Automate LinkedIn Content with n8n + AI
Discover how to implement a production-grade LinkedIn content automation pipeline using n8n, Apify, OpenAI, Telegram, and Airtable. This workflow continuously discovers relevant posts, extracts and repurposes them with AI, routes them through an editorial process, and publishes to LinkedIn on a schedule – all within a single, maintainable automation.
Strategic value of LinkedIn content automation
For many B2B companies, founders, and creators, LinkedIn is a primary channel for distribution and demand generation. The challenge is not knowing what to post, but maintaining a consistent cadence of high-quality, on-brand content.
Manual tasks such as monitoring competitors, extracting insights from their content, transcribing media, and rewriting posts consume significant time and are difficult to scale. By combining n8n with AI and lightweight data storage, you can build an end-to-end LinkedIn content engine that:
- Continuously discovers posts from selected competitors, influencers, and creators
- Extracts text from documents, images, and videos
- Uses OpenAI to repurpose content into multiple LinkedIn-ready formats
- Centralizes drafts, metadata, and status tracking in Airtable
- Automatically publishes approved posts to LinkedIn based on a defined schedule
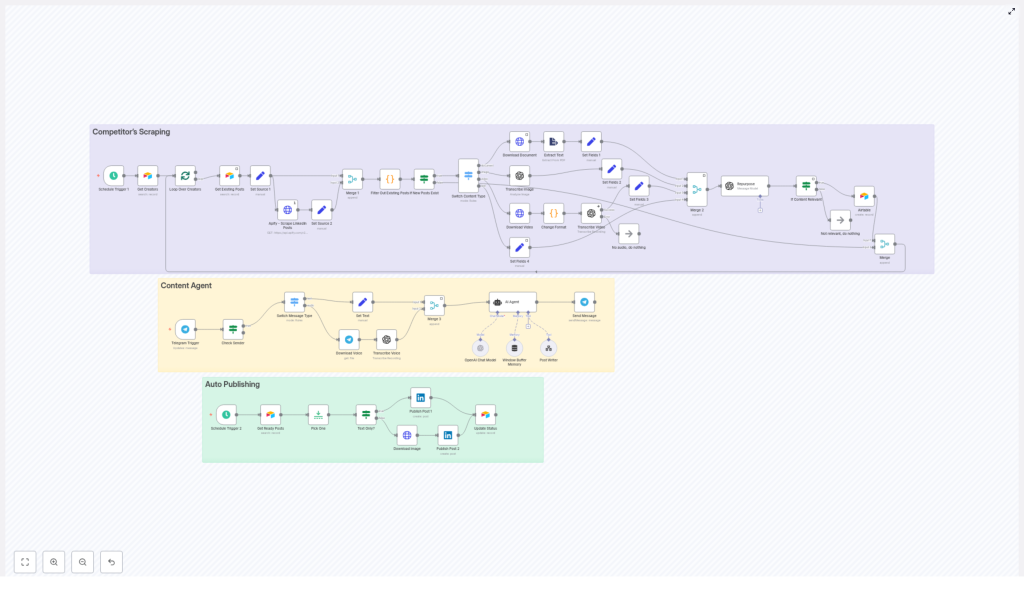
High-level architecture of the n8n workflow
The automation is organized into three main modules, each responsible for a distinct phase of the content lifecycle. In the n8n canvas these modules are typically color-coded for clarity:
- Competitor Scraping – Ingests LinkedIn posts and media from specified profiles using Apify or similar scrapers, prevents duplicates via Airtable, and normalizes raw content.
- Content Agent – Accepts content from scraping or Telegram, invokes OpenAI for transcription and repurposing, and applies structured prompt rules to generate multiple post variants.
- Auto Publishing – Pulls approved content from Airtable, determines the correct LinkedIn post type, and publishes automatically on a defined cadence.
This modular structure simplifies maintenance and makes it easy to extend or replace individual components without redesigning the entire workflow.
End-to-end workflow: from discovery to published post
1. Scraping and deduplication pipeline
The content lifecycle starts with automated discovery of relevant LinkedIn posts from your chosen creators or competitors.
- Triggering the scraper
A Schedule Trigger node runs at your defined intervals (for example, hourly or daily). This trigger calls an Apify actor or similar scraper via an HTTP Request node to retrieve the latest posts for a configured list of profiles. - Preventing duplicates with Airtable
Before any new content is processed, the workflow queries Airtable for existing post IDs. A simple Code node or IF node is then used to compare scraped items against these stored IDs.
