Automate Course Completion Certificates with n8n
Issuing course completion certificates manually does not scale and is prone to delays and inconsistencies. This article presents a production-ready n8n workflow template that automates certificate generation and logging using OpenAI embeddings, Supabase as a vector store, a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) agent, Google Sheets, and Slack alerts.
The goal is to provide automation professionals with a clear, technically accurate reference that can be deployed as-is, then extended for more advanced use cases such as PDF generation and LMS integration.
Business case for automating certificates
Automating course completion certificates delivers several operational advantages:
- Speed and scalability – Certificates are issued as soon as completion data is received, without manual intervention.
- Consistency and auditability – Every issuance is logged in a structured way, which simplifies compliance and reporting.
- Reduced human error – Rules and templates are applied programmatically, minimizing incorrect or missing certificates.
- Dynamic, context-aware content – A RAG-driven approach allows the system to incorporate course-specific rules, policies, and templates at runtime.
By combining n8n with a vector database and LLM-based reasoning, the workflow can generate accurate, personalized certificate content while keeping the architecture maintainable and cost-efficient.
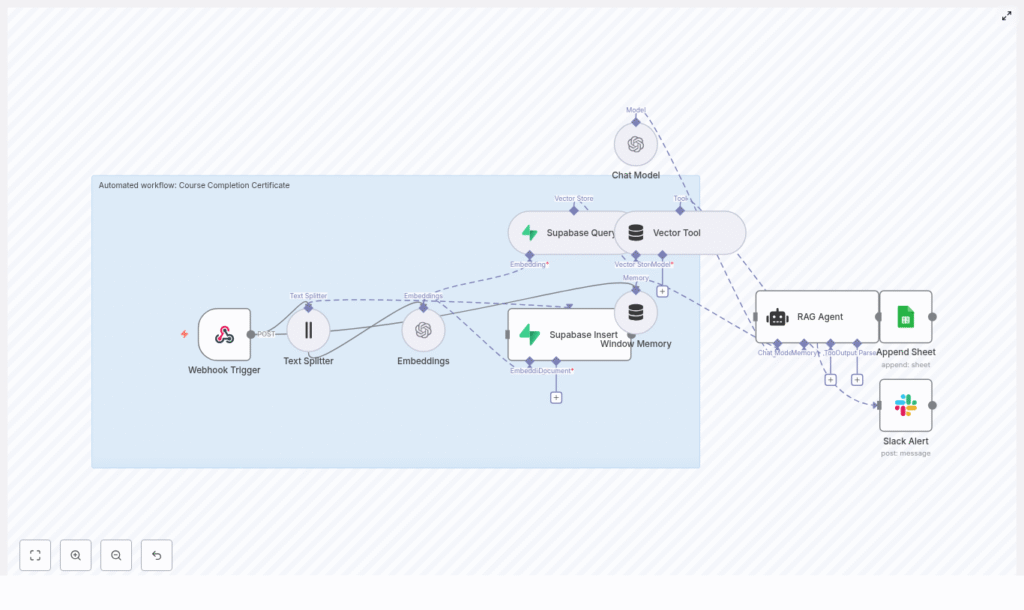
High-level architecture
The workflow is triggered when a learner completes a course and the LMS (or another system) sends a POST request to an n8n webhook. The request flows through a RAG-based pipeline that retrieves relevant context from Supabase, generates or validates certificate content using OpenAI, then logs results and handles errors.
Key components in the architecture:
- Webhook Trigger (n8n) – Receives course completion payloads.
- Text Splitter – Splits long documents into manageable chunks for embedding.
- OpenAI Embeddings – Converts text chunks into vector embeddings.
- Supabase Insert / Query – Stores and retrieves embeddings in a vector index.
- Vector Tool + Window Memory – Provides contextual retrieval and short-term memory to the RAG agent.
- Chat Model (OpenAI) & RAG Agent – Generates or validates certificate content based on retrieved context.
- Google Sheets (Append) – Persists the outcome and status as an audit trail.
- Slack (Alert on error) – Notifies operators when failures occur.
End-to-end request lifecycle
The following sequence describes what happens when a single course completion event is processed:
- The LMS or platform sends a POST request with student and course data to the n8n webhook endpoint.
- The RAG agent queries the Supabase vector store (through the Vector Tool) to retrieve relevant course rules, templates, and policy text filtered by
course_id. - Using the retrieved context and the incoming payload, the agent either:
- Generates the certificate text, or
- Validates that the learner satisfies issuance criteria and returns a structured status.
- The result is appended to a Google Sheet for logging and can be returned to the caller. This output can later be used for PDF generation or emailing.
- If any error occurs during processing, the workflow sends a Slack alert and records the failure in the log sheet.
Core workflow components in detail
1. Webhook Trigger configuration
The workflow begins with a POST webhook, for example at:
/webhook/course-completion-certificate
This endpoint should receive a JSON payload when a learner completes a course. A typical payload might look like:
{ "student_name": "Jane Doe", "course_id": "COURSE_101", "completion_date": "2025-08-01", "score": 95, "metadata": { "email": "jane@example.com" }
}
For production use, implement authentication or signature verification, especially if the webhook is publicly accessible. Common patterns include HMAC signatures, bearer tokens, or IP whitelisting, configured in front of or within n8n.
2. Preparing context with the Text Splitter
To support retrieval-augmented generation, course descriptions, certificate templates, and policy documents must be embedded and stored in the vector database. Long documents are first processed by a Text Splitter node.
Typical configuration values in this workflow:
chunkSize = 400chunkOverlap = 40
These parameters ensure that each chunk is small enough for high-quality embeddings while preserving continuity between segments. Adjust these values based on your average document length and complexity. Overly large chunks reduce retrieval precision and increase token usage.
3. Generating embeddings with OpenAI
The embeddings step uses the text-embedding-3-small model to convert text chunks into vector representations suitable for similarity search. This smaller model is cost-effective and sufficient for most certificate-related content.
When creating embeddings, store rich metadata alongside each vector so that future queries can be filtered efficiently. Recommended metadata fields include:
course_id– to scope retrieval to a specific course.chunk_index– to maintain ordering if needed.source– such as “template”, “policy”, or “course_description”.version– optional, useful when policies or templates change over time.
4. Supabase vector store: Insert and Query
Supabase is used as the vector store for this workflow. Two primary operations are involved:
- Insert – Embeddings are written into a Supabase vector index, for example named
course_completion_certificate. Each row contains the vector plus its associated metadata. - Query – At runtime, the workflow queries the index for nearest neighbors that match the context of the current request.
When querying, use metadata filters such as course_id or source to restrict results to relevant documents. This significantly improves the quality of the RAG agent’s responses and reduces noise.
5. Vector Tool and Window Memory
To expose the Supabase vector store to the language model, the workflow uses a Vector Tool node. This node turns the vector search capability into a callable tool that the RAG agent can invoke when it needs additional context.
Alongside this, a Window Memory node maintains short-term conversational context within the lifetime of a single request. It stores recent inputs and outputs, which allows the agent to reference prior steps without repeated retrieval or recomputation.
6. Chat Model and RAG Agent configuration
The Chat Model node is configured with your OpenAI API credentials and is used by the RAG Agent to perform the actual reasoning and text generation.
Typical setup includes:
- System message that defines the role of the agent, for example:
“You are an assistant for Course Completion Certificate.” - Task-specific prompt that passes the incoming JSON payload, for example:
“Process the following data for task ‘Course Completion Certificate’: {{ $json }}”
The RAG agent can:
- Call the Vector Tool to retrieve certificate templates, course rules, and policies.
- Use Window Memory to keep track of intermediate reasoning steps within the same run.
- Return either a finalized certificate text or a structured status object indicating whether issuance is allowed and why.
For robust downstream processing, instruct the agent to output structured JSON, for example with keys such as status, certificate_text, and reason. Clear output contracts simplify integration with other systems.
7. Logging to Google Sheets
On successful completion, the workflow appends a row to a Google Sheet to create a durable, human-readable log. In the template, the sheet is configured as:
- Sheet name:
Log - Columns: for example, a
Statuscolumn mapped to{{$json["RAG Agent"].text}}or to a more structured JSON field if you adopt a schema.
This provides an immediate, low-friction audit trail that can be reviewed by non-technical stakeholders or exported for reporting.
8. Slack alerting on errors
Any errors raised by the RAG Agent or other critical nodes are routed to a Slack node configured to post to an #alerts channel. The alert typically includes:
- A short description of the failure.
- Relevant error messages or codes.
- Optional identifiers such as
course_idorstudent_nameto assist in triage.
This pattern ensures that operational issues are visible in near real-time and can be addressed before they impact a larger number of learners.
Sample webhook payloads
The workflow expects a standard structure for course completion events. Here is a representative example:
{ "student_name": "Jane Doe", "course_id": "COURSE_101", "completion_date": "2025-08-01", "score": 95, "email": "jane@example.com"
}
You can extend this schema with additional fields such as localization preferences, certificate variants, or custom metadata, as long as the RAG prompt and downstream mapping are updated accordingly.
Implementation best practices
Chunking and retrieval quality
- Adjust
chunkSizeandchunkOverlapbased on your content. Smaller, overlapping chunks usually improve retrieval accuracy. - Test retrievals with representative queries to validate that the correct segments are returned for each
course_id.
Metadata strategy
- Always include
course_id,source, and optionallyversionin your embeddings metadata. - Use these fields as filters in Supabase queries to avoid mixing content from different courses or outdated templates.
Prompt and output design
- Define a strict output schema in the agent prompt, for example:
“Return JSON with keys: status, certificate_text, reason.” - Validate the agent output in n8n before logging or acting on it to handle malformed responses gracefully.
Cost and performance management
- Use
text-embedding-3-smallfor embeddings to control storage and query costs. - Reserve larger or more capable chat models only for the generation step when absolutely necessary.
- Monitor latency across embedding lookup and generation to keep SLAs under control.
Security and credential management
- Protect the webhook using tokens or HMAC-based signatures.
- Store all API keys (OpenAI, Supabase, Google, Slack) in n8n credentials, not directly in node fields.
- Apply role-based access control in Supabase and Google Sheets to limit who can view or modify sensitive data.
Extending the workflow
Once the core certificate automation is stable, you can extend the workflow with additional capabilities:
- Email delivery – Integrate with SendGrid, SMTP, or another email provider to send the certificate to the learner automatically.
- PDF generation – Add a PDF generation node or external service that uses a template to create a branded certificate populated with the learner’s details.
- Automated re-indexing – When course content, templates, or policies change, trigger a reindex job to update embeddings in Supabase so the RAG agent always uses current information.
- Resilience features – Implement retry logic for transient API failures and refine Supabase and Sheets permissions for stronger access control.
Monitoring and ongoing maintenance
To operate this workflow reliably at scale, treat it as a production service and monitor key indicators:
- Webhook metrics – Invocation volume, success rate, and HTTP error codes.
- RAG agent latency – Time spent on vector queries plus LLM generation.
- Supabase usage – Vector store size, query counts, and associated costs.
- Google Sheets growth – Daily row appends and sheet size to anticipate archival needs.
Schedule periodic jobs (for example, via n8n Cron nodes) to:
- Re-embed and re-index documents after major content changes.
- Run health checks that validate connectivity to OpenAI, Supabase, Google Sheets, and Slack.
Security and compliance considerations
Because certificate data often contains personally identifiable information, treat the workflow as part of your broader data protection strategy. Consider:
- Data minimization and masking – Encrypt or redact sensitive fields before storing them in logs or embeddings where possible.
- Retention policies – Define how long personal data is retained in Supabase and Google Sheets, and implement automated cleanup processes.
- Access controls – Restrict access to Supabase projects and Sheets using role-based access control aligned with your internal policies.
Key benefits summary
- Automated, consistent issuance of course completion certificates at scale.
- Context-aware generation powered by vector retrieval and a RAG agent.
- Transparent audit trail in Google Sheets and proactive error visibility via Slack alerts.
- Scalable, modular architecture based on n8n, Supabase vector store, and OpenAI embeddings.
Getting started with the template
This n8n workflow template combines webhooks, embeddings, a vector store, and a RAG agent to streamline certificate issuance. It can be used as a standardized foundation for your platform and then extended to include PDF creation, email delivery, or deep LMS integration.
To deploy:
- Import the workflow into your n8n instance.
- Configure credentials for OpenAI, Supabase, Google Sheets, and Slack.
- Set up your webhook at
/webhook/course-completion-certificate(or your preferred path). - Run a test POST using a payload similar to the sample JSON above.
- Verify that entries appear in your Google Sheet
Logtab and that Slack#alertsreceives notifications on failures.
For more advanced use, refine the RAG prompt to output structured JSON tailored to your downstream processes, or work with an automation specialist to integrate PDF signing and email dispatch.