Complete Guide to WA-SellFlow Booking Calendar Bot
1. Overview
The WA-SellFlow Booking Calendar bot is an n8n workflow template that automates appointment scheduling over WhatsApp. It combines WhatsApp message handling, database-driven state management, and Google Calendar integration to provide a guided booking experience for end users.
This guide explains the workflow in a technical, reference-style format, focusing on node behavior, control flow, and configuration details. It is intended for users who already understand n8n concepts such as triggers, nodes, credentials, and data mapping.
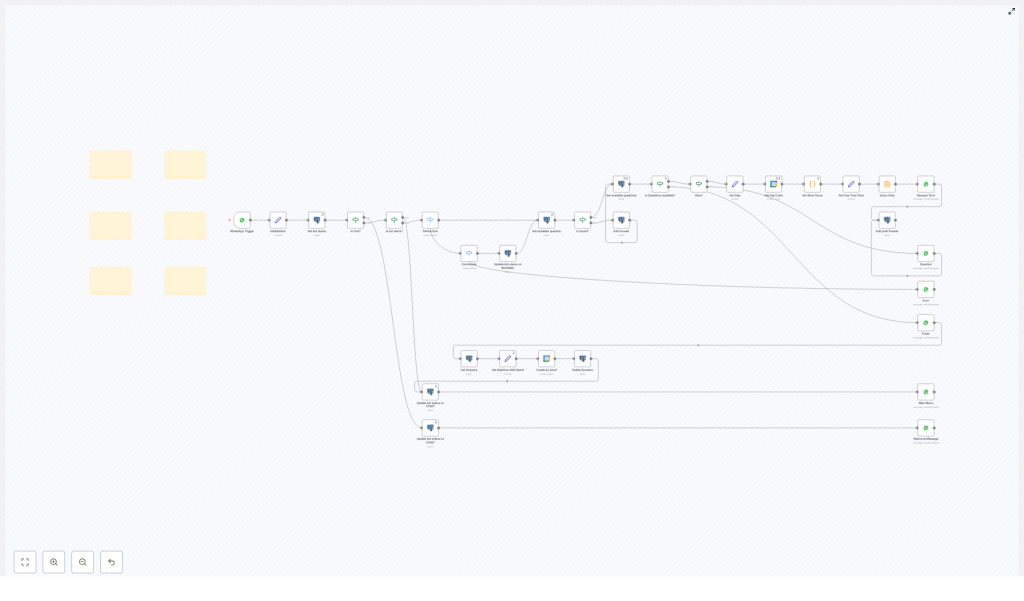
2. High-Level Architecture
At a high level, the WA-SellFlow Booking Calendar bot workflow consists of:
- WhatsApp Trigger – Starts the workflow whenever a WhatsApp message is received.
- Initialization & Status Management – Reads and writes the bot status in a database to track conversation state.
- Flow Definition Logic – Determines the next path based on the current status and user input (booking vs other commands).
- Booking Question Engine – Fetches booking questions from a database and validates user responses.
- Date & Slot Handling – Validates dates, queries Google Calendar, applies work hours, and computes available slots.
- Event Creation & Cleanup – Creates the final Google Calendar event, then clears temporary data and resets the bot status.
- Messaging Layer – Multiple WhatsApp nodes for sending welcome, menu, question, error, and completion messages.
3. Trigger and Initial Flow
3.1 WhatsApp Trigger Node
The workflow begins with a WhatsApp Trigger node. This node listens for incoming WhatsApp messages and exposes the message payload to downstream nodes. Typical data includes:
- Sender identifier (phone number or contact ID)
- Message text content
- Timestamp and metadata
The sender identifier is used as the conversation key for retrieving and updating the bot status in the database.
3.2 Initialization and Base Data
Immediately after the trigger, the workflow runs initialization logic. This typically includes:
- Normalizing the incoming message text (for example trimming, lowercasing).
- Extracting the user identifier to use as a primary key in database queries.
- Preparing any default variables that will be used in later nodes (for example default status values or flags).
3.3 Bot Status Retrieval
The Get bot status node queries the database to retrieve the current conversation state associated with the user. This status is central to how the workflow decides which branch to follow.
