Automate Gmail Replies with n8n & OpenAI Assistant
This guide teaches you how to use an n8n workflow template to turn labeled Gmail threads into AI-generated reply drafts using the OpenAI Assistant. You will learn what each node does, how data flows through the workflow, and how to customize prompts, schedules, and labels for your own use.
What you will learn
- Why automating Gmail reply drafts with n8n and OpenAI is useful
- How the workflow checks labeled threads and prepares AI-powered replies
- How to configure each n8n node, from Schedule Trigger to Gmail draft creation
- How to set up prompts, credentials, labels, and basic troubleshooting
- Ideas for advanced customizations, security, and cost management
Why automate Gmail reply drafting with n8n?
Handling a large volume of email is time consuming. Writing similar replies over and over can drain your focus.
With this n8n workflow template, you can:
- Let AI create a first-pass reply draft for labeled emails
- Keep human oversight by reviewing and editing drafts before sending
- Maintain a consistent tone, style, and structure in your replies
- Save time on repetitive composition while still controlling the final message
The workflow only acts on Gmail threads that have a specific label, so you stay in control of which emails are processed by the OpenAI Assistant.
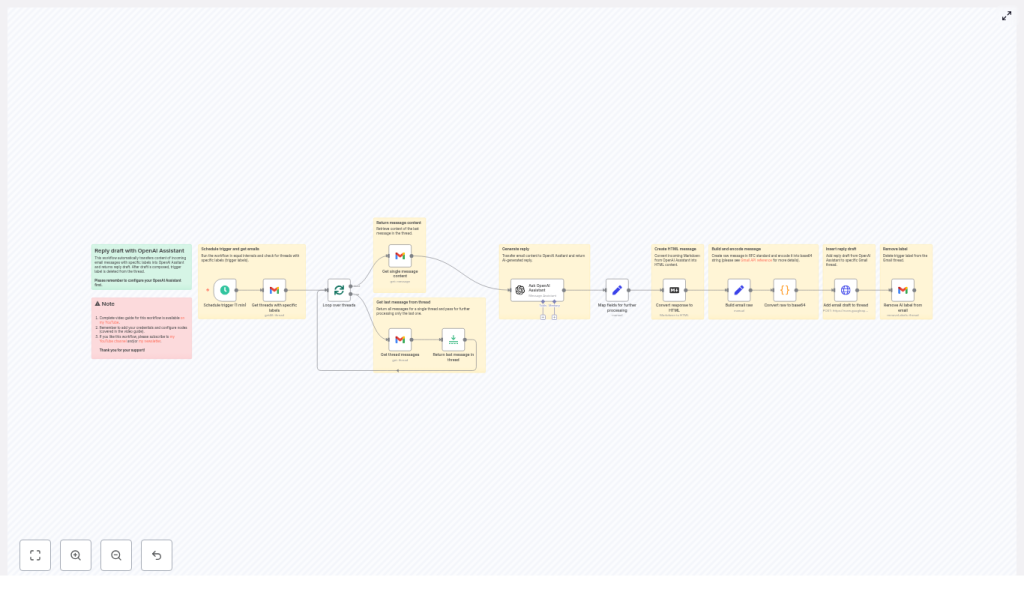
Concept overview: How the workflow works
At a high level, the template follows this sequence:
- Run on a schedule (for example, every minute)
- Find Gmail threads that have a specific label (your trigger label)
- Loop through each of those threads one by one
- Get the latest message in each thread
- Send that message content to your OpenAI Assistant in n8n
- Convert the assistant reply from Markdown to HTML
- Build a raw email message in RFC-822 style and encode it in base64
- Create a Gmail draft reply in the original thread
- Remove the trigger label so the thread is not processed again
Next, we will walk through each step inside n8n so you understand how to configure and adapt it.
Step-by-step: Building and understanding the n8n workflow
Step 1: Schedule when the workflow runs
Node: Schedule Trigger
Use the Schedule Trigger node to control how often n8n checks for labeled threads.
- Typical setting: Every 1 minute, so new labeled emails are picked up quickly
- Low volume tip: Increase the interval (for example, every 5 or 15 minutes) to reduce API usage and avoid hitting Gmail or OpenAI quotas
Once the trigger fires, it passes control to the next node that queries Gmail.
