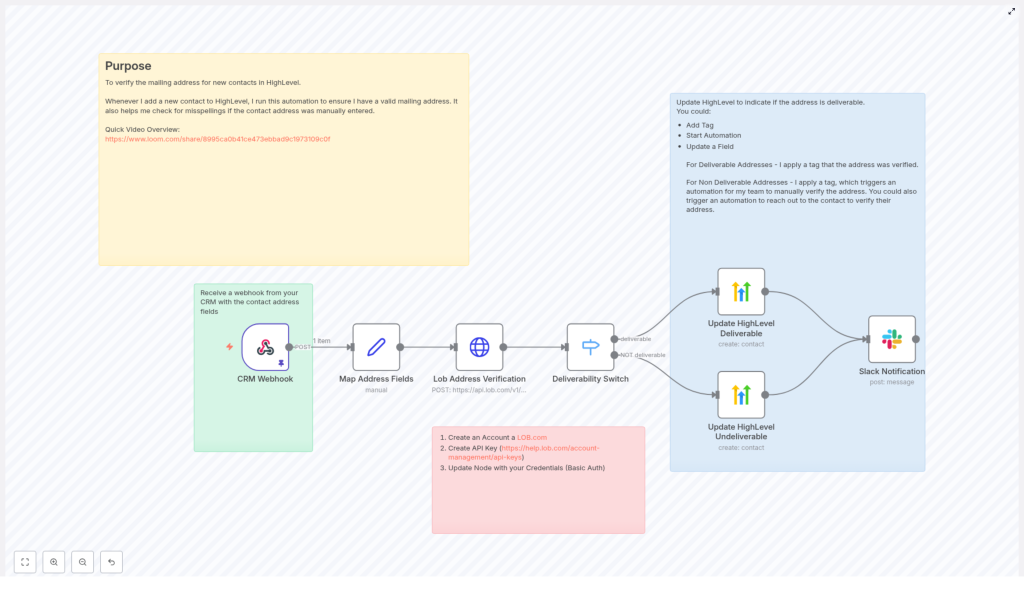
Automate Mailing Address Verification with n8n & Lob
Maintaining accurate and deliverable mailing addresses in your CRM is essential for direct mail campaigns, billing, and customer communications. This technical guide documents an n8n workflow template that validates new contact mailing addresses with Lob’s US address verification API, then updates HighLevel and notifies your team automatically.
The workflow is designed for operations, marketing, and engineering teams that want a reliable, repeatable address verification pipeline integrated into their CRM stack.
1. Workflow Overview
This n8n automation is triggered whenever a new contact is created in your CRM. The workflow:
- Receives a webhook payload from your CRM that includes contact and address data.
- Normalizes the incoming fields into a consistent structure.
- Submits the address to Lob’s
/v1/us_verificationsendpoint. - Evaluates the
deliverabilitystatus returned by Lob. - Updates the contact in HighLevel with appropriate tags based on deliverability.
- Sends a Slack notification so your team can review or act when needed.
The result is a fully automated address verification pipeline that reduces returned mail, improves data quality, and provides clear visibility into address status directly inside your CRM.
2. Components & Prerequisites
2.1 Tools and Services
- n8n – Open-source automation platform that orchestrates the workflow.
- Lob – Address verification API, using the US verifications endpoint.
- HighLevel – CRM where contact records and tags are updated.
- Slack – Used to send real-time notifications to a channel.
- Your CRM – Origin system that sends a webhook into n8n when a contact is created.
2.2 Required Data From Your CRM
The webhook payload from your CRM should include at minimum:
- Address line 1 (street address).
- City.
- State.
- ZIP / postal code.
- Contact identifier (email, phone, or contact_id) that can be used to locate the record in HighLevel.
Optional but recommended fields:
- Secondary address line (apartment, suite, unit, etc.).
- Phone number.
3. Architecture & Data Flow
The workflow follows a linear but branching architecture:
- Webhook node receives contact data from your CRM.
- Set node maps and normalizes address fields into a predictable format.
- HTTP Request node calls Lob’s US address verification API with the mapped fields.
