Automate Phone Calls with n8n and VAPI.ai
This guide walks you through an n8n workflow template that automatically places a phone call with VAPI.ai, checks the call status in a loop, and captures the assistant’s summary when the call is finished. The goal is to help you understand the logic behind each node so you can confidently customize or extend the workflow.
What You Will Learn
By the end of this tutorial, you will know how to:
- Trigger an automated phone call from n8n using VAPI.ai
- