AI-Powered RAG Chatbot with Qdrant & Google Drive
This guide explains how to implement a production-grade Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) chatbot using n8n as the automation orchestrator, Qdrant as the vector database, Google Drive as the primary content source, and a modern large language model such as Google Gemini or OpenAI. It covers the system architecture, key workflow components, integration details, and operational safeguards including human-in-the-loop controls.
Why Implement a RAG Chatbot on n8n?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation combines a language model with a vector-based retrieval layer so that responses are grounded in your organization’s documents rather than relying solely on the model’s internal training data. In practice, this:
- Reduces hallucinations and unsupported claims
- Improves factual accuracy and consistency
- Enables secure access to private knowledge stored in Google Drive or other repositories
- Provides an auditable link between answers and source documents
n8n adds a crucial orchestration layer on top of these capabilities. It coordinates ingestion, preprocessing, embedding, storage, retrieval, and human approvals in a single, maintainable workflow that can be adapted to enterprise requirements.
Solution Architecture Overview
At a high level, the RAG chatbot consists of a data ingestion pipeline, a vector storage layer, and a conversational interface. n8n connects all components into a cohesive automation:
- Google Drive – Primary source of documents to ingest, index, and query.
- n8n – Workflow engine that handles document retrieval, text extraction, chunking, metadata enrichment, embedding generation, vector upserts, and chat orchestration.
- Embeddings model (for example, OpenAI text-embedding-3-large or equivalent) – Converts text chunks into numerical vectors for semantic search.
- Qdrant – High-performance vector database that stores embeddings and associated metadata for similarity search and filtered retrieval.
- LLM (Google Gemini or OpenAI) – Produces natural language responses using both the user query and retrieved context from Qdrant.
- Telegram (optional) – Human-in-the-loop channel for critical actions such as vector deletion approvals.
Preparing the Environment
Before building the workflow, configure all required credentials and environment variables in n8n. This ensures secure and repeatable automation.
Required Integrations and Credentials
- Google Drive API credentials for listing and downloading files
- Embeddings provider API key (for example, OpenAI text-embedding-3-large)
- Qdrant endpoint URL and API key, if using a managed or remote deployment
- LLM credentials for Gemini or OpenAI, depending on your chosen model
- Telegram bot token and chat ID for sending approval and notification messages
Configure these as n8n credentials or environment variables rather than hardcoding them inside nodes. This aligns with security best practices and simplifies deployment across environments.
Data Ingestion and Indexing Pipeline
The first part of the workflow focuses on ingesting documents from Google Drive, preparing them for semantic search, and storing them in Qdrant with rich metadata.
1. Retrieve Documents from Google Drive
Use n8n’s Google Drive nodes to identify and download the documents that should be included in the chatbot’s knowledge base:
- Start from a configured Google Folder ID.
- List or search for file IDs within that folder using the appropriate Google Drive node.
- Loop over the returned file IDs to process each document individually.
- Download each file and extract its textual content using a text extraction step or node that matches the file type.
2. Split Text into Semantically Coherent Chunks
Large documents are not indexed as a single block. Instead, they are divided into smaller chunks to improve retrieval quality and fit within LLM context limits. In n8n:
- Use a token-based splitter node to segment content into chunks, typically in the range of 1,000 to 3,000 tokens.
- Preserve semantic coherence so that each chunk represents a meaningful section, not an arbitrary cut.
- Track the chunk index for each document to support better debugging and auditing later.
3. Enrich Chunks with Metadata
Metadata is critical for precise filtering and for understanding what the model is retrieving. An information extraction step can be used to generate structured metadata for each chunk or document, such as:
- Overarching theme or document summary
- Recurring topics and key concepts
- User or customer pain points identified in the content
- Analytical insights or conclusions
- Keyword list or tags
Alongside these derived attributes, also retain technical metadata such as:
file_idfrom Google Drive- Document title or name
- Source URL or folder reference
- Chunk index
- Author or owner, if relevant
This metadata is stored in Qdrant together with the embeddings and is later used for filtering queries by document, theme, or other criteria.
4. Generate Embeddings and Upsert into Qdrant
After chunking and metadata enrichment, the next step is to convert each chunk into a vector representation and store it in Qdrant:
- Call your selected embeddings model, for example OpenAI text-embedding-3-large, for each text chunk.
