AI Agent Chatbot with Jina.ai Web Scraper: Turn Live Web Data into Action
Imagine a chatbot that never goes out of date, that reads the web for you in real time, and that remembers what you talked about last time. With n8n, Jina.ai’s web scraper, and a language model, you can build exactly that. This guide shows you how to turn a simple idea into a powerful, automated AI agent that pulls fresh answers from live web pages and frees you to focus on higher-value work.
The problem: static information in a fast-moving world
Most chatbots are built on static knowledge. They are trained once, updated occasionally, and slowly drift out of sync with reality. Documentation changes, pricing pages get updated, competitors ship new features, and your chatbot keeps answering based on yesterday’s information.
If you are supporting customers, doing research, or tracking competitors, this lag can cost you time, money, and trust. You end up manually checking pages, copying content, summarizing it, and sending it on. It is repetitive, it is fragile, and it pulls you away from the work that truly moves your business forward.
From limitation to possibility: adopting an automation mindset
Instead of accepting manual lookups as “just part of the job,” you can turn them into an automated, repeatable workflow. With n8n, you do not need to be a full-time developer to build something powerful. You can:
- Let an AI agent fetch and read web pages for you
- Summarize and transform the content into clear, actionable answers
- Preserve conversation context so follow-up questions feel natural
- Scale from one use case to many without starting from scratch each time
Think of this workflow as a stepping stone. You start with a single chatbot that reads one documentation page, then you expand it to multiple sites, then to new teams and new processes. Each improvement compounds the time you save and the value you deliver.
The n8n template: your shortcut to a smarter AI agent
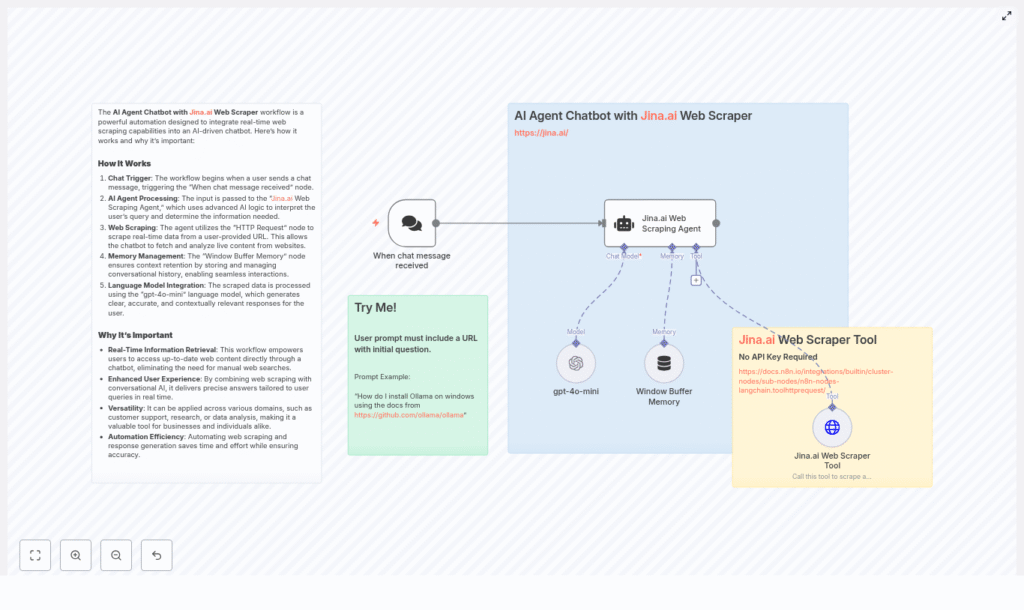
To help you move from idea to reality quickly, this n8n workflow template combines conversational AI, Jina.ai’s web scraper, and memory management into one practical, ready-to-adapt flow. You can plug it into your stack, experiment, and then customize it as your needs grow.
At a high level, the template connects:
- A chat entry point where users submit questions and URLs
- An AI agent that orchestrates tools, memory, and a language model
- The Jina.ai web scraper to pull readable text from live pages
- A language model like gpt-4o-mini to generate context-aware answers
- Window Buffer Memory to keep multi-turn conversations coherent
Let’s walk through each piece so you understand how it works and how you can extend it.