Only posts with IDs that do not yet exist in Airtable move forward. This ensures:- No accidental reposting of the same content
- Airtable remains the single source of truth for all processed posts
2. Content extraction across media types
Once a new post is identified, the workflow branches based on content type to extract usable text and metadata.
- Routing by content type
The workflow determines whether the input is a document, image, video, or plain text. This routing can be implemented using IF nodes or Switch nodes in n8n. - Documents (PDF and similar)
For document-based content, the workflow:- Downloads the file
- Runs it through a PDF or document extraction node or custom logic
- Returns clean text suitable for AI processing
- Images
Images are passed to an OCR or vision-capable model. Using OpenAI vision or a third-party OCR service, the workflow extracts any embedded text, captions, or overlays that are relevant for repurposing. - Videos
Video posts are downloaded and their audio is extracted. The audio stream is then sent to OpenAI Speech-to-Text for transcription. This step converts spoken content into structured text that can be repurposed. - Plain text posts
If the original LinkedIn post is already text-based, the workflow can skip media extraction and pass the content directly to the AI repurposing step.
Regardless of the input type, the pipeline consolidates the outcome into a consistent content object with fields such as:
idusernamedatePostedurllikesCountcontent(normalized text)contentType(text, image, video, document)
3. AI-driven repurposing with OpenAI
With normalized content available, the workflow delegates repurposing to an OpenAI node configured with a carefully designed prompt. This is the core of the “content agent” module.
The OpenAI (Chat) node receives the content object and returns a structured JSON with three primary deliverables:
- Text-only LinkedIn post – A stand-alone post suitable for direct publishing.
- Text + tweet-style image text – A post that includes copy for LinkedIn plus a short, punchy text overlay designed for an accompanying image.
- Text + infographic description – A post that includes copy plus a detailed specification for an infographic or carousel-style visual.
The prompt in the Repurpose node enforces:
- A defined JSON schema so the AI outputs are machine-readable
- Brand voice and narrative style, for example:
- Shareable personal or founder-style stories
- Clear, structured lists of tactics or lessons
- Actionable, tactical takeaways
- Three distinct variants per input to support different creative formats
- A relevance filter that flags non-marketing or off-topic content as not relevant
Typical prompt rules include:
- Keep each post between 300 and 400 words
- Use line breaks, bullet points, and numbered lists for readability
- End with a single, concise call to action such as “Follow for more” or “Share if useful.”
4. Editorial review and Airtable as the control layer
To maintain quality and compliance, the workflow never publishes AI output directly without human oversight.
- Writing to Airtable
For all content that passes the relevance gate, the workflow writes:- Original metadata and source references
- Repurposed text variants
- Media links or infographic specs
- A status field that tracks the lifecycle (for example,
review,ready,posted)
- Human review process
Editors or content owners work directly in Airtable to:- Review AI-generated copy for accuracy and brand alignment
- Refine or overwrite fields such as
finalText - Update the status to
readyonce a post is approved for publishing
This editorial gate is critical for risk management, especially when repurposing competitor content or opinionated posts.
5. Automated, scheduled publishing to LinkedIn
The final stage of the pipeline focuses on consistent, automated distribution.
- Publishing trigger
A second Schedule Trigger node runs at your chosen posting cadence. It queries Airtable for records wherestatus = "ready". - Selecting and preparing the post
The workflow selects one or more posts according to your logic (for example, next in queue, highest priority, or random). It then checks whether the selected record is:- Text-only
- Text plus image
- Text plus other media
- Media handling
If media is required, the workflow:- Downloads the relevant image or asset
- Prepares it in the format expected by the LinkedIn node
- Publishing via LinkedIn node
The LinkedIn node, configured with OAuth credentials, publishes the content as a LinkedIn post. On success, the workflow updates the Airtable record tostatus = "posted"for tracking and reporting.
Key n8n nodes and external integrations
The workflow relies on a combination of native n8n nodes and external services. At a glance:
- Schedule Trigger – Orchestrates both scraping and publishing cadences.
- HTTP Request (Apify) – Connects to Apify actors or APIs to scrape LinkedIn content and media from specified profiles.
- Airtable – Serves as the operational database for:
- Post metadata and source references
- Repurposed content variants
- Status tracking and audit logs
- Media URLs and related assets
- OpenAI (Chat + Speech-to-Text) – Handles:
- Transcription of audio from video posts
- Image or OCR analysis when using vision models
- Copy repurposing with structured prompts and JSON outputs
- Telegram Trigger (optional) – Provides an alternative input path for:
- Voice notes with content ideas
- Manual text snippets you want the content agent to expand or adapt for LinkedIn
- LinkedIn – Publishes text and media posts using your authenticated LinkedIn account via OAuth.
Prompt design and repurposing strategy
For automation professionals, the prompt is the primary control surface for quality. A robust prompt for this workflow typically includes:
- Explicit input and output specification
Provide the raw content and define the exact JSON schema the AI must return. This ensures downstream nodes can reliably parse the output. - Brand voice, tone, and structure
Specify:- Target persona and level of expertise
- Preferred tone (for example, authoritative but approachable)
- Structure such as hook, narrative, list of tactics, and closing CTA
- Variant requirements
Require three variants:- Primary LinkedIn text post
- Short, tweet-style image text for visual overlays
- Detailed infographic or carousel specification
- Relevance gate
Instruct the model to flag content as irrelevant when it does not relate to your focus area, for example, marketing or growth. This prevents polluting Airtable with off-topic posts. - Formatting rules
Include guidelines such as:- Maximum length (300 to 400 words)
- Use of headings, line breaks, and numbered lists
- Exactly one call to action at the end
Operational best practices for this automation
To run this workflow reliably at scale, consider the following best practices.
- Maintain an editorial checkpoint
Keep the Airtable review step mandatory. Fully automated publishing of AI-generated and competitor-derived content can drift from your brand voice, introduce factual errors, or increase copyright risk. - Respect content ownership and platform policies
Avoid reposting copyrighted content verbatim. Focus on transformation, commentary, and synthesis. Where appropriate, attribute original creators and always comply with LinkedIn’s API terms and the terms of your scraping provider. - Monitor usage, costs, and rate limits
Track:- OpenAI token usage for chat and transcription
- Apify or scraper rate limits and quotas
- LinkedIn API constraints
Batch requests where possible to reduce overhead and avoid throttling.
- Implement logging and observability
Store:- Raw scraped inputs
- AI outputs and final edited content
- Publishing responses and error messages
in Airtable or a secondary logging system. This supports audits, debugging, and rollback if needed.
Troubleshooting and scaling the workflow
As your content volume grows, you may encounter quality or performance challenges. Typical adjustments include:
- Improving transcription quality
If audio transcription is noisy or inaccurate:- Switch to a higher-fidelity OpenAI speech model
- Preprocess audio to reduce background noise
- Filter out very low-quality sources before transcription
- Scaling scraping operations
For larger creator lists:- Shard creators across multiple Schedule Trigger nodes or workflows
- Distribute requests and respect rate limits to avoid blocking
- Use caching for repeated media downloads
- Handling heavy processing tasks
For intensive workloads such as video transcription or image analysis:- Introduce worker queues or external job runners
- Offload long-running tasks to dedicated processing workflows
- Use n8n’s built-in concurrency and retry settings to improve robustness
Privacy, legal, and ethical considerations
Automating competitor analysis and content repurposing requires careful handling of legal and ethical issues.
- Manual oversight of scraped content
Always review scraped material before publishing. Avoid copying private, restricted, or clearly copyrighted content without transformation or permission. - Transparency about AI usage
If your audience expects disclosure, clearly indicate when content is AI-assisted or AI-generated. - Compliance with platform and data source terms
Follow:- LinkedIn’s API and platform policies
- Apify’s usage terms
- Robots.txt and any applicable site-level restrictions
Non-compliance can lead to account restrictions or legal exposure.
Conclusion: turning discovery into a repeatable LinkedIn engine
With this n8n + AI workflow, you can transform fragmented content discovery into a structured, repeatable LinkedIn publishing system. The pipeline:
- Aggregates insights from competitors and creators via scraping and Telegram
- Uses OpenAI to repurpose raw content into multiple LinkedIn-ready formats
- Centralizes review, governance, and status tracking in Airtable
- Publishes approved posts on a predictable schedule through the LinkedIn node
Once