AI Logo Sheet Extractor to Airtable – Automate Logo Sheets into Structured Data
Convert any logo-sheet image into clean, structured Airtable records using n8n and an AI-powered parsing agent. This guide walks through the full workflow design, from trigger to Airtable upsert, and explains how each n8n node, AI prompt, and data model contributes to a reliable, repeatable automation for extracting product names, attributes, and competitor relationships directly from images.
Use case and value proposition
Teams across product, research, and strategy frequently receive visual matrices of tools or vendors as a single image: slides with logo grids, market maps, or competitive landscapes. Manually transcribing these visuals into a database is slow, inconsistent, and difficult to scale.
This n8n workflow addresses that problem by combining computer vision and language models with Airtable as a structured backend. It allows you to:
- Identify product or tool names from logo sheets.
- Infer relevant attributes and categories from surrounding visual context.
- Detect visually indicated similarities or competitor relationships.
- Upsert all extracted information into Airtable in a deterministic, idempotent way.
The result is an “upload-and-forget” pipeline that transforms unstructured visual assets into a searchable, analyzable dataset.
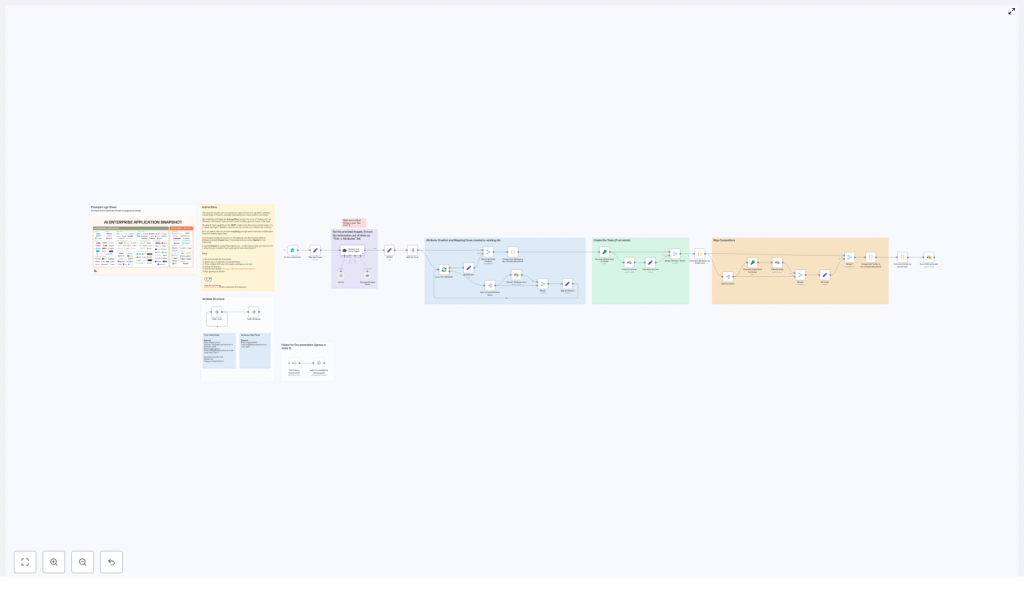
End-to-end workflow overview
The automation is implemented as a linear n8n workflow with clearly defined stages. At a high level, it performs the following operations:
- Accept a logo-sheet image via a public web form.
- Forward the image and optional context prompt to an AI parsing agent (LangChain / OpenAI).
- Validate and normalize the agent’s structured JSON output.
- Upsert all attributes into Airtable and capture their record IDs.
- Map attribute IDs back to tools and resolve similar-tool relationships.
- Create or update tool records in Airtable, linking attributes and competitors.
The sections below detail the key n8n nodes, the Airtable schema, and best practices for prompt design, testing, and scaling.
Core n8n components
Form-based trigger: logo-sheet intake
The workflow starts with a form submission node that exposes a simple upload endpoint at /logo-sheet-feeder. This form accepts:
- The logo-sheet image file.
- An optional free-text prompt to provide additional context to the AI agent.
This URL can be shared internally so any team member can submit new logo sheets without touching n8n. The node is configured to pass the binary image data downstream for analysis.
AI parsing agent (LangChain / GPT)
Once the image is received, a LangChain-based agent backed by an OpenAI model processes the binary image. Binary passthrough is enabled so the image is accessible to the agent. The agent is instructed to output a deterministic JSON structure that captures tools, attributes, and similar tools.
The target JSON structure for each tool is:
[{ "name": "ToolName", "attributes": ["category", "feature"], "similar": ["competitor1", "competitor2"]
}]
A well-designed system prompt is crucial. It should clearly define the schema, restrict output to JSON only, and explain that the input is a logo sheet with product logos and contextual cues.
Structured Output Parser
To minimize downstream errors, the next node validates and enforces the expected JSON schema. This Structured Output Parser node:
- Checks that the agent response is valid JSON.
- Ensures required fields such as
name,attributes, andsimilarare present for each item. - Normalizes the data shape so subsequent nodes can rely on a consistent structure.
This defensive step significantly reduces runtime failures and simplifies troubleshooting, since malformed outputs are surfaced early.
Attribute creation and deduplication in Airtable
Each attribute string returned by the agent is mapped to an Airtable record in an Attributes table. The workflow:
- Looks up existing attributes by name.
- Creates new attribute records if none are found.
- Returns the Airtable record IDs for all attributes, both existing and newly created.
These record IDs are then associated with the corresponding tools. This pattern ensures that attributes are consistently reused rather than duplicated, and that tools are always linked to a canonical attribute record.