Key building blocks of the workflow
1. Chat Trigger: where the conversation begins
The journey starts with the Chat Trigger node. This node listens for incoming user messages and passes them into the workflow. The user message should contain both a URL and a question, for example:
“How do I install Ollama on Windows using the docs from https://github.com/ollama/ollama?”
As soon as the Chat Trigger receives this prompt, the automation kicks in. No manual copy-paste, no switching between tabs. The workflow takes over from here.
2. AI Agent: the Jina.ai Web Scraping Agent as conductor
The AI Agent node is the brain of the operation. In this template, it acts as a Jina.ai Web Scraping Agent that:
- Extracts the URL from the user’s message
- Decides which web pages to fetch
- Calls the Jina.ai web scraper tool
- Combines scraped content with the user’s question and conversation history
- Hands the processed input to the language model
Agents in n8n let you bundle tools, memory, and a language model into one intelligent unit. This is where your workflow starts to feel less like a static script and more like a responsive assistant.
3. Jina.ai Web Scraper Tool (HTTP Request): clean text from live pages
To turn web pages into something an AI model can understand, you need structured, readable text. That is where the Jina.ai web scraper comes in.
In n8n, you configure an HTTP Request node that uses a URL template such as:
https://r.jina.ai/{url}With this pattern, you do not need an API key for many setups. The scraper endpoint returns the text content of the page, often already simplified or summarized, which makes it ideal for feeding into a language model.
4. Language model integration with gpt-4o-mini
Once the scraper has done its work, the content flows back to the agent and then into a language model like gpt-4o-mini. At this stage the model can:
- Summarize long documentation pages
- Extract step-by-step instructions
- Highlight prerequisites or common pitfalls
- Transform raw text into a concise, user-friendly answer
Instead of your users reading through entire pages, the model delivers exactly what they asked for, grounded in the latest version of the source.
5. Window Buffer Memory: keeping the conversation flowing
Real conversations are rarely one-and-done. Users ask follow-up questions, refine their requests, or need clarification. Window Buffer Memory keeps recent messages in scope so the agent understands context across multiple turns.
By storing only the most relevant recent exchanges, you keep the chatbot responsive and coherent without overwhelming the model with unnecessary history.
How the workflow runs: from question to real-time answer
Here is how all the pieces come together in n8n when a user interacts with your AI agent chatbot:
- The user sends a prompt that includes both a URL and a question.
- The Chat Trigger node activates and forwards the message to the Jina.ai Web Scraping Agent.
- The agent identifies the URL in the prompt and calls the Jina.ai Web Scraper Tool via an HTTP request to the scraper endpoint.
- The scraper returns clean text from the target page. The agent blends this content with the user’s question and any relevant memory.
- The combined input is sent to the language model (for example, gpt-4o-mini), which generates an accurate, concise response.
- The chatbot returns the answer to the user, and Window Buffer Memory is updated so that follow-up questions stay in context.
Once this is in place, you are no longer manually hunting for answers on the web. The workflow does it for you, consistently and at scale.
Designing for reliability: best practices that pay off
As you refine and expand this template, a few design habits will help you build something robust enough for real-world use.
Validate and sanitize user-provided URLs
Always check that the URL a user submits is valid and allowed. Consider:
- Ensuring the URL is well-formed
- Restricting scraping to a whitelist of trusted domains
- Applying rate limits to avoid abuse or accidental overload
Respect robots.txt and terms of service
Even though Jina.ai simplifies scraping, it is your responsibility to respect each site’s policies. Review:
robots.txtdirectives- Terms of service for the sites you plan to scrape
- Any limits on frequency or volume of requests
Keeping this in mind from the start helps you scale responsibly.
Keep responses focused and manageable
Long pages can easily turn into long answers. To keep your chatbot helpful and efficient:
- Ask the model to answer only the specific question
- Summarize lengthy content into actionable steps or bullet points
- Limit output length to control token usage and maintain clarity
Use memory strategically
Window Buffer Memory works best when it stores what is truly needed. Instead of keeping entire documents in memory, store:
- Short summaries
- Relevant metadata
- Pointers back to the source URL
This keeps your workflow efficient while still preserving context for meaningful conversations.
Seeing it in action: a concrete example
To make this feel more tangible, here is a simple scenario you can test as soon as your workflow is running.
