Automate Notion Updates with n8n & RAG
Imagine this: you finish a long meeting, dump all your notes into Notion, and then spend the next 20 minutes manually summarizing, tagging, and trying to remember what on earth “follow up w/ J” means. Again. For the third time this week.
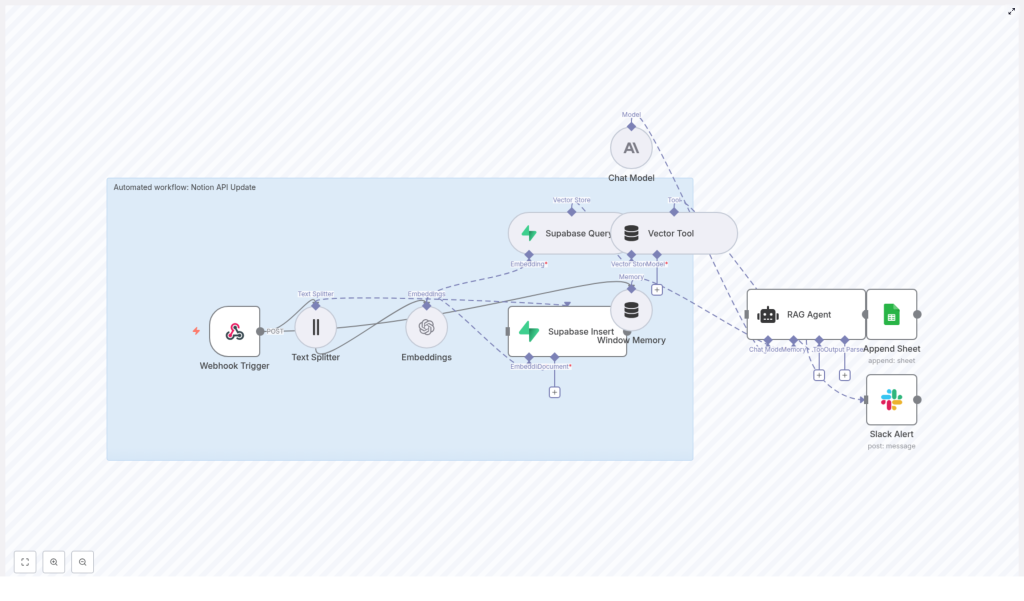
If that sounds familiar, it might be time to let automation do the boring bits. This reusable n8n workflow template, “Notion API Update”, takes care of the heavy lifting for you. It ingests content, creates embeddings, stores and queries vectors in Supabase, runs a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) agent, logs results to Google Sheets, and even pings Slack when something goes wrong.
In other words: you feed it content, it feeds you smart, contextual insights, and you get to stop copy-pasting your way through life.
What this n8n Notion automation actually does
This workflow turns your Notion content into something your AI tools can understand, remember, and reason about. Behind the scenes, it uses a series of n8n nodes that work together like a small, well-behaved robot army:
- Webhook Trigger – Listens for POST requests and kicks off the workflow.
- Text Splitter – Breaks long content into manageable chunks for embeddings.
- Embeddings – Uses OpenAI
text-embedding-3-smallto turn text chunks into vectors. - Supabase Insert – Stores those vectors in a Supabase vector table (
indexName: notion_api_update). - Supabase Query & Vector Tool – Fetches relevant context from Supabase when the RAG agent needs it.
- Window Memory – Keeps recent conversation or context handy for multi-step interactions.
- Chat Model + RAG Agent – Uses an Anthropic chat model plus retrieved vectors to generate smart, context-aware output.
- Append Sheet – Logs results to a Google Sheet for tracking and review.
- Slack Alert – Sends error notifications to a
#alertschannel if something breaks.
The result: your Notion pages can be enriched with AI-powered summaries, insights, and actions, with all the context stored in a vector database so your RAG agent does not forget what it just learned.
Why automate Notion updates in the first place?
Notion is already a favorite single source of truth for docs, meeting notes, and projects. The problem is that keeping it all up to date and context rich can feel like a part-time job. Automation with n8n and RAG helps you:
- Enrich Notion pages with summaries, insights, and suggested next steps without manual editing.
- Trigger updates via webhooks from other systems whenever something important changes.