- Switch node evaluates Lob’s
deliverabilityvalue and routes execution. - HighLevel node(s) update the contact record with tags for deliverable or non-deliverable addresses.
- Slack node sends a summary message to a chosen channel.
Error handling and retries can be layered on top of this architecture using n8n’s error workflows, Retry, and Delay nodes.
4. Node-by-Node Breakdown
4.1 Webhook Node – Inbound CRM Trigger
Purpose: Accepts HTTP POST requests from your CRM when a new contact is created or updated.
- HTTP Method:
POST - Payload: JSON body containing contact and address fields.
Typical expected payload fields:
address– Primary street address.city– City name.state– State or region (for example,DC).zip_code– ZIP or postal code.email– Contact email used for HighLevel lookup.phone– Contact phone number used for HighLevel lookup.contact_id– Optional unique identifier for the contact.
Configuration notes:
- Expose the Webhook URL that n8n generates and configure your CRM to send a POST request to that URL on contact creation.
- Ensure the CRM sends all required fields. Missing fields may cause Lob to return
riskyorundeliverable. - Include at least one stable identifier (email, phone, or contact_id) that matches how you plan to update contacts in HighLevel.
4.2 Set Node – Address Field Normalization
Purpose: Normalize incoming CRM fields into a uniform structure for use in the Lob API request.
Example mapping used in the template:
address: {{ $json.address }}
address2: (optional)
city: {{ $json.city }}
state: {{ $json.state }}
zip: {{ $json.zip_code }}
Key points:
address2can be left blank or mapped from a secondary address line if your CRM provides it.- Use this node to trim whitespace, adjust casing, or perform simple transformations if needed.
- Verify that the field names in this node match exactly with your CRM’s webhook payload keys.
4.3 HTTP Request Node – Lob Address Verification
Purpose: Call Lob’s US address verification API with the normalized address fields.
Endpoint:
POST https://api.lob.com/v1/us_verifications
Body parameters:
primary_line={{ $json.address }}
secondary_line={{ $json.address2 }}
city={{ $json.city }}
state={{ $json.state }}
zip_code={{ $json.zip }}
You can send these fields as form-encoded or JSON, depending on how the HTTP Request node is configured in your n8n instance.
Authentication:
- Use your Lob API key via Basic Auth or an
Authorizationheader. - Configure this in n8n’s credentials manager rather than hardcoding it into the node.
Response:
Lob returns a JSON object that includes a deliverability field, for example:
deliverableundeliverablerisky
This field is later evaluated by the Switch node. You can also choose to store the full response for auditing or debugging purposes.
4.4 Switch Node – Deliverability Evaluation
Purpose: Route the workflow based on Lob’s deliverability value.
Expression evaluated: $json.deliverability
In the template, at least two branches are defined:
- Case:
deliverable– The address is recognized as deliverable. The workflow proceeds to tag the contact as “Mailing Address Deliverable” in HighLevel. - Case: not
deliverable– For values such asundeliverableorrisky, the workflow tags the contact as “Mailing Address NOT Deliverable” and can trigger a manual verification process for your team.
Edge considerations:
- If Lob introduces new deliverability statuses, ensure the Switch node is updated accordingly.
- You can add additional branches to treat
riskydifferently from fullyundeliverableif your use case requires it.
4.5 HighLevel Node – Contact Update
Purpose: Update the corresponding contact record in HighLevel with deliverability tags.
The template is configured to update contacts by email or phone, but you can also pass contact_id if your CRM mapping supports it.
Example additionalFields configuration:
additionalFields: { tags: "Mailing Address Deliverable"
}
For non-deliverable addresses, the tag is adjusted accordingly, for example:
Mailing Address NOT Deliverable
Usage notes:
- Confirm the identifier used for the update (email, phone, or contact_id) matches what HighLevel expects.
- Once tagged, you can use HighLevel’s internal automation features to:
- Trigger manual verification workflows.
- Start follow-up sequences to request corrected addresses from contacts.
4.6 Slack Node – Team Notification
Purpose: Notify your team when an address verification has been processed.
After the HighLevel update, a Slack node sends a concise message to a chosen channel.
