Automate AI Newsletters with n8n: A Practical Guide
Imagine sitting down each week to publish an AI newsletter that your audience loves, without losing an entire afternoon to copy-pasting links, rewriting summaries, and wrestling with formatting. That is the promise of a well-designed n8n workflow template.
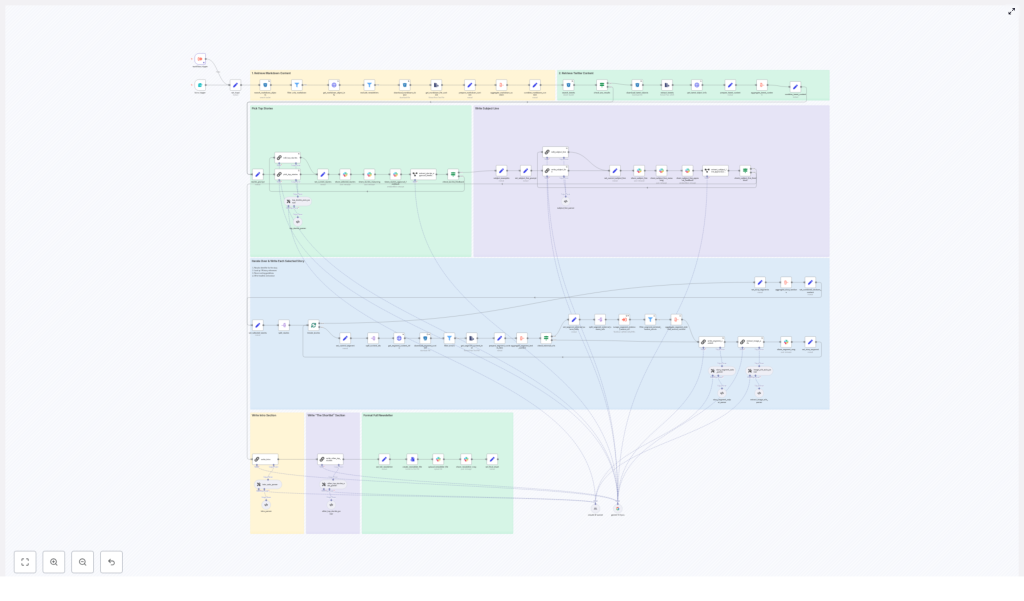
This guide walks you through a real n8n automation that ingests markdown and X/Twitter content, uses LLMs to pick top stories, writes newsletter sections, builds subject lines, and publishes drafts to Slack. The result is a repeatable, auditable pipeline that gives you back time and creative energy, while keeping your output consistent and professional.
The Problem: Newsletter Work That Eats Your Week
A weekly AI newsletter can be one of your most powerful channels for influence and growth. It keeps your community engaged, showcases your expertise, and creates a predictable touchpoint with readers or customers.
Yet the process behind it often feels heavy:
- Collecting links, markdown files, and tweets from different tools
- Removing duplicates and low quality content
- Summarizing, rewriting, and formatting everything by hand
- Trying to keep structure and tone consistent from week to week
Over time, this drains editorial bandwidth and can slow down your growth. The more your audience expands, the more pressure there is to publish on time and at a high standard.
The Shift: From Manual Production To Automated Systems
Instead of treating your newsletter as a weekly “one-off task,” you can treat it as a system. With n8n, you can build that system once, refine it over time, and let it carry more and more of the workload.
Automation is not about removing humans. It is about elevating them. When repetitive steps are handled by a workflow, you are free to focus on what only you can do:
- Choosing the right stories for your audience
- Adding unique commentary and perspective
- Defining the tone, voice, and editorial standards
The n8n workflow template in this guide is a concrete example of that mindset. It turns newsletter production into a reliable pipeline that you can improve week after week.
The Possibility: A Newsletter Pipeline You Can Trust
The workflow follows a clear pipeline pattern that you can understand, audit, and customize. At a high level, it:
- Triggers on a form submission with a date and optional previous newsletter content
- Ingests markdown files and X/Twitter posts from cloud storage
- Normalizes and aggregates all content
- Uses an LLM to select the top stories
- Uses LLMs again to write each newsletter section
- Generates intro, subject line, and preheader text
- Assembles the final newsletter and posts it to Slack for review
Every step is explicit and controllable. You can see what went in, what came out, and where to intervene. This is how automation becomes a partner in your editorial process instead of a black box.
The Template: Your Starting Point For Automation With n8n
Let us walk through the workflow node by node so you can see how it works and how you might adapt it. Think of this as a guided tour of a production-grade n8n template that you are free to customize and grow with.
1. Form Trigger – Start With Intent
The journey begins with a form trigger in n8n. Editors submit:
- The target date for this issue
- Optional previous newsletter content
The date anchors the entire workflow. It tells the pipeline which content to look for in storage. The previous newsletter content provides context so the system can avoid duplicating stories and apply date-specific selection rules. You remain in control, but the heavy lifting starts to move into the background.
2. Search And Download Source Files – Gather Your Raw Material
Next, the workflow uses S3 (or R2) nodes to search your bucket by a date-based prefix and list all relevant files. It then:
- Filters to only markdown objects with a
.mdextension - Downloads the markdown content for each file
- Captures per-file metadata such as authors, external-source-urls, and image-urls
Instead of manually hunting down articles, your system now pulls everything into one place in a structured, repeatable way.
3. Normalize Inputs – Create A Predictable Content Format
To make downstream processing reliable, the workflow normalizes each file into a canonical content item. Each item includes:
- An identifier
- A friendly content type
- Authors
- external-source-urls
- The full markdown payload
This standard format means every later step can assume the same structure. You are building a foundation for consistent automation, not a one-off script that breaks the moment your input changes.
4. Tweet Ingestion – Bring X/Twitter Into The Same Flow
In parallel, the pipeline searches for tweet objects for the same date. It:
- Downloads tweet data
- Extracts metadata such as handle, id, and impressions
- Converts tweets into the same canonical content format as markdown articles
The result is a unified pool of content, where X/Twitter posts can be evaluated alongside long-form web articles. Your workflow is now multi-channel by design.
5. Aggregate And Combine – Build A Rich Content Buffer
Once everything is normalized, the workflow aggregates all content items into a single rich-text buffer. This combined data set is what the curation LLM will analyze when choosing top stories.
Instead of scanning dozens of sources yourself, you are handing a structured, well prepared bundle of information to the model, with clear rules for what to do next.
6. Filter And Exclude – Protect Editorial Quality
Before calling the LLM for story selection, the pipeline applies lightweight filters to:
- Exclude content types you do not want, such as previous newsletters
- Remove items that do not meet editorial constraints
This ensures the model only sees candidate stories that are genuinely in scope. You are not just automating, you are encoding your editorial standards into the workflow.
7. Pick Top Stories With LLM / LangChain – The Curation Engine
This is the heart of the pipeline. A LangChain (or similar) node prompts an LLM with:
- A description of the target audience
- Clear selection rules
- A strict output schema
The model returns a structured list of four top stories, each with:
- An identifier
- A concise summary
- A source link
To keep this step reliable, the workflow uses several best practices:
- Constrain the output to a JSON schema so it is machine-parsable
- Optionally include a “chain of thought” or human-readable reasoning for traceability
- Validate model outputs with an output-parser node to guard against malformed responses
Now curation becomes faster and more consistent, while you still have full visibility into why stories were chosen.
8. Iterate And Write Segments – Turn Stories Into Sections
With the top stories selected, the workflow splits them and iterates over each one. For every story, it:
- Resolves the identifier back to the underlying content piece and downloads any referenced files
- Aggregates the original markdown with any scraped external source material
- Passes that combined content to an LLM along with a writing guide, for example an Axios or Rundown style with bullets and a “Why it matters” section
- Parses the LLM output into a well structured newsletter section
This is where you feel the time savings most directly. Instead of manually rewriting each story, you guide the model once with your style and let the workflow produce consistent sections you can review and lightly edit.
9. Intro, Subject Line, And Meta – Shape The Reader Experience
Separate LLM prompts generate important framing elements:
- A newsletter intro, such as a “Good morning, AI enthusiasts.” style opening
- An engaging subject line
- Pre-header text that complements the subject line
- A short shortlist of other notable stories
Each of these outputs is constrained by maximum tokens or word counts and validated through structured output parsers. The result is a polished, on-brand experience that you can refine over time without rewriting everything from scratch.
10. Final Assembly And Publish – Deliver A Ready-To-Review Draft
In the final stage, the workflow:
- Aggregates all written sections into a single newsletter body
- Converts the result into a markdown file
- Uploads the file to Slack or your CMS
- Posts preview messages and reasoning to Slack channels for editorial review and approval
Your newsletter is now generated as a draft you can quickly scan, tweak, and approve. The system handles assembly and delivery so you can focus on judgment, not logistics.
Prompt Engineering And Governance: Make Automation Trustworthy
Real-world automation is not just about clever prompts. It is about guardrails and governance that keep your workflow stable as you scale. This n8n pipeline uses several key practices:
- Explicit JSON schema prompts for story selection, ensuring exactly four items with identifiers and links
- Output parser nodes that automatically fix or reject malformed LLM outputs
- Chain-of-thought fields that are used only for internal review and never exposed to readers
These patterns help you build confidence in your automation and make it easier to share the workflow with your team.
Best Practices For A Robust n8n Newsletter Workflow
To keep your AI newsletter pipeline resilient and easy to maintain, consider these best practices:
- Idempotency: Use file identifiers and date prefixes so you can rerun the workflow safely without creating duplicates.
- Editorial gating: Add a human approval step, for example a Slack approve button, before final publishing.
- Source fidelity: Always attach original source identifiers and external-source-urls to sections for traceability.
- Error handling: Use continue-on-error for individual downloads, but flag failures for human review instead of silently skipping them.
- Rate limits and cost: Batch LLM calls when possible and cache scraped external source content to minimize API usage.
These patterns turn your workflow from a clever demo into a production-grade system that can grow with your audience.
Troubleshooting: Keeping The Pipeline Flowing
Even with a strong design, edge cases will appear. The goal is not perfection on day one, but a workflow that is easy to debug and improve.
Malformed LLM JSON
If the LLM occasionally returns invalid JSON, use an output-parser or autofixing node to correct minor issues. When the fix fails, route the result to a human-in-the-loop review queue instead of blocking the entire pipeline. This keeps your system resilient while still surfacing problems quickly.
Missing External URLs Or Incomplete Identifiers
Maintain strict string-copy rules for identifiers. Ingest the identifier exactly as it appears in the source to avoid mismatches. If a URL is missing, the story can still be used, but mark that in the metadata and avoid adding external links in the final output for that item.
Duplicate Coverage
To prevent repeating stories, compare candidate identifiers with the previous newsletter content that was passed in via the form trigger. Filter duplicates early in the flow so your readers always get fresh coverage.
From One Workflow To A New Way Of Working
This n8n pipeline is more than a single automation. It is a blueprint for how you can combine structured ingestion, programmatic filtering, and LLM-driven curation and writing to reliably produce an insightful AI newsletter.
With a few governance rules around approval, parsers, and caching, editorial teams can:
- Publish more consistently
- Protect quality and brand voice
- Free up hours each week for strategy and deep work
The real opportunity is what comes next. Once you have a working template, you can:
- Experiment with new prompts and tones
- Add extra content sources or channels
- Integrate directly with your CMS or email service
- Clone the pattern for other recurring content, like product updates or internal reports
Each improvement compounds. Over time, you build a library of automations that quietly multiply your impact.
Call to action: If you want this exact workflow exported and configured for your team, including prompts and parser templates, reach out to get a ready-to-run n8n package and onboarding support. You will be set up with a production-grade AI newsletter pipeline that you can customize and grow with.