AI Logo Sheet Extractor to Airtable (n8n Guide)
This guide presents a production-ready n8n workflow template that converts logo sheets or product comparison images into structured, relational data in Airtable. It explains the end-to-end architecture, the key nodes and integrations, and recommended best practices for running the workflow reliably in professional automation environments.
Overview: From logo sheet to structured Airtable records
The AI Logo Sheet Extractor to Airtable workflow accepts an uploaded image that contains multiple logos or product tiles. A vision-enabled language model extracts tool names and contextual information, then n8n orchestrates the creation and linking of corresponding records in Airtable.
At a high level, the workflow:
- Receives a logo sheet image and an optional user prompt from a public form.
- Uses an AI agent to detect tools and parse attributes and competitor relationships.
- Creates or reuses attributes in a dedicated Airtable Attributes table.
- Upserts tools into a Tools table using deterministic hashing for idempotency.
- Links tools to their attributes and maps similar or competitor tools as relational references.
The result is a clean, queryable dataset in Airtable that can power product research, competitive analysis, or internal tool directories.
Use case and automation design goals
This workflow is designed for teams that frequently work with:
- Marketing or analyst-created logo sheets summarizing vendor landscapes.
- Product comparison collages shared in slides or PDFs.
- Dense visual overviews of tools where manual data entry would be slow and error-prone.
The automation focuses on:
- Deterministic behavior, so repeated runs on similar input do not create duplicates.
- Extensibility, so additional enrichment or validation logic can be added with minimal refactoring.
- Separation of concerns between visual extraction, data normalization, and persistence in Airtable.
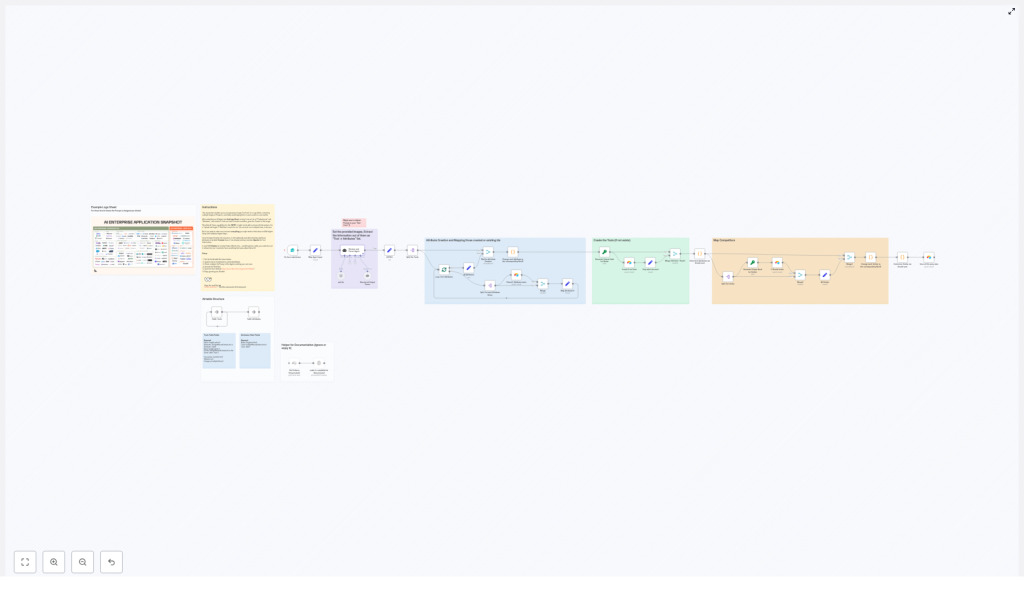
End-to-end workflow architecture
The workflow is organized into four logical stages:
- Input and trigger via an n8n Form.
- AI-based extraction and normalization into structured JSON.
- Attribute creation and mapping to Airtable IDs.
- Tool upsert, competitor linking, and optional post-processing.
1. Input: Form-based logo sheet submission
The entry point is an n8n Form Trigger. This node exposes a lightweight web form that allows non-technical users to submit:
- A logo sheet or product collage image file.
- An optional free-text prompt that provides context for the AI model.