- Batch requests where possible to optimize performance and cost.
- Upsert the resulting vectors into a Qdrant collection, including all associated metadata such as
file_id, title, keywords, and extracted attributes.
Properly structured upserts enable efficient similarity search combined with metadata filters, which is essential for high-quality RAG responses.
RAG Chat Flow and User Interaction
Once the index is populated, the second part of the workflow handles incoming user queries and generates responses using the RAG pattern.
5. Chat Trigger and Query Handling
Configure a chat or API trigger in n8n to receive user questions from your chosen interface. This could be a web front end, a messaging platform, or a custom integration. The trigger passes the user query into the RAG agent flow.
6. Retrieval from Qdrant
The RAG agent performs a semantic search in Qdrant:
- Run a similarity search using the query embedding against the Qdrant collection.
- Retrieve the top-k most relevant chunks, where k can be tuned based on quality and performance requirements.
- Optionally apply metadata filters, for example:
- Restricting results to a specific
file_idor folder - Filtering by theme, author, or label
- Limiting to certain document types
- Restricting results to a specific
7. Context Assembly and LLM Prompting
The retrieved chunks are then prepared as context for the LLM:
- Trim or prioritize chunks so that the assembled context fits within the LLM’s token window.
- Format the context in a structured prompt, clearly separating system instructions, context, and the user query.
- Invoke the LLM (Gemini or OpenAI) with the compiled prompt and context.
The model responds with an answer that is grounded in the supplied documents. This response is then returned to the user via the original channel.
8. Persisting Chat History
For auditing, compliance, or support workflows, it is often useful to log interactions:
- Store the user query, selected context snippets, and model response in Google Docs or another storage system.
- Maintain a clear association between answers and source documents for traceability.
This historical data can also inform future improvements to chunking, metadata strategies, or retrieval parameters.
Safe Deletion and Human-in-the-Loop Controls
Vector deletion in a production environment is irreversible. To avoid accidental data loss, the workflow incorporates a human-in-the-loop approval process using Telegram.
Controlled Deletion Workflow
- Identify the
file_idvalues that should be removed from the index. - Summarize the affected files into a human-readable message, including key identifiers and counts.
- Send a confirmation request via Telegram to designated operators, optionally requiring double approval.
- On approval, execute a deletion step that queries Qdrant for points matching
metadata.file_idand deletes them. - Log the deletion results and notify operators of success or failure.
This human-in-the-loop pattern significantly reduces the risk of unintended bulk deletions and ensures an auditable trail of destructive operations.
Best Practices for a Robust RAG Implementation
Metadata and Filtering Strategy
Consistent, rich metadata is one of the most important factors in achieving high-quality retrieval:
- Always store identifiers such as
file_id, source URL, and chunk index. - Include descriptive labels like themes, topics, and keywords.
- Use metadata filters in Qdrant queries to narrow the search space and improve relevance.
Chunking Configuration
Chunk size directly affects both retrieval granularity and context utilization:
- Align chunk size with your LLM’s context window to avoid unnecessary truncation.
- Prefer token-based splitting over character-based splitting for more consistent semantics.
- Experiment with different sizes within the 1,000 to 3,000 token range depending on document structure.
Embedding Model Selection
The quality of your embeddings determines how well similar content is grouped:
- Start with a strong general-purpose model such as text-embedding-3-large.
- Evaluate cost versus accuracy for your specific corpus and query patterns.
- Monitor retrieval quality and adjust model choice if you encounter systematic relevance issues.
Security and Access Control
A production RAG system typically handles sensitive or proprietary content. Follow strict security controls:
- Protect API keys using n8n’s credential store and avoid exposing them in workflow code.
- Restrict network access to the Qdrant instance and enforce authentication on all requests.
- Encrypt sensitive metadata at rest where required by policy or regulation.
- Apply least-privilege principles for service accounts that access Google Drive and other systems.
Monitoring, Logging, and Auditing
Observability is essential for maintaining performance and compliance:
- Log all upsert and delete operations in Qdrant.
- Track retrieval requests, including filters and top-k parameters.
