Automate Pitch Deck Analysis with AI and Airtable
Overview
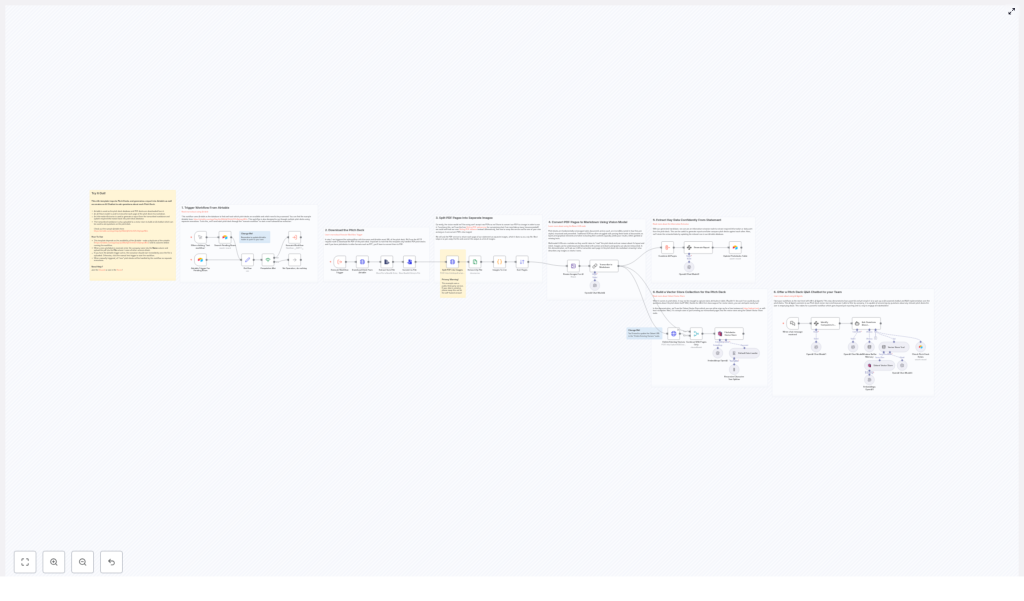
This n8n workflow template automates the end-to-end analysis of PDF pitch decks stored in Airtable. It is designed for venture capital teams, startup accelerators, and investors who need a scalable, repeatable process for extracting structured insights from pitch materials.
The automation performs the following high-level tasks:
- Polls Airtable for new pitch deck records with attached PDF files
- Downloads and converts each PDF into page-level images
- Transcribes the visual content into markdown using an AI vision model
- Extracts key investment-relevant data points using an AI information extractor
- Writes structured results and summaries back into Airtable
- Indexes the content in a Qdrant vector store for semantic search
- Exposes the indexed content via an AI chatbot using n8n AI Agents
This document-style guide explains the workflow architecture, node-by-node behavior, configuration requirements, and practical considerations for running this automation reliably in production.
Workflow Architecture
At a high level, the workflow can be divided into four main phases:
- Ingestion – Detect and download new pitch deck PDFs from Airtable.
- Document preparation – Convert PDFs into images, then into markdown text.
- Analysis and enrichment – Use AI to extract structured data and summaries, then persist results to Airtable.
- Knowledge access – Build a vector store and expose a Q&A chatbot interface over the processed pitch decks.
Each phase is implemented as a series of n8n nodes that pass data through the workflow using the standard items[] structure. The workflow is designed to handle multiple pitch decks asynchronously, so each Airtable record is processed independently as a separate execution path.
Node-by-Node Breakdown
1. Airtable Trigger – Detect New Pitch Decks
Role: Entry point that identifies which Airtable records are ready for processing.
Typical configuration:
- Trigger type: Polling or event-based trigger for Airtable (depending on your n8n setup).
- Table: The table that stores pitch decks, typically with columns such as
NameandFile. - Filter: Only records that have:
- A non-empty
Namefield, and - An attached PDF file in the designated attachment column (for example,
File).
- A non-empty
The trigger node periodically polls Airtable and outputs items representing each qualifying record. Each item typically contains:
- The Airtable record ID
- Company name or pitch deck name
- Attachment metadata, including the public file URL for the PDF
Scalability note: Since this is a modular polling-based design, you can safely process multiple pitch decks in parallel, subject to your n8n instance’s concurrency limits and Airtable rate limits.