Step 2: Fetch Gmail threads with a specific label
Node: Gmail (resource: thread, operation: list)
Here you tell n8n which threads to process by filtering on a Gmail label. The typical setup is:
- Create a dedicated Gmail label, for example
ai-draft - In the Gmail node, set Resource to
thread - Use the labelIds filter and supply your label ID (mapped from the label you created)
Only threads that have this label will be passed to the rest of the workflow. You can manually apply this label in Gmail whenever you want an AI-generated draft for that conversation.
Step 3: Loop through each thread individually
Node: SplitInBatches
The SplitInBatches node takes the list of threads from Gmail and processes them one at a time. This is helpful because:
- Each thread is handled separately, which keeps data mapping clean
- You can better control concurrency and avoid rate limits
In practice, the node outputs a single thread per iteration, and the workflow continues until all threads in the batch have been handled.
Step 4: Get the content of the latest message in the thread
You have two main patterns for retrieving the last message. The template can use either of these approaches.
Option A: Directly get a single message
Node: Gmail (operation: get message)
In this pattern, you already know which message to fetch (for example, by ID or from the thread data). The node returns the full message payload, including:
- Headers (From, To, Subject, etc.)
- Body text or HTML
- Other metadata
This payload is then forwarded to the OpenAI Assistant node.
Option B: Get all messages in the thread, then keep the last one
Nodes: Gmail (get thread messages) + Limit
Alternatively, you can:
- Use the Gmail node to fetch all messages in the thread
- Add a Limit node configured with lastItems to keep only the latest message
This approach ensures that the AI is always replying to the most recent email in the conversation, which is very important for multi-message threads.
Step 5: Send the message content to the OpenAI Assistant
Node: LangChain / OpenAI Assistant
Now that you have the last message, you can send it to your configured OpenAI Assistant. In the LangChain/OpenAI node:
- Set assistantId to the ID of the assistant you created in OpenAI
- Map the email message body (and optionally subject, sender, etc.) into the assistant input
- Provide a clear system or role prompt that explains how the assistant should draft the reply
The assistant will return a suggested reply, often in Markdown format. You will use this output in later nodes to build the Gmail draft.
Step 6: Map key fields for later nodes
Node: Set
To make the rest of the workflow easier to manage, use a Set node to store important values in clearly named fields. For example:
response→ the assistant output (reply text)threadId→ the original Gmail thread IDto→ the sender address from theFromheadersubject→ the original email subject
This step keeps your data organized and makes the email-building step more straightforward.
Step 7: Convert the AI response from Markdown to HTML
Node: Markdown
Many assistants return text formatted in Markdown. Gmail drafts, however, expect HTML for rich formatting.
Use the Markdown node to:
- Take the
responsefield as input - Convert it into HTML
- Output safe HTML that preserves lists, bold text, links, and other formatting
The resulting HTML will be used as the body of the Gmail draft.
Step 8: Build the raw email message
Node: Set
Gmail’s drafts API expects a raw RFC-822 style message that includes headers and body. In another Set node, create a text field that represents the full email, for example:
To: {{ $json.to }}
Subject: {{ $json.subject }}
Content-Type: text/html; charset="utf-8"
{{ $json.response }}Key points:
- The
Toheader uses the original sender address - The
Subjectmatches the original thread subject Content-Typeis set totext/html; charset="utf-8"- The body contains the HTML version of the assistant’s reply
Step 9: Encode the raw message in base64
Node: Code
The Gmail API requires the raw message field to be URL-safe base64 encoded. Use a Code node that relies on Node’s Buffer to perform this encoding.
Typical logic inside the Code node:
- Read the raw email string
- Convert it to base64 using
Buffer - Output an
encodedfield with the base64 or base64url value
If your client or library requires base64url, make sure to apply the required character replacements.
Step 10: Create a Gmail draft in the original thread
Node: HTTP Request
To create the actual Gmail draft, use an HTTP Request node that calls the Gmail drafts API:
- Method: POST
- URL:
https://www.googleapis.com/gmail/v1/users/me/drafts
Set the JSON body to something like:
{ "message": { "raw": "{{ $json.encoded }}", "threadId": "{{ threadId }}" }
}This creates a draft reply attached to the original Gmail thread, which you can then review and send directly from your inbox.
