Automate Habit Form Weekly Summaries with n8n: A Story About Saving Time, Sanity, and Data
By Thursday afternoon, Mia had already written three weekly habit summaries for her coaching clients. Two more were waiting in her inbox, and another would arrive before the end of the day. Each one meant copying notes from a form, skimming through daily entries, trying to spot patterns, and then writing a thoughtful recap with a few actionable tips.
She believed in the power of weekly reflection. Her clients loved seeing trends in their habits. But the process was slow, repetitive, and full of tiny opportunities for mistakes. A missed note here, a misread date there, or simply the fatigue of writing similar summaries over and over again.
That Thursday, staring at yet another Habit Form submission, Mia finally asked herself: “Why am I doing this manually when I already use n8n for half my business?”
The Problem: Manual Habit Summaries That Do Not Scale
Mia’s coaching business relied heavily on a simple idea: every week, clients submitted a Habit Form with daily notes about what they did, how they felt, and what got in their way. Mia would then send them a weekly summary that:
- Highlighted their wins and consistent behaviors
- Surfaced issues or skipped habits
- Suggested 1 or 2 actionable tips for the next week
Her clients saw real progress. But as her client list grew, so did the time she spent:
- Manually reading each Habit Form submission
- Copying content into a document or spreadsheet
- Trying to remember what happened last week for that same client
- Writing a unique, human-sounding summary from scratch
It was valuable work, but deeply repetitive. And it was exactly the kind of work that an automation-friendly mind like Mia’s knew could be improved.
She had heard of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), vector databases, and embeddings, but had never tied them all together for her own workflow. That changed when she decided to build an automated Habit Form Weekly Summary using n8n, OpenAI embeddings, Supabase vector storage, and Google Sheets.
The Breakthrough Idea: Let Automation Handle the First Draft
Mia did not want to remove herself from the process. She wanted a smart assistant that could:
- Receive Habit Form data automatically
- Store context in a structured, searchable way
- Generate a concise, AI-written weekly summary using RAG
- Log all summaries to Google Sheets for tracking
- Alert her on Slack if anything went wrong
Her role would shift from “manual writer” to “editor and strategist.” The heavy lifting of reading and summarizing would be handled by an n8n workflow
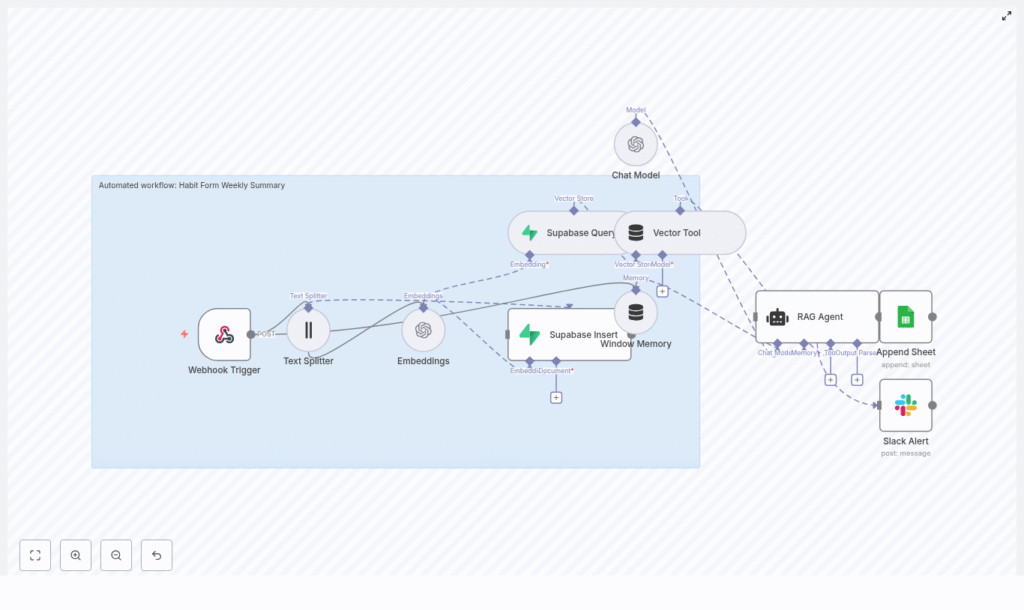
So she opened her n8n canvas and started designing what would become her favorite automation: the Habit Form Weekly Summary n8n workflow. Before touching any node, Mia sketched out the high-level architecture. She wanted a clear flow from raw form data to polished weekly insights. The core pieces looked like this: With the blueprint ready, she started building, one node at a time. The first thing Mia needed was a way to get Habit Form submissions into n8n. She created a Webhook Trigger node and configured it to accept a POST request on the path: Her habit-tracking form now sent payloads like this directly into n8n: Because she cared about security and data integrity, she: With that, every new weekly Habit Form submission would trigger the automation. Some of Mia’s clients wrote short, bullet-like notes. Others treated the form like a journal. Long reflections could easily overwhelm a single embedding and hurt retrieval. To keep things accurate, she added a Text Splitter node. She used a character-based approach with settings like: This meant that long notes would be broken into overlapping chunks, each small enough to capture local meaning. The result was better embeddings and more precise context when the RAG agent later searched for relevant information. Next, Mia connected those chunks to an OpenAI Embeddings node. She chose a model like For every chunk, she stored important metadata alongside the vector: She knew this metadata would be crucial later. It would let her filter by user and week, making sure the RAG agent only looked at the right entries when generating a weekly summary. To persist the embeddings, Mia used Supabase as her vector store. She created a dedicated index in a vector table, for example: Her workflow now did two important things with Supabase: She made sure to: At this point, Mia had a searchable memory of her clients’ weekly habit entries, ready to be used by AI. The next challenge was giving the RAG agent access to both short-lived context and long-term stored data. For that, Mia combined two n8n features: The Window Memory made sure the agent could “remember” what had already been discussed in the flow, while the Vector Tool gave it direct access to the retrieved habit entries. Together, they provided the RAG agent with everything it needed to produce a coherent, grounded weekly summary. Now came the heart of the system. Mia created a Chat Model node using an OpenAI model such as She spent time crafting the system prompt, because she knew prompt engineering would make or break the usefulness of the summaries. A version she liked looked something like this: You are an assistant for Habit Form Weekly Summary. Using the retrieved entries, generate a concise, human-friendly weekly summary with highlights, consistency notes, and an actionable tip. Later, she refined it using best practices: She also experimented with a 3-part output structure: When she finally hit “Execute” on the workflow, the RAG agent read the retrieved entries and produced something like this: Highlights: 5/7 walks completed; notable consistency on mornings. Missed Tuesday and Thursday workouts. Suggestion: schedule a 20-minute morning walk alarm and set an accountability reminder on mid-week. Consider replacing one long session with two shorter sessions if time is constrained. Mia smiled. It was exactly the kind of feedback she used to write by hand. She did not want these summaries to disappear into email threads. She wanted a simple, auditable log of every weekly summary, accessible at a glance. So she added an Append to Google Sheets node. Each time the RAG agent produced a summary, n8n would append a new row to her “Habit Weekly Log” sheet with columns such as: Google Sheets became her lightweight analytics and audit layer. She could filter by client, compare weeks, and quickly spot patterns across her entire coaching practice. Automation is only helpful when you know it is working. To avoid silent failures, Mia created an onError path in her n8n workflow. If anything went wrong at runtime, an Slack Alert node would send a message to her This gave her peace of mind. She could let the system run in the background, knowing she would be notified if a summary failed to generate. As Mia refined her n8n workflow, she realized that small changes in prompt design or retrieval setup had a big impact on summary quality. She adopted a few core best practices: These adjustments turned the RAG agent from “pretty good” into “reliably useful” for her coaching workflow. As more clients joined, Mia started thinking like a systems architect as much as a coach. She made sure her habit form weekly summary automation was secure and scalable. When she thought about future growth, she prepared strategies such as: Her workflow was no longer just a clever shortcut. It was an automation she trusted to grow with her business. Before fully handing over weekly summaries to automation, Mia stress-tested the workflow. She sent a variety of payloads through the webhook: For each run, she compared the AI-generated summary to a human-written version. When the AI missed nuances or overemphasized minor details, she adjusted: After a few iterations, she reached a point where the AI’s summaries were so close to her own that she often only made small tweaks before sending them to clients. Two weeks after deploying the n8n Habit Form Weekly Summary workflow, Mia opened her calendar and noticed something unusual. She had free time on Friday afternoons. Before, Fridays were for catching up on habit summaries she had not written yet. Now, by the time Friday rolled around, n8n had already:
The Architecture Behind Mia’s Automated Habit Summary
Rising Action: Building the n8n Workflow Step by Step
1. Capturing the Habit Form Data with a Webhook
/habit-form-weekly-summary
{ "userId": "123", "weekStart": "2025-08-25", "entries": [ {"day": "Monday", "note": "Walked 30 minutes"}, {"day": "Tuesday", "note": "Skipped workout"} ]
}
2. Preparing Text for Embeddings with a Text Splitter
chunkSize = 400overlap = 403. Turning Notes Into Vectors with OpenAI Embeddings
text-embedding-3-small to convert each piece of text into a fixed-length vector.
userIdweekStartday4. Storing and Retrieving Context with Supabase Vector Storage
indexName: habit_form_weekly_summary
userId and weekStart
userId and weekStart5. Supplying Context with Window Memory and a Vector Tool
6. Generating the Weekly Summary with a Chat Model and RAG Agent
gpt-4o or gpt-4, depending on availability. She then wrapped it in a RAG Agent configuration so it could:
“Produce a 5-sentence weekly summary with 1-2 actionable tips.”userId + weekStart)
7. Logging Everything in Google Sheets
userIdweekStartgeneratedSummarytimestamp8. Staying in Control with Slack Alerts on Error
#alerts channel with:
Behind the Scenes: Prompt Engineering and RAG Best Practices
She always defined the agent’s role and output format. For example:
“You are a habit coach assistant. Produce a concise weekly summary with 1 short highlights paragraph, 1 issues paragraph, and 1-2 actionable tips.”
She limited retrieval to the same userId and weekStart so the agent never mixed up different clients or weeks.
When auditability mattered, she had the agent return chunk IDs or brief excerpts, so she could trace which notes influenced each summary.
She set a max token or character limit, keeping summaries readable and avoiding oversized Google Sheets cells.
Security, Monitoring, and Scaling as the Client List Grows
Securing the Workflow
Monitoring and Cost Control
Scaling Vector Storage
Testing, Edge Cases, and Getting the Details Right
The Turning Point: How Mia’s Week Changed