity across multiple events or calls. Instead of responding in isolation, it can remember what happened recently and build on that.
Vector Tool
The Vector Tool node wraps the Supabase Query so that the RAG agent can call it as needed. When the agent needs more context, it can use this tool to search your vector store and pull in the most relevant chunks.
Together, memory and tools turn your workflow from a simple pipeline into a flexible reasoning system.
Step 6: Power the workflow with a Chat Model and RAG agent
Now you bring everything together. The Chat Model node provides the LLM that performs natural language reasoning. In this template, Anthropic is used as the chat model, but you can adapt it to another provider if needed.
The RAG Agent node integrates three key pieces:
- The Chat Model as the core reasoning engine
- The Vector Tool for semantic retrieval from Supabase
- Window Memory for conversational continuity
When a new Notion update arrives, the RAG agent:
- Receives the processed input and relevant metadata
- Queries Supabase via the Vector Tool to fetch related chunks
- Uses the Chat Model to synthesize a summary, decision, suggestion, or other output
To guide the agent, configure its system prompt to align with your goals. For example:
You are an assistant for Notion API Update.
You can refine this prompt over time to emphasize tone, level of detail, or specific actions you want the agent to take. This is one of the easiest and most powerful ways to evolve your workflow as your needs change.
Step 7: Log results and stay informed with Sheets and Slack
Automation is most valuable when it is transparent and traceable. The final steps in this template help you keep a clear record of what your workflow is doing and alert you when something breaks.
Append results to Google Sheets
Use the Append Sheet node to write structured outputs from the RAG agent into a Google Sheet. Typical columns might include:
- Timestamp
- Notion page ID
- Summary or decision
- Status or outcome
This sheet becomes your lightweight dashboard and audit log. Over time, you can analyze patterns, track performance, and share insights with stakeholders.
Send Slack alerts on errors
When something fails, you want to know quickly. Configure a Slack Alert node to send error notifications to a channel such as #alerts. Include the error message and, when useful, JSON debug output so engineers or operators can respond efficiently.
With this in place, you can trust your workflow to run in the background, knowing that you will be notified if it needs attention.
Configuration checklist: prepare your environment
Before you hit run, make sure these pieces are in place:
- n8n Webhook URL: Expose n8n via tunneling (for example ngrok) or deploy it with a public domain so Notion can reach it.
- OpenAI API key: Required for embeddings. Confirm the model name (
text-embedding-3-small) and ensure compliance with your organization policies. - Supabase credentials: Configure your project and create a vector index or table named
notion_api_update. - LLM key (Anthropic or other): Provide credentials for the Chat Model node.
- Google Sheets OAuth: Grant access to the target spreadsheet (use your
SHEET_IDand a specific Log sheet name). - Slack token: Enable the Slack node for error notifications and, optionally, success alerts.
- Notion integration token & webhook routing: Configure Notion to POST change events to your n8n webhook endpoint.
Security and best practices as you scale
Automating private workspace content brings responsibility. As you expand this workflow or adapt it to new use cases, keep these practices in mind:
- Store all API keys and credentials in n8n’s credential manager, not in plain text inside nodes.
- Limit your Notion integration scope to only the pages and databases that are truly needed.
- Encrypt sensitive data at rest. Supabase offers built-in protections, and you can configure row-level security policies where appropriate.
- Sanitize or redact sensitive content before sending it to public destinations such as shared Google Sheets.
- Rate-limit webhook consumers and validate incoming payloads to reduce the risk of spoofing or abuse.
Building with security in mind gives you the confidence to automate more of your workflows without sacrificing trust.
Troubleshooting: turning roadblocks into learning moments
Every automation journey includes a few bumps. When something does not work as expected, use it as a chance to deepen your understanding of the system.
- If embeddings fail, double-check your OpenAI API quota and ensure the model name is set to
text-embedding-3-small. - If Supabase queries do not return results, confirm that the
notion_api_updateindex or table exists and that your Supabase credentials are correct. - If retrieval quality is poor, experiment with
chunkSizeandchunkOverlapin the Text Splitter to produce more coherent chunks. - Use the Slack Alert node to surface detailed error messages. Including JSON debug output can make diagnosing issues much faster.
Each fix you apply strengthens your workflow and builds your intuition for future automations.
Ideas to extend and customize your workflow
Once the base template is running, you can start shaping it to match your unique needs. Here are a few directions to explore:
- Auto-tagging: Use the LLM to extract tags, topics, or categories from each update and write them back to Notion or a separate metadata table.
- Change-diffing: Store previous content snapshots and generate summarized diffs for each update so you quickly see what changed.
- Multi-model routing: Route different content types (for example technical docs vs meeting notes) to different prompts or LLMs optimized for those domains.
- Realtime dashboards: Feed your summarized updates into a BI dashboard to give stakeholders a live view of what is happening in Notion.
Each enhancement builds on the same core pattern you have already implemented, making it easier to experiment and iterate.
Bringing it all together
This n8n workflow template is more than a collection of nodes. It is a practical pattern for turning continuous Notion updates into searchable, reasoned outputs using embeddings and a RAG agent. By combining reliable integration points like webhooks, Supabase, Google Sheets, and Slack with modern NLP capabilities, you create a system that surfaces insights instead of raw noise.
Most importantly, this is a reusable foundation. The skills you apply here translate directly to other automations across your stack. Every time you refine a prompt, adjust a chunk size, or extend the workflow, you are building your own automation toolkit.
Your next step: try, iterate, and grow
You do not need to design the perfect workflow on day one. Start by importing this template into your n8n instance, connect your keys, and run a simple test with a sample Notion event. Watch how the pieces interact, then adjust one thing at a time.
As you grow more comfortable, you can:
- Refine the RAG agent prompt for your specific use case
- Add new destinations or notifications
- Scale embeddings and storage as your Notion workspace expands
Each improvement is a step toward a more focused, less reactive way of working, where automation handles the flow of information and you stay free to make the decisions that matter.
Ready to move from