This pattern keeps your n8n instance secure while enabling broad access to the ingestion interface. The default path is:
/form/logo-sheet-feeder
2. AI retrieve-and-parse agent
After the image is received, the workflow calls a vision-capable language model (for example, OpenAI or another provider that supports image plus text extraction).
The agent is instructed to return a strictly structured JSON payload, typically an array of tools with associated metadata:
[{ "name": "ToolName", "attributes": ["category", "feature"], "similar": ["competitor1", "competitor2"]
}]
Each object should include:
- name – the tool or product name as read from the image.
- attributes – descriptive tags such as category, capabilities, or features.
- similar – competitor or closely related tools detected on the sheet.
This structured output becomes the canonical intermediate representation that downstream nodes consume. Keeping this structure consistent is critical for deterministic processing.
3. Attribute creation and mapping to Airtable
Once the AI output is available, the workflow normalizes and persists attributes:
- Each attribute string is cleaned (for example, trimmed, optionally lowercased) to avoid accidental duplicates.
- For every unique attribute, the workflow checks whether it already exists in the Airtable Attributes table.
- If an attribute does not yet exist, a new record is created.
A mapping step then converts attribute names into their corresponding Airtable record IDs. These IDs are used when creating or updating tool records, so the Tools table stores proper multiple-record links rather than raw text.
4. Tools upsert and competitor relationship mapping
For each tool returned by the AI agent, the workflow:
- Normalizes the tool name and computes a stable hash (MD5-like) used as a unique key.
- Performs an upsert into the Tools table using the hash as the primary match field.
- Attaches linked attributes by using the previously generated attribute ID mapping.
This hash-based strategy ensures idempotent behavior. Re-running the workflow with the same or similar logo sheets does not create duplicate tool records as long as the normalized names remain consistent.
After the tool records exist, the workflow processes the similar field:
- Resolves each listed competitor name to its corresponding Airtable record (creating or upserting as needed).
- Writes these links back into the Similar field of the Tools table as multiple-record links.
This creates a network of related tools, enabling downstream analysis of competitive clusters or vendor ecosystems.
Required Airtable base and schema
The workflow assumes a minimal Airtable base with two interconnected tables: Tools and Attributes.
Tools table
Recommended fields:
- Name (single line text) – human-readable tool name.
- Hash (single line text) – deterministic key used for upserts.
- Attributes (link to Attributes, multiple) – associated tags or properties.
- Similar (link to Tools, multiple) – competitor or related tools.
- Description (optional) – free-text description, can be auto-enriched later.
- Website (optional) – official URL.
- Category (optional) – high-level classification.
Attributes table
Recommended fields:
- Name (single line text) – attribute label such as “AI infrastructure” or “Storage Tool”.
- Tools (link to Tools, multiple) – reverse relation to tools that carry this attribute.
Configuration checklist in n8n
Before running the workflow in production, complete the following configuration steps:
- Form Trigger path
Ensure the Form Trigger node is enabled and accessible, for example at:/form/logo-sheet-feeder
- LLM / vision API credentials
Configure your language model credentials in n8n credentials. Use a provider that supports both image analysis and text generation. - Airtable credentials and base configuration
Set up an Airtable Personal Access Token in n8n and configure all Airtable nodes with:- Correct base ID.
- Correct table IDs for Tools and Attributes.
- Field mappings that align with your schema.
- System prompt and extraction instructions
Adjust the system-level message used by the AI node so it reflects your domain, attribute taxonomy, and strict JSON requirements. - End-to-end testing
Run the workflow with several sample logo sheets and verify:- Tools are created or updated as expected.
- Attributes are deduplicated and correctly linked.
- Similar / competitor relationships are correctly mapped.
Prompt design for reliable AI extraction
The robustness of the workflow depends heavily on how the AI agent is instructed. Consider the following best practices when crafting your prompt:
- Specify strict output structure
Define the exact JSON schema you expect, including field names and types. Instruct the model to output JSON only, without explanatory text. - Separate categories from features
If the sheet includes explicit product categories, for example “Storage Tool”, direct the model to distinguish between categories and functional attributes, or to tag them differently if required by your schema. - Use contextual hints
Leverage the optional prompt field in the form to provide context such as: “Logos are AI tooling for memory and vector DBs.” This reduces ambiguity and improves classification quality. - Encourage conservative extraction
Ask the model to return only tools it can confidently identify. Optionally, include a confidence flag in the JSON or instruct the model to omit uncertain entries for later manual review.
