How to Connect WordPress Forms to Mautic Using n8n (Step-by-Step)
Build a robust automation pipeline that captures WordPress form submissions, standardizes and validates the data, then creates or updates contacts in Mautic using an n8n workflow. This guide explains the use case, architecture, and implementation details of the n8n template so you can deploy it confidently in production environments.
Why integrate WordPress forms with Mautic via n8n?
For teams that rely on WordPress for lead generation and Mautic for marketing automation, manual export and import of form data is inefficient and error-prone. An automated n8n workflow between WordPress and Mautic ensures that:
- Leads are captured in real time, directly into your Mautic instance
- Data is normalized and validated before contact creation
- Invalid or suspicious email addresses are filtered out or flagged
- Stakeholders are notified when manual review is required
This approach improves lead quality, accelerates follow-up, and protects your CRM from polluted or incomplete data.
Solution architecture and workflow design
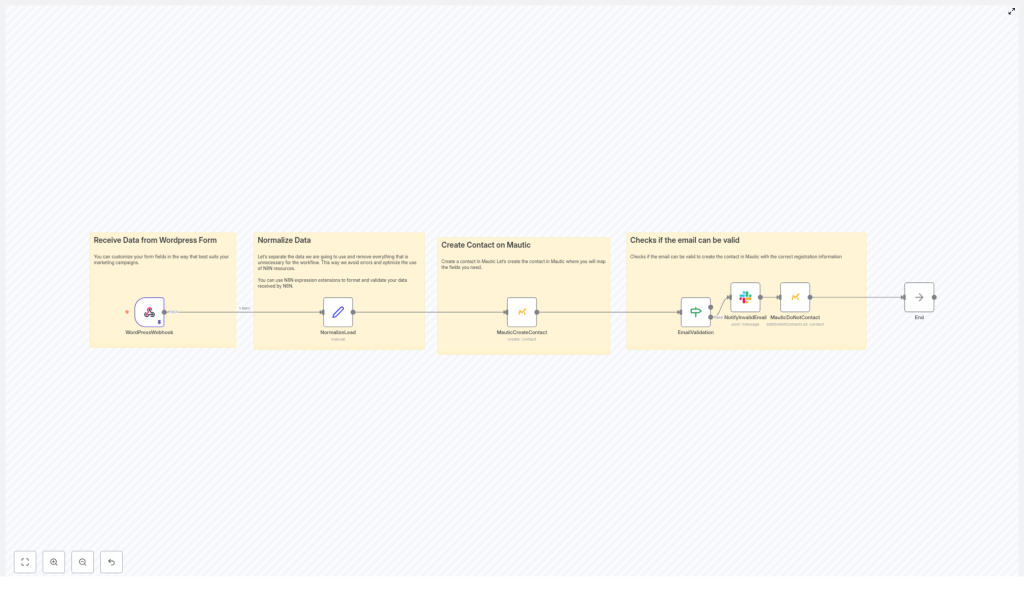
The n8n template implements a controlled data pipeline from WordPress to Mautic. It uses a webhook trigger, transformation logic, contact creation, and conditional handling for invalid emails.
Core workflow stages
- Inbound webhook from WordPress A Webhook node in n8n receives POST requests from your WordPress form plugin.
- Lead normalization A Set node (NormalizeLead) standardizes key fields such as name, email, mobile, and form identifier.
- Contact creation in Mautic A Mautic node creates or updates a contact using the normalized data.
- Email validation decision An If node evaluates whether the email address satisfies basic validation criteria.
- Invalid email handling If the email is invalid, the workflow sends a notification and marks the contact in Mautic as Do Not Contact or tags it for cleanup.
- Workflow termination The flow ends after successful processing or after handling invalid data.
This structure separates responsibilities: intake, transformation, validation, persistence, and exception handling. It also makes the workflow easy to extend with additional validation or enrichment steps.
Configuring the n8n workflow step by step
1. Configure the WordPress webhook trigger
Start by exposing an HTTP endpoint in n8n that your WordPress form can call.
- Create a Webhook node in n8n and set the HTTP method to
POST. - Choose the appropriate
Content-Typeaccording to your form plugin:application/x-www-form-urlencodedfor many classic WordPress form pluginsapplication/jsonif your plugin supports JSON payloads
- Copy the generated webhook URL.
- In your WordPress form plugin (such as Contact Form 7, Gravity Forms, WPForms, and others), configure a webhook or integration endpoint and paste the n8n webhook URL there.
- Ensure the form is configured to send data using the POST method.
2. Normalize and clean incoming lead data
Once the webhook receives data, the next priority is to standardize the payload into a reliable internal schema.
Use a Set node in n8n, often named NormalizeLead, to:
- Map raw form fields to canonical names
- Apply formatting and basic validation logic
- Preserve metadata such as form identifiers for segmentation
Typical mappings might include:
- name: convert to title case
- email: convert to lower case and run a simple syntax check
- mobile: remove formatting or country prefixes according to your conventions
- form: keep the original
form_idor form name for later segmentation in Mautic
Example n8n expressions for the Set node:
name = {{$json.body.Nome.toTitleCase()}}email = {{$json.body['E-mail'].toLowerCase()}}Adapting these expressions to your actual field names from WordPress is essential. Keep naming consistent across WordPress, n8n, and Mautic to reduce mapping issues.
