How to Detect and Fix Workflow Connection Issues in n8n
What You Will Learn
In this guide, you will learn how to use a ready-made n8n workflow template to:
- Understand a migration bug that can affect workflows with multiple-output nodes after upgrading to n8n
0.214.3 - Scan all your workflows automatically using the n8n API
- Detect nodes with missing or incorrect output connections
- Include community or third-party nodes in the scan
- Review the results and manually repair broken connections
This article is written as a step-by-step teaching resource. You will first understand the problem, then see how the template works, and finally follow a clear walkthrough to use it safely in your own n8n instance.
1. Understanding the Problem After Upgrading n8n
1.1 When this issue appears
If you recently upgraded your n8n instance to version 0.214.3, some workflows may start behaving in unexpected ways. The problems often appear in workflows that use nodes with more than one output, for example:
IfnodeSwitchnodeCompare Datasetsnode- Any community or custom node that exposes multiple outputs
1.2 What goes wrong
Due to a migration bug in this version, nodes that have multiple outputs can be rewired incorrectly during the upgrade. This can lead to situations where:
- Some outputs are disconnected entirely
- Connections get attached to the wrong output index
- Only part of the expected outputs are still connected
As a result, your workflow logic might be broken, even though the workflow appears to load normally in the editor.
1.3 Why this is risky
The main risk is that these issues are not always obvious at first glance. A workflow might still run, but branches that should execute under certain conditions will never trigger, or data might flow through the wrong branch. This is especially critical for:
- Conditional flows using
IforSwitch - Comparisons or branching based on datasets
- Complex automations that depend on precise routing
2. How the Diagnostic Workflow Template Helps
2.1 Purpose of the template
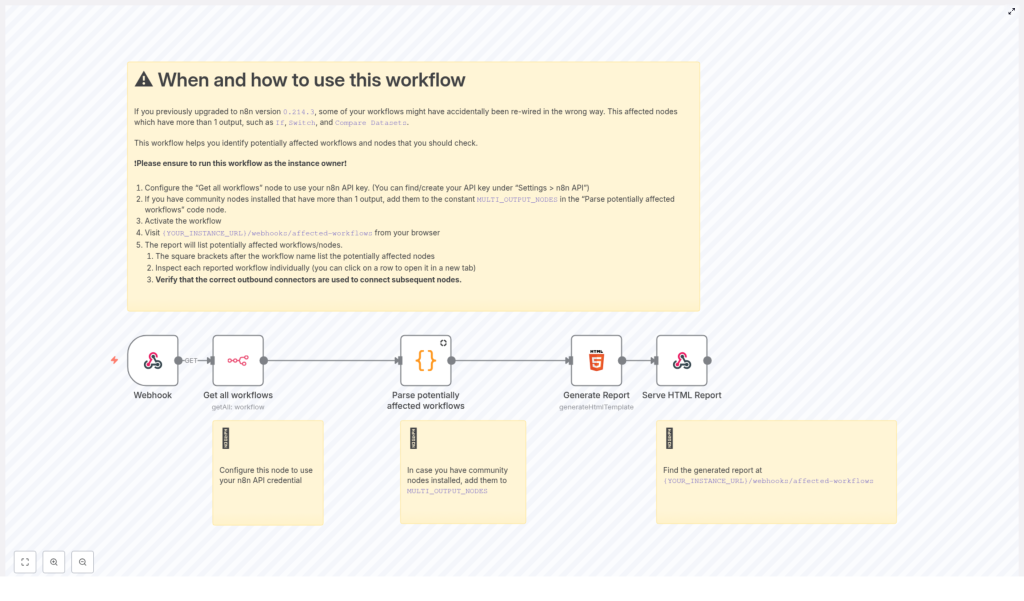
The provided n8n workflow template acts as a diagnostic tool. Its goal is to:
- Scan all workflows in your n8n instance through the n8n API
- Identify workflows that might be affected by the multi-output migration bug
- Highlight specific nodes that appear to have missing or partial output connections
2.2 What the workflow actually does
At a high level, the workflow:
- Calls the n8n API to retrieve a list of all workflows
- Parses each workflow’s JSON definition
- Looks for nodes that are known to have multiple outputs
- Checks whether all expected outputs are connected correctly
- Collects a report of workflows and nodes that look suspicious
The output is a clear list that includes:
- The workflow ID
- The workflow name
- The nodes within that workflow that may have flawed or incomplete output connections
You can then use this report to manually inspect and fix each affected workflow.