Step 11: Remove the trigger label so the thread is not reprocessed
Node: Gmail (resource: thread, operation: removeLabels)
Finally, remove the AI trigger label from the thread. This prevents the same conversation from being processed again in the next scheduled run.
Configure the Gmail node to:
- Operate on the thread resource
- Use the removeLabels operation
- Specify the label ID of your trigger label (for example,
ai-draft)
At this point, the workflow has created a draft and cleaned up the label, so the loop can continue with the next thread.
Prompt examples for the OpenAI Assistant
Your prompt has a huge impact on the quality, tone, and length of the AI-generated reply. Below are some ready-to-use examples you can plug into the Ask OpenAI Assistant node and then adapt to your needs.
- Professional short reply:
“You are a professional assistant. Read the user message and draft a concise, polite reply (3-5 sentences) summarizing next steps and questions if needed.” - Detailed support reply:
“You are a friendly support agent. Use the last customer message to draft a helpful, empathetic response with an actionable next step and a closing line offering further help.” - Custom signature:
“Add this signature at the end: \n-\nJohn Doe\nCustomer Success”
Combine these ideas or customize them to match your brand voice, internal guidelines, or different types of emails.
Configuration and credentials you need
Before the workflow can run end to end, make sure you have the following configured:
- n8n instance: A secure n8n setup where you have permission to create and edit workflows.
- Gmail OAuth2 credentials: Create OAuth2 credentials in Google Cloud and grant at least these scopes:
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/gmail.modifyhttps://www.googleapis.com/auth/gmail.compose
Broader scopes may be used if your use case requires them.
- OpenAI API key: Add your OpenAI API key to n8n and configure your assistant (
assistantId) in the LangChain/OpenAI node. - Gmail label: Create a label such as
ai-draftand apply it to any emails you want the workflow to process.
Testing the workflow and basic troubleshooting
How to test
- In Gmail, pick a test conversation and manually add your trigger label (for example,
ai-draft). - In n8n, run the workflow manually or wait for the Schedule Trigger to execute.
- Check the execution details in n8n to see if all nodes run successfully.
- Open Gmail and confirm that a new draft reply appears in the original thread.
If something goes wrong
- No drafts created:
- Verify that the Gmail label is correctly applied and that the label ID is correct in the workflow
- Check the Code node to ensure the raw message is properly base64 or base64url encoded
- Confirm that Gmail API quotas have not been exceeded
- Malformed or broken HTML:
- Inspect the output of the Markdown node
- Adjust your assistant prompt so it produces cleaner Markdown
- Optionally sanitize or post-process the HTML before building the raw email
- Errors in n8n:
- Open the execution log and inspect each node’s input and output
- Check that all credentials (Gmail, OpenAI) are valid and authorized
Security, privacy, and best practices
Automating email with AI involves sensitive data. Keep these guidelines in mind:
- Review your data policies before sending sensitive or personally identifiable information to third-party AI services.
- Limit the assistant to processing only emails you control or have explicit permission to handle.
- Use dedicated service accounts or OAuth credentials for automations and rotate keys regularly.
- Where possible, log only metadata (for example, timestamps, IDs) instead of full message content.
Costs, quotas, and rate limits
Both OpenAI and Gmail APIs have usage limits and potential costs.
- OpenAI: Billing is token based. Monitor token usage in your OpenAI account and set limits or alerts so you stay within budget.
- Gmail: API quotas apply per project and per user. Use reasonable schedule intervals, and avoid unnecessarily frequent checks to prevent hitting limits.
Adjusting the Schedule Trigger and batching logic can significantly reduce the chance of quota issues.
Advanced customizations
Once the core workflow works, you can extend it for more advanced scenarios:
- Auto-send for trusted workflows: Add a conditional step that sends drafts automatically for specific categories or from specific senders. Use this only when you are confident in the AI output.
- Multi-language replies: Detect the language of the incoming message and route it to different assistants or prompts tailored to that language.
- Attachment-aware replies: Extend the workflow to fetch and analyze attachments, then include summaries or references to those attachments in the prompt.
- Audit trail: Save AI-generated replies and related metadata