Example prompt
How do I install Ollama on Windows using the docs from https://github.com/ollama/ollama?
What the agent should do
- Detect the GitHub URL in the user’s message and send it to the Jina.ai scraper.
- Pull back the relevant installation instructions from the page.
- Generate a concise, step-by-step Windows installation guide.
- Highlight any prerequisites and common pitfalls.
- Include a link back to the original documentation for deeper reading.
This is the kind of repetitive task that automation excels at. Once you see it working for one page, it becomes easy to imagine how many similar tasks you can offload.
Security and privacy: building trust into your automation
As you scale an AI agent that reads the web and interacts with users, security and privacy are essential. Treat scraped data and user inputs with care:
- Avoid collecting or exposing sensitive or personally identifiable information (PII).
- Redact sensitive content where necessary.
- Maintain logs for auditing, but ensure they are access-controlled and protected.
- If you scrape authenticated or internal pages, manage credentials securely and follow your organization’s security policies.
Thoughtful safeguards help your automation become a trusted part of your workflow rather than a risk.
Where this template can take you: real-world use cases
Once you have this n8n template running, it becomes a flexible platform you can adapt to many scenarios.
Customer support that scales with your product
Connect your chatbot to product docs, support articles, or knowledge base pages. The agent can:
- Fetch the latest documentation in real time
- Offer tailored troubleshooting steps
- Reduce the number of tickets that require human intervention
Research assistants for teams and individuals
Researchers and knowledge workers can point the agent at:
- Academic articles or technical documentation
- GitHub READMEs and project pages
- Long-form blog posts and reports
The chatbot can summarize key findings, extract citations, and surface the details that matter, all from live web content.
Competitive monitoring and market awareness
Use the same template to stay informed about your market by:
- Scraping competitor product pages and release notes
- Tracking pricing changes or feature updates
- Delivering concise summaries directly to stakeholders
Instead of manually checking sites, you can have an automated AI layer that keeps you up to date.
Practical implementation tips for n8n
As you adapt this template, a few technical details will help you get the most out of it:
- Use the built-in toolHttpRequest node and configure it to call the Jina.ai endpoint:
https://r.jina.ai/{url} - Create an agent node that:
- Receives input from the Chat Trigger
- Attaches the Jina.ai scraper tool
- Uses Window Buffer Memory
- Connects to a language model such as gpt-4o-mini
- Add pre-processing steps to clean or normalize scraped text.
- Add post-processing to limit tokens, enforce concise outputs, and format answers clearly.
- Test with different site types like docs, blogs, and GitHub READMEs so you can fine-tune scraping and summarization behavior.
Each iteration you run in n8n will make the workflow more aligned with your specific needs and your users’ expectations.
Pros and cons: knowing your toolset
Advantages of this approach
- Access to live, up-to-date information directly from web pages.
- Automation of repetitive research and support tasks.
- No API key required for the Jina.ai scraper endpoint in many configurations.
- A flexible n8n template that you can extend and adapt over time.
Trade-offs and considerations
- Legal and ethical constraints around web scraping must be respected.
- Page layouts and structures can change, which may require adjustments.
- Production setups need careful rate limiting, error handling, and monitoring.
Understanding these trade-offs helps you design a solution that is both powerful and responsible.
Bringing it all together: your next step in automation
By combining Jina.ai’s web scraper, a capable language model, and memory in an n8n workflow, you create more than a chatbot. You build an AI agent that can read the web for you, answer with context, and grow alongside your business and your ideas.
Start small. Connect a Chat Trigger node, an agent that uses the Jina.ai Web Scraper Tool, Window Buffer Memory, and a model like gpt-4o-mini. Limit it to a handful of whitelisted domains. Watch how much time you reclaim when routine questions answer themselves.
Then, iterate. Add new sources, refine prompts, and experiment with different memory strategies. Each improvement is an investment in a more focused, automated workflow where your energy goes into strategy and creativity, not repetitive lookup tasks.
Ready to build your own AI agent chatbot? Deploy this workflow in n8n and test it with a documentation URL today. If you want a step-by-step template or a sample n8n workflow file, reach out to the team or download the starter flow from the project repository, and use it as the foundation for your own automation journey.