- Persist context in a vector database so your AI queries get faster and more relevant over time.
- Track what happened with logging and error monitoring in Google Sheets and Slack.
In short, you get the benefits of AI-enhanced Notion content without the “copy, paste, tweak, repeat” routine.
How the Notion API Update workflow is wired together
Let us walk through the core building blocks of this n8n workflow so you know what is going on under the hood and where to tweak things.
1. Webhook Trigger – your workflow entry point
The workflow starts with a Webhook Trigger node that exposes an HTTP POST endpoint at:
/notion-api-update
External systems can call this endpoint whenever a Notion page changes or when you want to process some new content. You can:
- Connect it to a Notion webhook.
- Trigger it from another automation tool.
- Send test payloads manually during development.
Keep it secure by protecting the webhook with an API key, secret token, or IP allowlist. You want automation, not random strangers updating your knowledge base.
2. Text Splitter – turning walls of text into bite-sized chunks
Long Notion pages are great for humans, but embeddings models work better with smaller pieces. The Text Splitter node:
- Uses a chunkSize of 400 characters.
- Adds an overlap of 40 characters between chunks.
This setup preserves enough context between chunks while keeping token and embedding costs reasonable. You can tune these values based on how long and structured your typical Notion content is.
3. Embeddings – giving your content a vector brain
Next, the Embeddings node uses the OpenAI model text-embedding-3-small to convert each text chunk into a vector.
Each chunk gets:
- A vector representation for semantic search.
- Metadata like source page ID, chunk index, and original text.
That metadata is important later when you want to trace where a specific answer or piece of context came from.
4. Supabase Insert & Supabase Query – your vector store
The workflow uses Supabase as the vector database. You will:
- Insert new embeddings into a vector table with
indexName: notion_api_update. - Store fields such as:
- Document or page ID
- Chunk text
- Vector
- Tags, timestamps, or other useful metadata
When it is time to answer a query, the Supabase Query node retrieves the top-k most similar vectors. This gives the RAG agent solid context to work with instead of guessing in the dark.
5. Vector Tool – making Supabase searchable for the agent
The Vector Tool node wraps the Supabase index so the RAG agent can call it as a searchable tool. Whenever the agent needs extra context, it can query the vector store directly instead of relying only on the incoming text.
6. Window Memory – short-term memory for multi-step flows
Window Memory keeps recent inputs and outputs available to the RAG agent. This is especially useful when:
- You have multi-step interactions.
- The webhook includes conversational context.
- You want the agent to “remember” what just happened across a few steps.
Think of it as a small, rolling memory buffer so the agent is not constantly asking “wait, what were we talking about again?”
7. Chat Model & RAG Agent – where the magic happens
The workflow uses an Anthropic chat model inside the RAG Agent node. It is configured with:
- A system message that defines how the agent should behave.
- A prompt template tailored for the “Notion API Update” use case.
The RAG approach combines:
- Retrieved vectors from Supabase.
- The language model’s reasoning abilities.
This leads to more accurate, domain-specific responses that are grounded in your actual Notion content rather than generic internet knowledge.
8. Append Sheet – logging everything in Google Sheets
To keep an audit trail, the workflow uses an Append Sheet node that writes agent outputs to a Google Sheet with:
sheetName: Log
This gives you a simple way to:
- Review what the agent generated.
- Approve or reject changes before pushing them back into Notion.
- Monitor how the workflow behaves over time.
9. Slack Alert – when things go sideways
Automation is great until an API key expires or a service hiccups. The Slack Alert node catches errors from the RAG Agent and posts them to a Slack channel, typically:
#alerts
Your engineering or ops team can then jump in quickly, fix the issue, and get your automation back on track before anyone has to manually copy-paste again.
Quick setup guide for the Notion API Update template
Here is a simplified checklist to get this n8n workflow template up and running without losing an afternoon to configuration screens.
Step 1 – Prepare your n8n environment
- Host n8n on your preferred option:
- n8n.cloud
- Self-hosted
- Other cloud setups
- Make sure you have HTTPS and a stable domain so the webhook endpoint is reliable.
Step 2 – Configure OpenAI embeddings
- Create an OpenAI API key.
- In n8n, set up credentials for OpenAI.
- Configure the Embeddings node to use:
text-embedding-3-small
Step 3 – Connect Anthropic or your chosen LLM
- Get API credentials for Anthropic (or another supported LLM provider).
- Configure the Chat Model node in n8n with these credentials.
- Ensure the RAG Agent node is wired to this chat model.
Step 4 – Set up Supabase as your vector database
- Create a Supabase project and table for embeddings.
- Enable pgvector support.
- Add Supabase credentials to n8n.
- Ensure your table includes:
- Document or page ID
- Chunk text
- Vector column
- Optional tags or timestamps
Step 5 – Hook up Google Sheets logging
- Set up OAuth credentials for Google Sheets in n8n.
- Create a spreadsheet with a Log sheet.
- Point the Append Sheet node to this sheet for logging agent outputs.
Step 6 – Configure Slack alerts
- Create a Slack bot token with permission to post to channels.
- Add the bot to your
#alertschannel. - Set up the Slack Alert node to send error messages there.
Step 7 – (Optional) Let the agent write back to Notion
- If you want full end-to-end automation, add a Notion API node after the agent.
- Configure it to:
- Update the relevant Notion page.
- Respect page permissions and workspace access.
Security and best practices so your automation stays friendly
Automation is powerful, so it is worth locking things down properly.
- Authentication – Protect the webhook with an API key or webhook secret, and rotate keys regularly.
- Least privilege – Scope your Supabase, Google Sheets, and Notion credentials so they only have the access they truly need.
- Data retention – Store only the necessary data in your vector store. For sensitive data, consider redaction or hashing.
- Rate limits – Keep an eye on OpenAI, Anthropic, and Supabase usage so you do not hit rate limits at the worst possible moment.
- Error handling – Use n8n’s onError connections, as in this template, to notify Slack and optionally retry transient issues.
Testing and validating your workflow
Before you hand real data over to your shiny new automation, run a few simple tests:
- Send a POST request to the webhook with sample Notion content or a Notion webhook payload.
- Confirm that the Text Splitter creates chunks and the Embeddings node generates vectors. You can check n8n logs or verify rows in Supabase.
- Run a test query to ensure the Supabase Query node returns relevant vectors.
- Check that the RAG agent’s output is appended to the Google Sheet and that no error messages appear in Slack.
If everything looks good and Slack stays quiet, your automation is ready for real workloads.
Optimization tips for performance and cost
Once you have the basics working, you can tune things to be faster, cheaper, and more accurate.
- Adjust chunkSize and overlap – Try different values to balance retrieval quality and embedding costs.
- Use metadata filters – In Supabase queries, filter by project, workspace, or tags to reduce noise and get more relevant context.
- Cache frequent queries – If you see repeated queries, consider caching results to cut down on repeated vector searches.
- Limit top-k results – Keep the number of returned vectors aligned with your prompt size and model capabilities so you do not overload the LLM with unnecessary context.
Real-world use cases for this Notion + n8n + RAG combo
This workflow is flexible enough to support a variety of Notion workflows that usually involve a lot of manual labor.
- Auto-summarize meeting notes into clear action items and store the summary on the same Notion page.
- Enhance product documentation with AI-generated troubleshooting steps while preserving links back to the original context.
- Monitor Notion databases for important field changes and trigger alerts or updates when something critical shifts.
If you have ever thought “I wish this Notion page would just summarize itself,” this template is for you.
Where to go next with this template
The “Notion API Update” n8n template gives you a solid, production-friendly pattern:
webhook intake → chunking → embeddings → vector storage → RAG + LLM processing → logging and alerting
You can clone it, customize it, and extend it with extra steps like automatic Notion updates, approval flows, or additional tools.
To get started right away:
- Clone the template in your n8n instance.
- Provision the Supabase vector table.
- Plug in your OpenAI, Anthropic, Google Sheets, Slack, and Supabase credentials.
- Send a test POST to the webhook and watch your logs and Sheets fill up.
Call to action: Try the workflow today, import the template into n8n, connect your OpenAI and Supabase credentials, and run a test POST. Then subscribe for more automation patterns and step-by-step guides to scale AI-driven workflows in your stack.