The status might be stored in a dedicated table with fields such as:
- User or chat ID
- Current bot status (for example
START,BOOKING, or other custom states) - Additional metadata (last question index, timestamps, etc., if implemented in your database schema)
3.4 New Session vs Existing Session
An Is First? conditional node evaluates the result from Get bot status to determine if the user is starting a new conversation or resuming an existing one:
- New session – No existing status found for the user, or status indicates a fresh start.
- Ongoing session – Status exists and indicates the user is mid-flow (for example in a booking conversation).
4. Session Handling and Status Updates
4.1 New Session Handling
If the Is First? node indicates a new session:
- The workflow updates the bot status in the database to START.
- A WhatsApp node sends a Welcome Message, introducing the bot and presenting initial options or instructions.
At this point, the user is presented with the main menu or command options that will be interpreted in subsequent messages.
4.2 Ongoing Session Handling
If the conversation is not new, the workflow does not reset the status to START. Instead, it:
- Continues with the core dialogue logic based on the existing status.
- May present a menu, a follow-up question, or other context-aware responses depending on how the template is configured.
This design allows the bot to continue a multi-step booking process across multiple messages.
5. Flow Definition and Command Routing
5.1 Define Flow Switch Node
The Define flow switch node evaluates the user input and current status to route execution to one of the main branches:
- Booking Command Flow
- Other Commands Flow
Typical criteria for the switch include:
- Specific keywords or commands in the message, such as “book”, “appointment”, or menu options.
- The existing bot status, for example if status is already
BOOKING, the workflow continues the booking sequence even if the user does not repeat the booking keyword.
5.2 Booking Command Flow
When the user initiates or continues a booking:
- The bot status is updated to BOOKING in the database.
- The workflow transitions into the Booking Flow, which handles:
- Fetching booking questions
- Validating user responses
- Calculating available time slots
- Creating a calendar event
5.3 Other Commands Flow
For non-booking intents, the same Define flow switch node routes the execution to alternative branches. These branches can:
- Send different menus or informational messages via WhatsApp nodes.
- Return error responses if the command is not recognized.
- Optionally reset or adjust the bot status depending on the template configuration.
This separation keeps the booking logic isolated from other conversational features.
6. Booking Flow Logic
6.1 Retrieving Booking Questions
The booking flow starts by querying the database for configured booking questions using a node typically named Get available question. This node:
- Filters questions based on the current user, service, or bot configuration.
- Returns a list of questions that the bot should ask to complete a booking.
6.2 Verifying Question Availability
The Is found? conditional node checks whether any booking questions were returned from the database:
- Questions found – The workflow proceeds to the question-asking sequence.
- No questions found – The workflow can send an error or fallback message, informing the user that booking is unavailable or misconfigured.
6.3 Iterative Question Handling
Once questions are available, the workflow:
- Uses WhatsApp nodes to send each booking question to the user.
- Receives the user’s response via subsequent WhatsApp Trigger invocations.
- Stores each answer in the database through dedicated insert or update nodes.
A conditional node such as Is Questions available? is used to determine:
- Whether there are still unanswered questions.
- When to move from the question-collection phase to the date and slot validation phase.
6.4 Date Validation
For date-related questions, the workflow uses a conditional node often labeled Date? to validate the user’s input:
- Checks that the input can be parsed as a valid date.
- Ensures the date meets any basic criteria, such as not being in the past, if configured.
If the date is invalid, the workflow:
- Can send an error or clarification message via a WhatsApp node.
- Prompts the user to re-enter a valid date.
6.5 Working with Google Calendar
Once a valid date is confirmed, the workflow integrates with Google Calendar to identify free booking slots.
6.5.1 Fetching Day Events
A Google Calendar node is configured to fetch events for the selected day:
- Uses authenticated Google Calendar credentials.
- Reads all events for the requested date or date range.
- Returns existing busy periods that must be excluded from booking slots.
6.5.2 Setting Work Hours
The workflow then applies predefined work hours. This usually involves:
- Defining the start and end of the working day for bookings.
- Optionally specifying slot duration (for example 30 minutes, 1 hour) if implemented in the template.
6.5.3 Computing Available Slots
Using the list of existing events and the configured work hours, the workflow:
- Calculates time ranges that are not occupied by existing Google Calendar events.
- Merges and formats these into user-friendly time slots.
- Prepares the slots for presentation via WhatsApp messages.
These available slots are then sent to the user so they can choose a specific time for the appointment.