Tool creation, hashing, and linking
Tools are stored in a separate Tools table. To ensure deterministic upserts, each tool is assigned a stable hash (for example, an MD5-style hash of the tool name). The workflow uses this hash to decide whether to create or update a record:
- If a record with the same hash exists, it is updated with the latest attributes and relationships.
- If no matching hash is found, a new tool record is created.
During this step, the workflow also:
- Links tools to their associated attribute record IDs.
- Resolves and links similar tools using self-referential relationships in the Tools table.
This approach yields a consistent, de-duplicated tool catalog that can be enriched over time as more logo sheets are processed.
Recommended Airtable schema
For predictable behavior and clean relationships, configure Airtable with two main tables: Attributes and Tools.
Attributes table
- Name – Single line text, used as the primary matching key for attributes.
- Tools – Linked records to the Tools table.
Using a simple text field for the name allows the n8n workflow to perform reliable lookups and upserts.
Tools table
- Name – Single line text, human readable tool name.
- Hash – Single line text, unique key derived from the tool name (for example, MD5 hash).
- Attributes – Linked records to the Attributes table.
- Similar – Linked records to the Tools table (self-link to represent similar or competitor tools).
- Description, Website, Category – Optional metadata fields for enrichment.
This schema is optimized for deterministic upserts and for building a graph of tools and their relationships that can support analysis, reporting, or downstream automation.
Prompt engineering guidelines for the agent
The reliability of the workflow depends heavily on the quality of the AI agent’s output. When designing the system and user prompts, consider the following best practices:
- Explicitly instruct the model to output JSON only, with no natural language commentary.
- Provide a concrete example of the expected JSON schema, including field names and types.
- State clearly that the input is an image containing logos and contextual layout, and that the model should
extract names, plausible attributes, and visually indicated similarities
. - Expose an optional prompt field in the form so users can add context, such as the meaning of the graphic or the market segment it represents.
- Emphasize conservative inference: when the model is uncertain, it should use generic but accurate attributes such as
AI infrastructure
rather than fabricating specific features.
Example agent output
A typical response, after prompt tuning, might look like this:
{ "tools": [ { "name": "airOps", "attributes": ["Agentic Application", "AI infrastructure"], "similar": ["Cognition", "Gradial"] }, { "name": "Pinecone", "attributes": ["Storage Tool", "Memory management"], "similar": ["Chroma", "Weaviate"] } ]
}
The Structured Output Parser node then normalizes this to the internal representation used for Airtable upserts.
Testing, debugging, and quality control
Before deploying at scale, it is important to validate the workflow with a variety of logo sheets and monitor how the AI agent and Airtable integration behave.
- Missed logos: If some logos are not detected, try higher resolution images or cropping the relevant section. Vision models perform better with clear, high-quality inputs.
- Inspect raw agent output: Use a JSON node or similar in n8n to view the unmodified agent response. This helps distinguish between parsing issues and Airtable integration issues.
- Structured Output Parser errors: If JSON parsing fails frequently, adjust the prompt to be more explicit about the schema and JSON-only output, or tighten validation logic.
- Attribute normalization: Watch for near-duplicates such as capitalization variants. You can normalize attribute names in the prompt (for example, instruct the model to output lowercase) or add a preprocessing step in n8n.
Scaling, performance, and reliability
As usage grows, consider the following operational aspects.
- Rate limits: Both the LLM provider (for example, OpenAI) and Airtable enforce API rate limits. Implement retries and exponential backoff in n8n when you expect high throughput.
- Batch processing: For large batches of images, use a queue-based design and process logo sheets asynchronously rather than synchronously at form submission time.
- Human-in-the-loop: For high-stakes datasets, add a review step after AI extraction. A human reviewer can approve, correct, or reject parsed results before they are upserted into Airtable.
Privacy and security considerations
Logo sheets and accompanying context may contain sensitive information. Treat these assets according to your organization’s security and compliance policies.
- Store API keys (OpenAI, Airtable, etc.) in environment variables or n8n credentials, not in plain text.
- Restrict access to the
/logo-sheet-feederform endpoint if the data is confidential. - Ensure that any third-party AI provider is acceptable under your company’s data handling standards.
Advanced enhancements
Once the base workflow is stable, you can extend it with more advanced techniques to improve recall, precision, and monitoring.
- Multi-agent verification: Run two different prompts or models against the same image and merge their outputs. This can improve coverage and help identify discrepancies.
- OCR and vision hybrid: Combine traditional OCR results with the vision-language agent. Use OCR to capture exact text and the agent to interpret semantics and relationships.
- Confidence scores: Ask the agent to return a confidence value for each tool or attribute. Use this to decide which records to auto-upsert and which to route for human review.
Deployment checklist
Before putting the workflow into production, verify the following steps:
- Configure your Airtable base with the Attributes and Tools tables and generate an Airtable API token. Add this token as credentials in n8n.
- Set up OpenAI or your chosen LLM provider credentials in n8n.
- Refine the agent system prompt to align with your specific use case, industry terminology, and language requirements.
- Activate the n8n workflow and test with several representative logo-sheet images.
- Review the raw JSON output and Airtable records, then iterate on prompt wording and normalization rules to minimize false positives and duplicates.
Conclusion and next steps
This AI Logo Sheet Extractor workflow provides an efficient and scalable way to convert visual logo sheets into a structured Airtable database using n8n, an AI parsing agent, and a robust upsert strategy. It is particularly effective for competitive intelligence, vendor mapping, market research, and any scenario where visual tool matrices are common.
Ready to automate your logo sheets? Import the workflow into n8n, connect your Airtable and OpenAI credentials, and start sending images to the /logo-sheet-feeder endpoint. If you need a preconfigured workflow file or support with prompt tuning and schema customization, reach out for a tailored implementation.