Automate Twitter Sentiment Analysis with n8n Workflow
Why Bother With Twitter Sentiment In The First Place?
If your brand, product, or project lives on the internet, people are probably talking about it on Twitter. Some of those conversations are glowing, some are not so flattering, and some are pure gold for insights. The tricky part is keeping up without spending hours scrolling your feed.
That is where a Twitter Sentiment ETL workflow in n8n comes in. It quietly runs in the background, pulls in tweets, analyzes how people feel about them, saves everything neatly in your databases, and pings you when something important pops up. No manual checking, no copy-pasting, no “I’ll do it later”.
In this guide, we will walk through a ready-made n8n workflow template that automates Twitter sentiment analysis using MongoDB, PostgreSQL, Google Cloud Natural Language, Slack, and email. We will look at what it does, when to use it, and how each step works so you can confidently tweak it for your own needs.
What This n8n Twitter Sentiment Workflow Actually Does
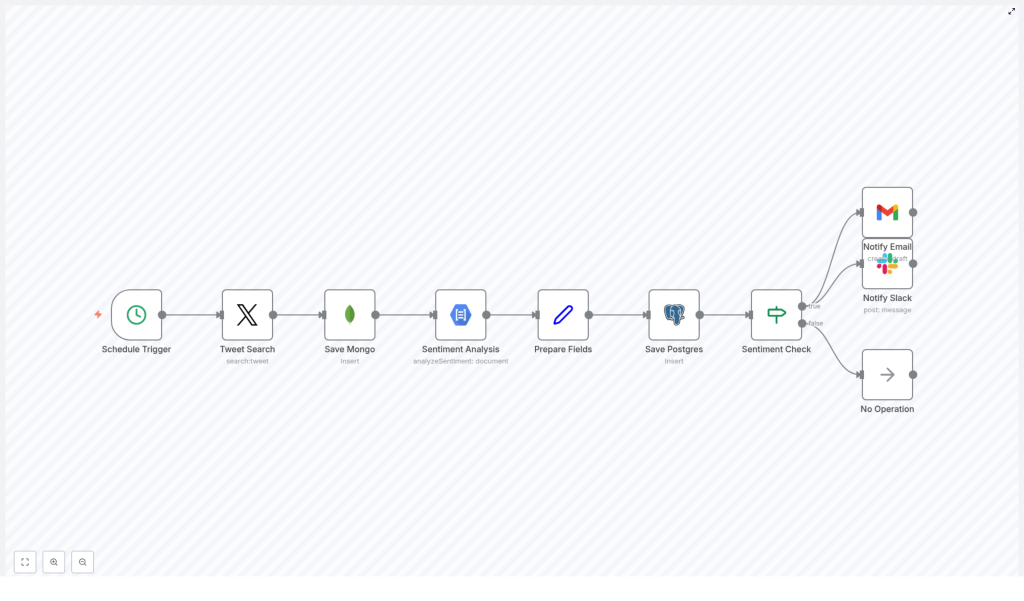
Let us start with the big picture. Once you plug in your credentials and turn it on, this workflow will:
- Run automatically every morning at a scheduled time.
- Search Twitter for recent tweets containing the hashtag
#OnThisDay. - Archive raw tweets in MongoDB for historical reference.
- Analyze tweet sentiment using Google Cloud Natural Language API.
- Prepare clean, structured data ready for reporting and dashboards.
- Store processed sentiment data in PostgreSQL for querying and analysis.
- Check if the sentiment passes a threshold so you only get alerted when it matters.
- Send alerts to Slack and email for tweets with notable sentiment.
- Quietly exit if nothing meets the criteria, so you are not spammed with noise.
In short, it is a neat little ETL pipeline: Extract tweets, Transform them with sentiment analysis, and Load them into databases, with smart notifications on top.
When Should You Use This Workflow?
This template is handy anytime you care about how people feel about something on Twitter and you do not want to monitor it manually. Some great use cases include:
- Brand reputation monitoring – Keep an eye on how people talk about your company or product.
- Event sentiment tracking – Track reactions to conferences, campaigns, or special days using a consistent hashtag.
- Market research – Understand public opinion around topics, competitors, or trends.
- Real-time alerts for PR teams – Get notified quickly when sentiment spikes up or down so you can respond.
Even though the template uses the #OnThisDay hashtag by default, you can easily adapt it to your own brand or campaign hashtags.
Why Use n8n For Twitter Sentiment Analysis?
You could cobble this together with separate scripts, cron jobs, and custom code, but n8n gives you a few big advantages:
- Fully automated and scheduled – Once set up, it runs by itself at the time you choose.
- Visual workflow builder – You can see every step, change nodes, and debug without digging through code.
- Multiple storage options – Use MongoDB for raw archives and PostgreSQL for structured analytics.
- Real-time sentiment insights – Google Cloud Natural Language gives you precise sentiment scores and magnitudes.
- Multi-channel alerts – Notify your team in Slack and via email so no one misses important tweets.
- Easy to extend – Want to add dashboards, other APIs, or extra filters? Just drop in more nodes.
Step-by-Step: How The Workflow Runs
Let us walk through each node in the workflow so you know exactly what is happening under the hood.
1. Schedule Trigger – Start The Day Automatically
The workflow kicks off with a Schedule Trigger node. It is configured to run every day at 6 AM. That means:
- No manual start required.
- Fresh sentiment data every morning.
- A predictable routine you can plan reporting around.
You can easily adjust the time or frequency in the node settings if you prefer a different schedule.
2. Tweet Search Node – Pull In Relevant Tweets
Next up is the Tweet Search node. Using your Twitter OAuth credentials, it searches for tweets that match a specific query. In this template, it looks for tweets containing the hashtag #OnThisDay.
By default, the node:
- Fetches up to 3 recent tweets.
- Filters based on the hashtag
#OnThisDay.
That small limit keeps the workflow lightweight and fast, which is perfect for a daily sentiment sample. If you want more coverage, you can simply bump up the limit in the node configuration.
3. Save Mongo – Archive Raw Tweets In MongoDB
Once the tweets are fetched, the workflow passes them into a MongoDB node, often labeled something like Save Mongo.
Here is what this step does:
- Saves the raw tweet data into a MongoDB collection.
- Creates a historical archive you can go back to later.
- Makes debugging easier if you ever want to see the unprocessed tweets.
Think of MongoDB as your long-term, flexible “just in case” storage for the original tweet payloads.
4. Sentiment Analysis – Use Google Cloud Natural Language
Now comes the fun part. A Google Cloud Natural Language node runs sentiment analysis on each tweet text stored in MongoDB.
This node returns two key metrics for each tweet:
- score – A value between -1.0 and 1.0 that shows how negative or positive the text is.
- magnitude – A value that reflects how strong or intense the sentiment is, regardless of being positive or negative.
So, for example, a tweet with a high positive score and high magnitude is very enthusiastic, while a negative score with high magnitude might signal a serious complaint or frustration.
5. Prepare Fields – Clean Up Data For Storage
After the sentiment analysis is done, the workflow uses a Set node (often named something like Prepare Fields) to organize the data.
This step:
- Extracts the sentiment score and magnitude.
- Grabs the original tweet text.
- Formats everything into a clean structure that is ready to be stored in a relational database.
It is basically the “tidy up” step, making sure the data is consistent and easy to work with later.
6. Save Postgres – Store Processed Data In PostgreSQL
Next, the workflow inserts the prepared data into a PostgreSQL table, typically named tweets.
This table stores at least:
- The tweet text.
- The sentiment score.
- The sentiment magnitude.
Why PostgreSQL? Because it is great for:
- Running advanced SQL queries.
- Building reports and dashboards.
- Joining sentiment data with other business data you might already have in Postgres.
7. Sentiment Check – Decide If An Alert Is Needed
With everything stored, the workflow uses an If node to decide what happens next. This is your simple but powerful filter.
The node checks whether the sentiment score is greater than 0, which means:
- Score > 0 – The tweet is considered positive or at least more positive than negative.
- Score ≤ 0 – The tweet is neutral or negative.
You can adjust this threshold if you want to only alert on strongly positive tweets or even flip the logic to focus on negative sentiment instead.
8. Notify Slack & Email – Alert The Right People
If the sentiment passes the threshold (score > 0 in this template), the workflow branches into two notification paths:
- Slack Notification
- A Slack node posts a message to a channel named
tweets. - The message includes the tweet text and its sentiment score.
- Your team can see positive mentions right in Slack without checking any dashboards.
- A Slack node posts a message to a channel named
- Email Notification
- An Email node sends an alert to
alerts@example.com. - The email contains the tweet details plus the sentiment metrics.
- Perfect for people who prefer email over Slack or for archiving alerts.
- An Email node sends an alert to
9. No Operation – Quietly Finish When Nothing Matches
If the sentiment score does not meet the threshold, the workflow reaches a No Operation node. This node simply ends the run without doing anything else.
The benefit is simple: you are not flooded with alerts for every neutral or negative tweet. Only the tweets that match your criteria trigger Slack or email notifications.
Putting It All Together: A Simple, Powerful ETL Pipeline
So to recap, here is what this n8n Twitter Sentiment ETL workflow gives you out of the box:
- Automated daily schedule so you never forget to check Twitter.
- Integration with Twitter, MongoDB, PostgreSQL, Google Cloud NLP, Slack, and email.
- Raw data archive in MongoDB for historical and debugging purposes.
- Structured sentiment dataset in PostgreSQL for analysis, reporting, and dashboards.
- Smart alerts only when sentiment crosses your defined threshold.
- Flexibility to customize hashtags, thresholds, channels, and schedule as your needs evolve.
Ready To Try It Yourself?
If you have been thinking about automating your social media monitoring, this workflow template is a great place to start. You get a complete, working pipeline that you can adapt to your own hashtags, brands, or events without writing everything from scratch.
Want to see it in action? Load the template in n8n, plug in your credentials, and let it handle the daily sentiment checks for you.