2. HTTP Request – Download the Pitch Deck PDF
Role: Retrieve the PDF file from the URL stored in Airtable.
Typical configuration:
- Method:
GET - URL: The file URL from the Airtable attachment field (for example,
{{$json["fields"]["File"][0]["url"]}}). - Response format: Binary data
The node downloads the pitch deck as binary content and attaches it to the current item. This binary data is passed to downstream nodes for further processing.
Format limitation: The workflow is designed to handle PDF files only. If a deck is uploaded as PPT, PPTX, or another format, it must be converted to PDF before this workflow runs. Non-PDF files can cause conversion failures in later steps.
3. External Conversion – Split PDF into Page Images
Role: Convert the PDF into one image file per page, suitable for processing by an AI vision model.
The workflow uses an external service, such as Stirling PDF, to convert the PDF into a series of high-resolution JPEG images. This service:
- Accepts the PDF as input
- Splits it into individual pages
- Renders each page as a JPEG image
- Returns all images bundled as a ZIP archive
An n8n node (typically an HTTP Request or a custom integration) sends the binary PDF to the Stirling PDF endpoint and receives the ZIP file as binary output.
Next, a separate node is used to:
- Extract the ZIP archive
- Expose each JPEG file as a separate binary item or as an array of binaries on the item
These image files represent the individual pages of the pitch deck, which are then passed to the vision model.
Privacy warning: The conversion service described here is publicly hosted. If you are working with confidential or sensitive pitch decks, you should:
- Self-host Stirling PDF or an equivalent PDF-to-image service in your own infrastructure, or
- Use a secure, compliant document conversion solution under your control.
Sending sensitive content to a public third-party service can violate confidentiality or data protection requirements.
4. Vision AI Node – Convert Page Images to Markdown
Role: Perform OCR and layout-aware transcription of each pitch deck page, outputting markdown text.
Each JPEG page is forwarded to an AI vision model node. The node processes the image and returns a markdown representation of the content. The resulting markdown aims to preserve:
- Headings and section structure
- Bullet lists and numbered lists
- Tables, represented as markdown tables
- Charts and graphics, described in text form where possible
- Key visual elements that are relevant for understanding the pitch
Depending on how you configure the workflow, the markdown can be:
- Stored per page (one markdown block per image), or
- Concatenated into a single markdown document representing the entire pitch deck.
This markdown text becomes the canonical textual representation used in all downstream AI and indexing steps.
5. AI Information Extractor – Derive Key Investment Data
Role: Analyze the markdown transcription and extract structured, investment-focused insights.
An AI information extraction node is configured to behave like an experienced venture capitalist. It receives the full markdown representation of the pitch deck as input and outputs:
- Key company attributes, such as:
- Founding year
- Team size
- Market traction and key metrics
- Funding stage
- Other relevant attributes present in the deck
- A concise but detailed executive summary of the pitch
- Flags, caveats, or fact-check indicators where the model is uncertain or data is missing
The output is structured so it can be mapped directly to Airtable fields. For example, you might have columns such as Founding Year, Team Size, Stage, Traction Summary, and AI Summary.
Edge cases:
- If a specific data point is not present in the deck, the extractor may return an empty value or a clearly marked “unknown” or “not specified” value.
- Ambiguous or conflicting information can be surfaced via fact-check flags or notes so that analysts can review manually.
6. Airtable Node – Update Record With AI-Generated Report
Role: Persist the extracted data and summary back into the original Airtable record.
Using the Airtable record ID from the trigger step, an Airtable node performs an Update operation on the corresponding record. Typical field mappings include:
- Executive summary: The narrative summary generated by the AI extractor
- Founding year: Parsed numeric or text value
- Team size: Numeric or categorical value
- Funding stage: Seed, Series A, etc., based on the deck content
- Traction / metrics: Text or structured fields, depending on your base design
- Flags / notes: Any fact-check or uncertainty indicators
Once this step completes, Airtable effectively becomes a structured, searchable database of your pitch decks, enriched with AI-generated insights.
7. Qdrant Node – Build a Vector Store for Semantic Search
Role: Index the pitch deck content to enable semantic search and question answering.
The markdown transcription produced earlier is now passed into a Qdrant node. The node:
- Embeds the markdown text into vector representations using a configured embedding model
- Writes these vectors into a Qdrant collection
- Links each vector back to the corresponding pitch deck (for example via record ID or company name)
This vector store enables:
- Semantic search across all decks, not limited to keyword matching
- Context retrieval for question answering and AI agents
You can store:
- One vector per page, or
- A single vector per deck, or
- Chunked segments of the markdown for more granular retrieval
The template uses Qdrant to maintain a dedicated collection for pitch decks, which can be queried later by the chatbot or other workflows.
8. AI Agent / Chatbot Node – Pitch Deck Q&A Interface
Role: Provide a conversational interface that allows your team to query any pitch deck in natural language.
Using n8n’s AI Agents, the workflow sets up a chatbot that:
- Accepts user questions about a specific pitch deck or across multiple decks
- Uses the Qdrant collection to retrieve semantically relevant content
- Generates answers grounded in the indexed markdown content
Typical use cases include:
- “What is the company’s business model?”
- “How large is their current customer base?”
- “What are the main risks identified in this deck?”
The chatbot can be exposed to your internal team via an n8n webhook, a UI integration, or other interfaces supported by your n8n setup.
Configuration Notes
Airtable Setup
Before running the template, prepare your Airtable base:
- Duplicate the provided sample Airtable base referenced by the template.
- Ensure the table contains at minimum:
- A Name column for the company or deck name.
- A File column (attachment type) where you upload the pitch deck PDFs.
- Add any additional fields you want to populate, such as:
- Founding Year
- Team Size
- Funding Stage
- Traction
- AI Summary
- Flags / Notes
Configure Airtable credentials in n8n and verify that the workflow can read and update records in the relevant table.
File Handling and Formats
- Upload only PDF pitch decks into the
Filecolumn. Other formats must be converted manually or via a separate workflow before this template runs. - If a record has multiple attachments, ensure you define how the workflow selects the correct file (for example, using the first attachment or a specific naming convention).
External Conversion Service
- Configure the endpoint URL and parameters for Stirling PDF or your chosen PDF-to-image service.
- Validate that the service returns a ZIP archive containing JPEG images for each page.
- Ensure that the ZIP extraction node correctly exposes all pages to the vision model.
For sensitive pitch decks, plan a self-hosted or private deployment of the conversion service to avoid sending documents to a public instance.
AI Model Configuration
- Vision model: Confirm that the model supports image input and returns markdown output. Configure temperature, max tokens, and any instruction prompts to prioritize faithful transcription.
- Information extractor: Provide clear instructions to the model to act as a VC-style analyst and return structured JSON or key-value pairs that map cleanly to Airtable fields.
- Embedding model (for Qdrant): Choose an embedding model that is compatible with Qdrant and suitable for long-form business content.
Error Handling and Edge Cases
While the template focuses on the happy path, you should consider:
- Missing or invalid files: If the Airtable record has no file or a non-PDF file, the workflow should skip processing or log an error.
- Conversion failures: If the PDF-to-image service fails, capture the error and optionally write a status field back to Airtable for manual follow-up.
- AI timeouts or rate limits: For large decks or high throughput, implement retry logic or throttling where necessary.
- Partial data extraction: If some fields cannot be extracted, ensure the workflow does not fail the entire record update. Instead, store what is available and optionally mark missing fields.
How to Use This n8n Template
- Duplicate the sample Airtable base and configure your tables and fields as described above.
- Upload your PDF pitch decks into the File column and set company names in the Name column.
- Import and configure the n8n template, including Airtable credentials, external PDF conversion endpoint, AI model credentials, and Qdrant connection details.
- Trigger the workflow:
- Manually, for initial testing or batch processing, or
- Automatically, by enabling the Airtable trigger to listen for new or updated records.
- Monitor workflow executions in n8n and verify that:
- Airtable records are updated with AI-generated summaries and structured data.
- The Qdrant vector store is populated with entries for each processed pitch deck.
- Use the configured Q&A chatbot to interactively query your pitch decks, test typical investor questions, and refine prompts or settings as needed.
Advanced Customization Ideas
- Additional fields: Extend the information extractor prompt to capture more metrics, such as revenue, growth rate, or sector classification, then map them to new Airtable columns.
- Multi-stage review: Add nodes that route decks to different reviewers based on stage, geography, or sector extracted from the content.
- Alerting: Integrate email or Slack notifications when a new deck is processed or when certain criteria are met (for example, “Series B, ARR > $5M”).
- Versioning: Track multiple versions of a pitch deck by adding a version field and indexing each version separately in Qdrant.