3. Create or update the contact in Mautic
With normalized data available, you can safely interact with Mautic.
- Add a Mautic node and configure it with your Mautic API credentials (OAuth or API key, depending on your setup).
- Map the normalized fields to Mautic contact fields:
- email → primary email field in Mautic (required)
- name →
firstNameor an equivalent field - mobile → mobile or phone field, often via
additionalFields - form or form_id → a custom field for attribution or segmentation
At minimum, ensure that email and firstName are mapped. Additional fields such as mobile are valuable for SMS or WhatsApp follow-up flows in Mautic.
4. Validate email addresses and branch the workflow
To prevent invalid data from entering Mautic, the template uses a conditional step based on email validity.
- Insert an If node after normalization or after initial validation logic.
- Evaluate a boolean flag such as
$json.email_validor a similar expression that represents your validation result. - Configure two paths:
- Valid path: continue normal processing or simply end the workflow.
- Invalid path: trigger notifications and mark the contact as Do Not Contact or tag it appropriately in Mautic.
On the invalid path, the workflow typically performs two actions:
- Notification: send a Slack message, email, or internal alert so a human can review or correct the record.
- Mautic flagging: use a Mautic node to add the contact to a Do Not Contact list or assign a tag indicating an invalid email.
5. Final validation and testing
Before moving to production, thoroughly test the integration.
- Submit sample forms from your WordPress site with:
- Valid data
- Intentionally malformed emails
- Edge cases such as missing fields
- Inspect n8n execution logs to confirm:
- Incoming payloads are parsed correctly
- Normalized fields match your expectations
- Contacts appear in Mautic with correct field mappings
- Invalid emails follow the correct branch and trigger notifications
Security, data quality, and reliability best practices
Secure the webhook endpoint
Webhook endpoints are potential attack surfaces. Protect them with multiple layers where possible:
- Add a secret token as a query parameter or header and validate it in n8n.
- Restrict access by IP address if your infrastructure allows it.
- Serve n8n behind HTTPS and, ideally, behind an authenticated proxy or gateway.
Strengthen email verification
Basic regex or syntax validation is useful, but for production-grade lead management consider augmenting the workflow with more advanced checks:
- Call an external email verification API (for example ZeroBounce or Kickbox).
- Perform MX record lookups to identify invalid or non-existent domains.
- Maintain a list or heuristic rules for disposable email providers and treat them differently.
These enhancements can be integrated into the n8n workflow as additional nodes before the If condition.
Map extended fields for richer Mautic profiles
To improve segmentation, attribution, and reporting in Mautic, consider mapping more than just name and email:
- UTM parameters such as
utm_source,utm_medium, andutm_campaign - Landing page URL or referrer
- Form identifier or form type (for example, demo request, newsletter, webinar)
Ensure that corresponding custom fields exist in Mautic and that naming is consistent across WordPress, n8n, and Mautic.
Handle rate limits and transient errors
Mautic or third-party services may impose rate limits or experience temporary downtime. To increase reliability:
- Monitor Mautic API rate limits and adjust request frequency accordingly.
- Use n8n retry settings on nodes that call external APIs.
- Consider queueing mechanisms, such as n8n’s Execute Workflow node or external message queues, to buffer requests during high load or outages.
Troubleshooting and operational monitoring
Common configuration issues
- No data received in n8n Verify that:
- The webhook URL in WordPress exactly matches the one in n8n.
- The form is configured to use the POST method.
- There are no firewall or proxy rules blocking outbound requests from WordPress.
- Malformed or unexpected JSON If payloads are not parsed correctly:
- Check the
Content-Typeheader sent by the form plugin. - Switch the webhook configuration between
application/jsonandapplication/x-www-form-urlencodedto match what the plugin sends.
- Check the
- Mautic authentication failures If the Mautic node fails to authenticate:
- Revalidate OAuth or API key credentials.
- Check token expiration and refresh flows.
- Confirm that the Mautic API is enabled and accessible from the n8n environment.
Logging, alerts, and observability
For production automations, visibility into failures is essential.
- Enable detailed logging in n8n to capture request payloads, errors, and node-level details.
- Configure Slack or email notifications for failed executions or error branches.
- Maintain a lightweight dashboard or report to track webhook success and failure rates, which helps identify systemic issues or plugin changes on the WordPress side.
Extending the n8n template for advanced use cases
The base workflow is intentionally simple so it can serve as a foundation for more sophisticated automations. Common extensions include:
- Contact enrichment Integrate services such as Clearbit or FullContact to append company, role, or social data to contacts before they reach Mautic.
- Automated onboarding sequences Trigger specific Mautic campaigns or email sequences based on the form type, form_id, or UTM parameters.
- Real-time lead scoring and routing Implement scoring logic in n8n or Mautic and route high-value leads to sales channels, such as Slack alerts, CRM tasks, or direct notifications.
Because the workflow already centralizes intake and normalization, adding new branches and integrations is straightforward.