3. Key Concepts Before You Start
3.1 Multi-output nodes in n8n
A multi-output node is any node that can send data to more than one path depending on conditions or configuration. For example:
Ifnode – often has outputs for “true” and “false”Switchnode – can have many different outputs, each for a different caseCompare Datasetsnode – may output matched, unmatched, or other comparison results
These nodes rely on correct output indexing. If the order or mapping of outputs is changed during a migration, the logic of your automation can silently break.
3.2 The MULTI_OUTPUT_NODES constant
Inside the template, a Code node named something like Parse potentially affected workflows uses a constant called MULTI_OUTPUT_NODES. This constant is essentially a configuration list where you define:
- The node types that have multiple outputs
- How many outputs each type is expected to have
The built-in n8n nodes with multiple outputs are already handled. If you use community nodes or custom nodes with multiple outputs, you will need to add them here so the workflow can scan them correctly.
3.3 Using the n8n API
The template relies on the n8n API to fetch workflow definitions. To do this securely, it uses an API key configured in a node usually called Get all workflows. You must:
- Enable and configure the n8n API in your instance
- Use an API key with sufficient permissions to read all workflows
- Preferably use instance owner credentials for complete coverage
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Using the Template
Step 1 – Configure n8n API credentials
- Open the diagnostic workflow template in your n8n editor.
- Locate the node named Get all workflows (or similarly named API node).
- In this node, select or create credentials for the n8n API.
- Generate or find your API key by going to:
Settings > n8n API in your n8n instance. - Paste the API key into the credentials configuration for the Get all workflows node.
Make sure that the account associated with this API key has access to all workflows you want to scan. Using the instance owner account is recommended for a complete audit.
Step 2 – Add community or custom nodes to the scan (if needed)
If you only use core n8n nodes, you can usually skip this step. However, if you have installed community or custom nodes that expose multiple outputs, you need to make sure they are included in the check.
- Find the Parse potentially affected workflows
Codenode in the template. - Open the code editor for this node.
- Locate the
MULTI_OUTPUT_NODESconstant in the code. It will look like a list or object that describes node types and their output counts. - Add entries for your community nodes, specifying:
- The internal node type (for example,
n8n-nodes-community.myMultiOutputNode) - The number of outputs that node is expected to have
- The internal node type (for example,
- Save the changes to the node.
This ensures the workflow correctly checks those nodes for missing or miswired outputs.
Step 3 – Activate the diagnostic workflow
- Once your API credentials and optional community node list are set, turn on the workflow like any other n8n workflow.
- Ensure the workflow is saved and the status is set to active.
Activation allows the workflow to respond to its trigger, which in this case is a webhook.
Step 4 – Trigger the scan via webhook
The template uses a webhook trigger so you can manually start the scan whenever you like.
- Identify your n8n instance base URL. For example:
https://your-n8n-instance.comfor a hosted setuphttp://localhost:5678for a local instance
- Open your browser and navigate to:
{YOUR_INSTANCE_URL}/webhooks/affected-workflows
For example:
https://your-n8n-instance.com/webhooks/affected-workflows - This URL call triggers the diagnostic workflow. The workflow will then:
- Fetch all workflows via the n8n API
- Analyze nodes with multiple outputs
- Compile a list of potential issues
Step 5 – Review the generated report
After the scan finishes, the workflow produces a report of potentially affected workflows. Depending on how the template is built, you will typically see:
- A list of workflows that might be impacted by the migration bug
- For each workflow:
- The workflow ID
- The workflow name
- A list of nodes within that workflow that have missing or partial output connections
Use this report as your checklist. Each listed workflow should be opened and inspected in the n8n editor.