- Monitor index growth, search latency, and error rates.
- Ensure each returned result can be traced back to its original source file and chunk.
Troubleshooting and Optimization Tips
- Low relevance of answers – Increase the top-k parameter, adjust chunk size, refine metadata quality, or tighten filters to focus on more relevant document subsets.
- High embedding or inference costs – Batch embedding calls, avoid re-indexing unchanged documents, and consider a more cost-efficient model where acceptable.
- Token limit or context window errors – Reduce context length, prioritize the most relevant chunks, or condense retrieved passages before calling the LLM.
- Deletion failures – Verify that metadata keys and data types align with the Qdrant collection schema, and confirm network connectivity and API permissions.
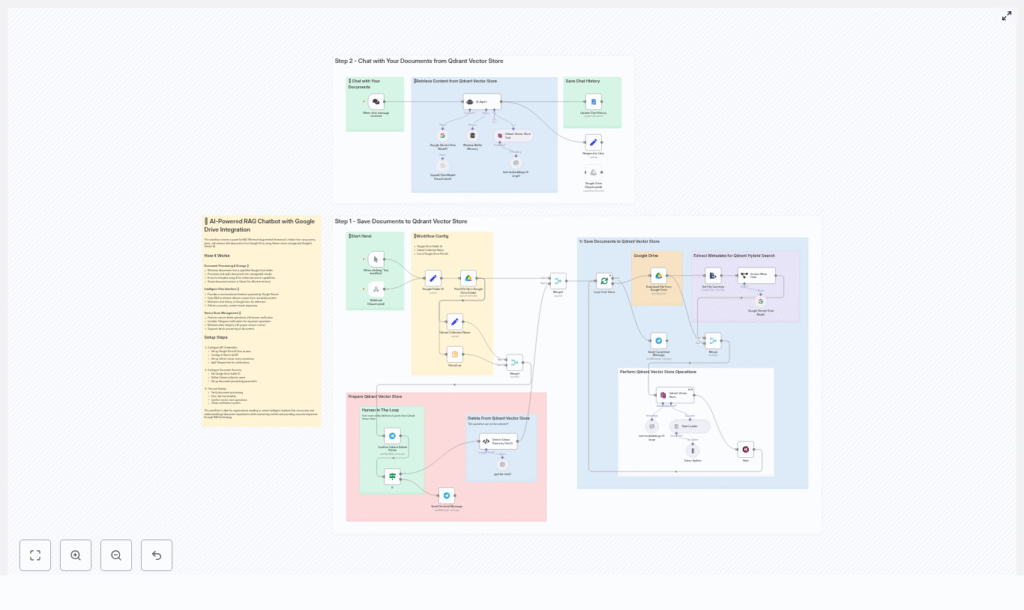
Example n8n Node Flow
The template workflow in n8n typically follows a structure similar to the one below:
- Google Folder ID → Find File IDs → Loop Over Items
- Download File → Extract Text → Token Splitter → Embeddings → Qdrant Upsert
- Extract Metadata → Attach metadata fields → Save to Qdrant
- Chat Trigger → RAG Agent → Qdrant Vector Store Tool → LLM → Respond & Save Chat History
- Deletion Path: Summarize File IDs → Telegram Confirmation → Delete Qdrant Points by File ID (Code Node)
Conclusion
By combining n8n with Qdrant, Google Drive, and a powerful LLM, you can build a flexible and auditable RAG chatbot that delivers accurate answers grounded in your private documents. Thoughtful chunking, high-quality embeddings, robust metadata, and human verification for destructive operations are key to achieving a reliable, production-ready system suitable for enterprise use.
Next Steps and Call to Action
To validate this approach in your environment, start with a small proof-of-concept:
- Export a subset of Google Drive folder IDs.
- Deploy the n8n workflow template.
- Index a limited set of documents and test relevance, latency, and cost.
If you require a ready-to-deploy template, assistance with authentication and compliance, or help scaling to larger document sets, contact our team or download the n8n template. Use the sample workflow as a foundation and adapt it to your specific data, security, and operational requirements.
Ready to build your RAG chatbot? Reach out for a consultation or download the sample workflow and begin integrating your Google Drive knowledge base today.