Automate Client Feedback with n8n, LangChain & HubSpot
Modern support, success, and product teams need a reliable way to capture client conversations, extract the key information, and push it into their CRM and internal communication channels with minimal manual work. This guide documents a reusable n8n workflow template that integrates LangChain, OpenAI, HubSpot, and Gmail (or Mailjet) to automate transcript intake, summarization, CRM note creation, and routing to the correct internal team.
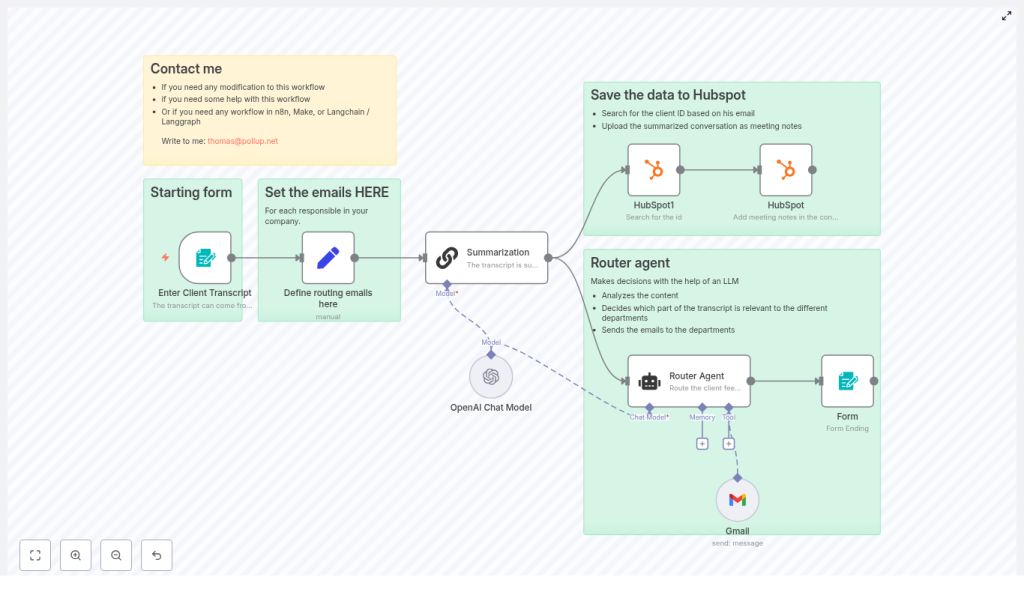
1. Workflow overview
This n8n automation is built around a linear data flow:
- Capture the client email address and transcript via an n8n Form Trigger.
- Load a configurable list of routing targets (department email addresses) in a Set node.
- Use a LangChain summarization node with OpenAI to produce a 2-3 sentence summary.
- Invoke a LangChain Router Agent to determine which department should be notified and to generate an HTML email body and subject line.
- Use HubSpot nodes to look up the contact and store the summary as a meeting engagement.
- Send the generated HTML email to the selected department via Gmail or Mailjet.
- Return a completion message to the user through the form response.
The result is a standardized, repeatable process that turns raw client transcripts into structured meeting notes in HubSpot and delivers context-rich notifications to the right internal stakeholders.
2. Architecture and data flow
2.1 High-level architecture
- Input layer: n8n Form Trigger node collects client email and transcript text.
- Configuration layer: Set node defines routing targets (Support, Product, Administrative, Commercial).
- LLM processing layer:
- LangChain summarization node using OpenAI for concise summaries.
- LangChain Router Agent using OpenAI (for example,
gpt-4o-mini) for intent-based routing and email generation.
- CRM integration layer: HubSpot nodes to search contacts and create meeting engagements.
- Notification layer: Gmail or Mailjet node to send HTML emails to the routed department.
- Response layer: Form completion response in n8n confirming that the workflow executed.
2.2 Data objects and transformations
- Input fields:
client_email(string) – the email address of the client.transcript(string) – full conversation or call transcript.
- Derived fields:
summary(string) – 2-3 sentence LLM-generated summary, same language as the transcript.target_department_email(string) – one of the configured routing emails.email_subject(string) – concise subject line for the internal team.email_body_html(string, HTML) – formatted email body including:- Client email prefixed with
FROM CLIENT: - Original conversation content.
- Client email prefixed with
- HubSpot payload:
- Contact identifier: looked up by
client_email. - Engagement type:
meeting. - Engagement body:
summaryas the meeting notes text.
- Contact identifier: looked up by
3. Node-by-node breakdown
3.1 Form Trigger – client transcript intake
Node type: Form Trigger
Purpose: Collect the client email and the raw conversation transcript.
Key configuration:
- Define form fields for:
- Email – client email address.
- Transcript – full conversation or call transcript text.
- Expose the form URL to either:
- Internal support staff who manually paste transcripts, or
- A transcript provider integration (for example, Fireflies, Zoom, or similar) that can post transcripts into the form endpoint.
Data output: The node outputs a JSON object containing client_email and transcript, which is then passed to subsequent nodes.
3.2 Set node – department routing configuration
Node type: Set
Purpose: Store a centralized mapping of department names to routing email addresses.
Key configuration:
- Define fields for each routing target, for example:
support_emailproduct_emailadministrative_emailcommercial_email
- Use static values or environment variables for email addresses to avoid hardcoding them in prompts.
Benefit: This keeps routing logic maintainable. Updating addresses does not require any changes to the LangChain agent configuration, only to this node.
3.3 LangChain summarization node – transcript summarization
Node type: LangChain (Summarization)
Backend: OpenAI model (for example, gpt-4o-mini or similar)
Purpose: Generate a compact, human-readable summary of the transcript.
Key configuration:
- Input text: Pass the full
transcriptfrom the Form Trigger node. - Prompt: Instruct the LLM to:
- Produce a 2-3 sentence summary.
- Return the summary in the same language as the input transcript.
- Output field: Store the result in a field such as
summaryfor later use by the HubSpot node.
Usage: This summary is used as the body of a meeting engagement in HubSpot, providing a concise, searchable record of the interaction.
3.4 LangChain Router Agent – intent-based routing and email generation
Node type: LangChain Agent (Router Agent)
Backend: OpenAI model (for example, gpt-4o-mini)
Purpose: Analyze the conversation content, choose the most appropriate department, and generate an HTML email body and subject line.
Inputs:
- Full
transcripttext. - Client email address (
client_email). - Routing email addresses from the Set node:
support_emailproduct_emailadministrative_emailcommercial_email
System message / instructions: Configure the Router Agent with a system prompt that explicitly instructs it to:
- Select exactly one person or team to notify from:
- Product
- Administrative / invoicing
- Support
- Commercial
- Prepend the client email to the message body with the label
FROM CLIENT:. - Return:
- An HTML-formatted email body that includes the client conversation.
- A clear, concise subject line tailored to the selected department.
Typical outputs:
target_department_email– one of the configured routing emails.email_subject– LLM-generated subject.email_body_html– LLM-generated HTML content with:FROM CLIENT: <client_email>- The conversation transcript or a formatted version of it.
Routing accuracy advantages: Compared to keyword-based routing, the LLM can interpret intent, tone, and context, so it is more robust when clients use varied phrasing or mix topics. It reduces misrouted tickets and ensures that each issue is handled by the most relevant team.
3.5 HubSpot nodes – search and meeting note creation
Node types: HubSpot Search, HubSpot Create (Engagement)
Purpose: Store the summarized conversation as a meeting note on the correct HubSpot contact.
Step 1: Contact lookup
- Use a HubSpot search node to query contacts by
client_email. - If a contact exists, capture its internal identifier for use in the engagement creation step.
Step 2: Create meeting engagement
- Use a HubSpot node configured to create an engagement of type
meeting. - Set the engagement body to the
summaryproduced by the LangChain summarization node. - Associate the engagement with the found contact.