Step 6 – Manually verify and repair connections
The diagnostic workflow does not automatically fix your workflows. Instead, it points you to where you need to look.
- Open the n8n editor for each workflow reported as affected.
- Locate the nodes that the report flagged as having problematic outputs.
- Inspect their outgoing connections:
- Confirm that every expected output has the correct connection
- Check that each branch (for example, “true” vs “false”, or each
Switchcase) points to the intended next node - Compare with a previous backup or your original design if available
- Reconnect any outputs that are missing or miswired:
- Drag from the correct output index to the correct target node
- Remove any connections that should not exist
- Save the workflow and run a test to confirm the logic behaves as expected.
5. Best Practices When Using This Template
- Use instance owner credentials: Run the scan with credentials that can access all workflows in your instance. This ensures you do not miss any affected automations.
- Perform manual verification: The diagnostic report highlights potential issues, but you should still manually confirm and fix each node in the editor. Do not assume every flagged node is broken, but treat it as a strong hint.
- Keep the workflow for future audits: Store this workflow in your instance and reuse it:
- After upgrading n8n in the future
- After installing or updating community nodes with multiple outputs
- As part of your regular workflow health checks
- Maintain backups: Whenever possible, keep exports or backups of critical workflows before major upgrades so you can compare structures if something looks wrong.
6. Quick Recap
- Upgrading to n8n
0.214.3can introduce a migration bug that affects nodes with multiple outputs likeIf,Switch, andCompare Datasets. - The bug can disconnect or miswire outputs, which silently breaks workflow logic.
- The provided diagnostic workflow template:
- Uses the n8n API to fetch all workflows
- Scans for multi-output nodes with missing or partial connections
- Produces a report listing affected workflows and nodes
- You configure:
- API credentials in the Get all workflows node
- Optional community node types in the
MULTI_OUTPUT_NODESconstant
- You trigger the scan by visiting
{YOUR_INSTANCE_URL}/webhooks/affected-workflows. - You then manually inspect each flagged workflow in the editor and repair any broken connections.
7. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Do I need to run this workflow if I have not upgraded to 0.214.3?
The workflow is primarily designed to address issues introduced by the migration bug in 0.214.3. However, it can also be useful as a general audit tool to verify that multi-output nodes are wired correctly, especially after any major upgrade.
Can this workflow automatically fix broken connections?
No. The template is intentionally designed as a diagnostic tool only. It identifies suspicious nodes and workflows, but you must manually confirm and reconnect outputs in the n8n editor. This avoids accidentally changing workflows that are already correct.
What happens if I do not add my community nodes to MULTI_OUTPUT_NODES?
If you skip this step, the diagnostic workflow will not check those community nodes for missing or partial connections. They may still be affected by the migration bug, but they will not appear in your report. For accurate results, always add multi-output community nodes to the MULTI_OUTPUT_NODES constant.
Is it safe to run this workflow on a production instance?
Yes. The workflow only reads workflow definitions using the n8n API and does not modify them. It is safe to run in production environments. Still, any changes you make afterward when fixing workflows should be tested carefully.
How often should I run this diagnostic?
At minimum, run it immediately after upgrading to version 0.214.3 or any later version where you suspect similar migration changes. You can also schedule periodic checks as part of your maintenance routine, especially in critical automation environments.
Take Action: Protect Your n8n Automations
Do not wait for broken logic to cause data issues or missed automations. Set up and run this diagnostic workflow to scan your n8n instance, identify affected multi-output nodes, and fix any problems before they impact your operations.
Keep the workflow available for future upgrades so you can quickly verify that all outputs are intact and your automations remain reliable.