Error handling, validation, and production hardening
For production deployments, add controls around validation, idempotency, and rate management.
Validation strategies
- Secondary validation agent
Introduce a second AI or rules-based step that validates tool names against a curated reference list or performs lightweight web checks to confirm existence. - Confidence thresholds
If your model exposes confidence scores or detection probabilities, use them to decide whether to auto-create records or route them to a manual review queue.
Idempotent upserts and data consistency
- Maintain the hash-based upsert logic to avoid duplicates when users resubmit similar sheets.
- Avoid matching solely on the tool name, since minor formatting differences can lead to fragmentation.
- Ensure attribute normalization (trimming, consistent casing) before creating new attribute records.
Rate limits, retries, and resilience
- Add retry logic on Airtable and AI nodes to handle transient API failures.
- Throttle form submissions or introduce queueing if you expect high volume, to stay within Airtable and LLM rate limits.
- Consider alerting on repeated error states so issues are surfaced quickly.
Customization patterns and extensions
The base workflow is intentionally modular so it can be adapted to different data models or enrichment strategies.
Auto-enrichment of tool records
After the initial upsert into Airtable, you can extend the workflow with:
- Web-scraper nodes to retrieve website metadata, descriptions, or logo URLs.
- Lookup microservices or APIs that return standardized product information.
- Additional AI calls that summarize product positioning into a concise description field.
User validation and approval queue
For stricter governance, introduce a review layer:
- Create an Approval or Review table with a status field such as “unverified”.
- Route newly extracted tools into this table and send an automated email to a reviewer with the parsed data.
- Link approval actions back into the workflow so only verified tools are connected to production lists.
Multi-agent extraction for complex sheets
For dense or low-quality images, it can be beneficial to split responsibilities across multiple agents:
- One agent focused on OCR and visual detection of names and logos.
- Another agent focused on semantic classification into categories and attributes.
- A merge step that reconciles their outputs deterministically before writing to Airtable.
Troubleshooting and common issues
AI agent misreads or mislabels tool names
If you see systematic misreads:
- Improve the quality of the source image, for example by increasing resolution or adjusting contrast.
- Pre-process the image using n8n or an external service to crop out irrelevant regions.
- Refine the prompt with explicit guidance on handling partial or blurry text and instruct the model to omit uncertain entries.
Airtable upserts failing or behaving unexpectedly
When upserts fail, check:
- That Airtable credentials and base IDs are correct and not expired.
- That the Hash and Name fields are present and mapped correctly in the Airtable node.
- That the node is explicitly configured to upsert based on the Hash field.
Duplicate attributes or broken attribute links
If you notice multiple records representing the same attribute:
- Confirm that attribute strings are normalized before the “create if not exists” logic runs.
- Review the mapping step that converts attribute names to Airtable IDs and ensure it uses the cleaned values.
- Run a one-time deduplication pass in Airtable if historical data already contains inconsistencies.
Security and privacy considerations
Since images are sent to external AI and vision providers, align the workflow with your organization’s security and compliance policies:
- Avoid uploading images that contain confidential, proprietary, or personal data unless the provider and processing pipeline are approved for such content.
- Review the data retention and usage policies of your LLM or vision provider.
- Restrict access to the form and to the n8n instance as appropriate for your environment.
Sample AI JSON output
The following example illustrates the type of JSON structure the agent should return for optimal compatibility with the workflow:
{ "tools": [ { "name": "airOps", "attributes": ["Agentic Application", "AI infrastructure"], "similar": ["Cognition", "Gradial"] }, { "name": "Pinecone", "attributes": ["Storage Tool", "Memory management"], "similar": ["Chroma", "Weaviate"] } ]
}
Deployment and operational checklist
For a stable production deployment:
- Run the workflow on an n8n production instance or hosted n8n cloud and secure the form endpoint.
- Store Airtable and LLM credentials in n8n’s encrypted credential store and rotate keys regularly.
- Set up monitoring for workflow