7. Completing the Booking
7.1 Final Data Assembly
After all required questions have been answered and a time slot is selected, the workflow consolidates the data:
- Combines the chosen date and time into a single datetime value.
- Retrieves the user’s name or other identifying details from previous answers.
- Ensures that all mandatory fields for a calendar event are available.
7.2 Creating the Google Calendar Event
A Google Calendar node is then used to create a new event:
- Uses the computed datetime for the event start and end times.
- Sets the event title, description, and any other configured fields based on user responses.
- Writes the event to the configured Google Calendar using the authenticated credentials.
If the event creation fails (for example due to credential issues or invalid data), the workflow can be extended to:
- Send an error notification to the user via WhatsApp.
- Log the error using an additional node or internal documentation.
7.3 Cleanup and Status Reset
After a successful event creation, the workflow performs cleanup tasks:
- Deletes or clears temporary answers from the database to avoid stale data.
- Resets the bot status to an appropriate value, for example back to
STARTor an idle state, so the user can start a new booking later. - Sends a final WhatsApp message confirming the booking and summarizing the appointment details.
8. Messaging, Database, and Utility Nodes
8.1 WhatsApp Messaging Nodes
The workflow uses multiple WhatsApp nodes for different communication types:
- Welcome messages – Sent at the beginning of a new session.
- Menu messages – Present options such as booking or other commands.
- Question messages – Ask for user details required for the booking process.
- Error messages – Inform users about invalid input, unavailable slots, or unexpected issues.
- Finish messages – Confirm successful booking and provide final details.
Each WhatsApp node is configured with:
- The target phone number or chat ID from the trigger data.
- Message templates or dynamic text built from workflow variables and database fields.
8.2 Database Operations
Database nodes handle all persistent state and user data:
- Get bot status – Reads the current conversation status.
- Update status – Sets the status to values like
STARTorBOOKING. - Insert / update answers – Stores user responses to booking questions.
- Delete / cleanup answers – Removes temporary data after booking completion.
Careful configuration of table names, fields, and query conditions is required so that each user’s data is isolated and correctly associated with their WhatsApp identifier.
8.3 Sticky Notes for Documentation
The template also includes Sticky notes within the n8n canvas. These are not executed as part of the workflow but are used to:
- Document logic segments.
- Explain decision points and data handling.
- Provide implementation notes for future maintainers.
9. Configuration Notes
9.1 Credentials
- WhatsApp – Ensure your WhatsApp provider or gateway is correctly configured in n8n so the WhatsApp Trigger and send-message nodes operate reliably.
- Google Calendar – Configure Google credentials with permission to read events and create new events on the target calendar.
- Database – Set up credentials for your database (for example MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc.), and verify that the tables used for statuses and answers exist and match the queries defined in the nodes.
9.2 Data Model Considerations
To avoid conflicts and maintain consistent state:
- Use a unique key per user or chat (typically the WhatsApp phone number).
- Ensure that status and answer records are either updated in place or versioned in a predictable way.
- Validate that the date and time formats stored match what the Google Calendar node expects.
9.3 Error Handling Basics
Although the template focuses on the happy path, you can extend it to handle:
- Missing or misconfigured database tables or queries.
- Credential or network errors when calling Google Calendar.
- Unexpected or malformed user input that cannot be parsed as a date or command.
In each case, an additional WhatsApp message node can be used to notify the user that something went wrong and optionally provide a way to restart the process.
10. Advanced Customization Ideas
The WA-SellFlow Booking Calendar bot template provides a solid base for WhatsApp booking automation. You can further customize it by:
- Adding more granular booking questions in the database, such as service type or staff member.
- Implementing different booking flows based on user type, language, or selected service.
- Adjusting work hours or slot duration logic to match your business rules.
- Enhancing logging and monitoring with additional nodes to track errors and usage.
11. Conclusion
The WA-SellFlow Booking Calendar bot shows how n8n can combine WhatsApp messaging, database-driven state, and Google Calendar APIs to deliver a complete, automated appointment scheduling experience. By using structured status management, conditional routing, and dynamic question handling, it keeps the booking flow clear and consistent for users.
If you are looking to improve customer interaction and reduce manual work around appointment scheduling, integrating this n8n workflow into your stack can significantly streamline your booking operations.
Ready to automate your appointment bookings?