Example message template:
Mailing address verification for {{ $json.email }}: {{ $json.deliverability }}
Configuration notes:
- Use n8n’s Slack credentials to authenticate with your workspace.
- Set the channel where operations, support, or marketing teams can monitor verification results.
- Consider including additional context such as contact_id or tags if your team needs more detail.
5. Error Handling & Reliability
Address verification calls can fail due to transient network issues, API limits, or malformed input. To increase reliability:
- Use n8n error workflows: Configure an error workflow to catch failures from the Lob HTTP Request node and apply a retry strategy.
- Retry and delay: Use Retry or Delay nodes to back off and retry requests that fail due to rate limits or temporary network errors.
- Logging failed verifications: Log failures to a spreadsheet, database, or another system of record for manual follow-up.
- Rate limiting: If your CRM generates high volumes of new contacts, consider batching or queuing requests to avoid hitting Lob rate limits.
6. Security & Credentials Management
Protecting API keys is critical when integrating external services like Lob and HighLevel.
- Use n8n credentials manager: Store Lob and HighLevel API keys in n8n’s credentials system rather than hardcoding them into nodes.
- Avoid plaintext in exports: Do not embed API keys directly in node parameters or expressions, which could end up in exported workflow JSON.
- Environment variables: Where appropriate, use environment variables in combination with n8n credentials for secure configuration.
7. Testing with Sample Data
n8n allows you to pin test data to the Webhook node, which is extremely useful for developing and validating the workflow without relying on live CRM events.
Sample payload used in the template:
{ "city": "Washington", "email": "mr.president@gmail.com", "phone": "877-555-1212", "state": "DC", "address": "1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW", "zip_code": "20500", "contact_id": "5551212"
}
Recommended test steps:
- Pin this JSON payload on the Webhook node.
- Execute the workflow manually from the Webhook node onward.
- Inspect the Lob response and confirm the
deliverabilityfield is being evaluated correctly by the Switch node. - Verify that the HighLevel contact is updated and that the Slack notification is sent as expected.
8. Best Practices for Production Use
- Normalize inputs: Trim whitespace, standardize casing, and ensure fields are not null before sending data to Lob.
- Persist Lob responses: Store the raw Lob response in a custom field or external store for auditing and troubleshooting.
- Timestamped verification tags: Use tags such as
address_verified_2025-10-24to track when an address was last validated. - Manual verification queue: For contacts tagged as “Mailing Address NOT Deliverable”, build a small queue or view where your team can work through corrections and outreach.
9. Common Pitfalls & How to Avoid Them
- Field mapping mismatches: Ensure CRM field names match what the Set node expects. A mismatch can result in empty or incorrect values being sent to Lob.
- Missing authentication: Lob requires a valid API key and sufficient quota. Double-check credentials if you see authentication or quota-related errors.
- Partial or incomplete addresses: Incomplete inputs can cause Lob to return
riskyorundeliverable. Make sure your CRM enforces required fields where possible.
10. Summary & Next Steps
This n8n workflow template delivers a complete, production-ready address verification pipeline:
- Accepts a webhook from your CRM when a new contact is created.
- Normalizes address fields for consistent processing.
- Calls Lob’s US address verification API.
- Branches on the
deliverabilityresult using a Switch node. - Updates the corresponding contact in HighLevel with clear deliverability tags.
- Notifies your team via Slack so they can respond quickly when an address is not deliverable.
By automating mailing address verification, you reduce returned mail and wasted postage, improve campaign deliverability, and maintain higher quality CRM data while freeing your team from manual checks.
How to get started:
- Import the n8n workflow template into your n8n instance.
- Configure Lob and HighLevel credentials securely via the n8n credentials manager.
- Pin the sample data to the Webhook node and run a few test executions.
- Connect your CRM’s webhook to the n8n Webhook URL once testing is successful.
If you need help adapting the template to your CRM schema or internal processes, you can extend the mapping logic, add additional branches for specific deliverability states, or integrate more notification channels as required.
Call to action: Import the template into n8n and verify your first 10 addresses today. If you need assistance integrating this workflow into your stack, reach out or leave a comment and we can help tailor the flow to your specific CRM and data model.