Result: HubSpot becomes the single source of truth for client interactions, with structured meeting notes that are searchable and available to all customer-facing teams.
3.6 Gmail or Mailjet node – notification delivery
Node type: Gmail or Mailjet (Email send)
Purpose: Deliver the LLM-generated HTML email to the selected internal department.
Key configuration:
- To: Use
target_department_emailfrom the Router Agent output. - Subject: Use
email_subjectgenerated by the agent. - Body: Use
email_body_htmlas the HTML content.
The body should already include the label FROM CLIENT: followed by the client email and the original conversation content, so that the receiving team immediately understands the context.
3.7 Form completion – user feedback
Node type: Form Trigger response / terminal node
Purpose: Return a confirmation message or record that the workflow finished successfully.
This can be as simple as a text confirmation to the staff member or system that submitted the transcript, indicating that the feedback has been processed and routed.
4. Configuration notes and credentials
4.1 Credentials and connections
- OpenAI / LangChain:
- Configure OpenAI credentials in n8n for both the summarization node and the Router Agent.
- Use models such as
gpt-4o-minior another supported model, depending on your performance and cost requirements.
- HubSpot:
- Use scoped API credentials with access to contacts and engagements.
- Ensure the HubSpot nodes are pointed at the correct portal and environment.
- Gmail / Mailjet:
- Set up OAuth (for Gmail) or API keys (for Mailjet).
- Verify sending domains and from-address policies as required.
4.2 Prompt design and routing logic
- Keep all routing email addresses in the Set node, not directly in the prompt.
- In the Router Agent system message, explicitly:
- List the available departments and their email variables.
- Specify that only one department must be selected per conversation.
- Instruct the agent to always prepend
FROM CLIENT:and the client email to the email body.
4.3 Handling edge cases
While the workflow is designed for straightforward routing, keep in mind:
- Multi-topic conversations: A single transcript may contain product feedback and billing questions. The existing approach instructs the agent to choose only one department. If needed, you can refine the prompt to prefer certain categories or adjust expectations around routing.
- Missing contacts in HubSpot: If the HubSpot search does not find a contact, you can:
- Log the event for follow-up, or
- Extend the workflow to create a new contact before creating the meeting engagement.
- Invalid email addresses: If the client email is malformed, the HubSpot search and email routing may fail. Use n8n validation or a simple function node to check email format before proceeding.
5. Testing and validation strategy
Before deploying this n8n workflow into production, test it with a representative set of transcripts.
5.1 Test scenarios
- Product feedback: Feature requests, UX complaints, usability issues.
- Support issues: Bug reports, error messages, troubleshooting requests.
- Administrative inquiries: Invoicing questions, payment failures, billing corrections.
- Commercial requests: Pricing questions, contract negotiations, discount discussions.
5.2 Validation checklist
- Verify that the Router Agent:
- Chooses exactly one department for each input.
- Uses the correct department email from the Set node.
- Includes
FROM CLIENT:plus the correct client email in the email body.
- Confirm that HubSpot:
- Finds the correct contact by email.
- Creates a meeting engagement with the LLM-generated summary as the body.
- Check that the selected department:
- Receives a properly formatted HTML email.
- Sees both the client attribution and the conversation context clearly.
6. Security and privacy considerations
Client transcripts may contain sensitive or personally identifiable information. When running this workflow in production, follow standard security and privacy practices:
- Only send data to LLM providers and third-party services that meet your data protection and contractual requirements.
- Mask or strip highly sensitive data, such as payment card numbers or full identity documents, before sending content to OpenAI or email providers.
- Use scoped, least-privilege API keys for HubSpot and Gmail / Mailjet, and rotate them regularly.
- Secure any public endpoints associated with the Form Trigger and log only the minimum data necessary for troubleshooting.
7. Tips to improve routing accuracy
- Iterate on prompts: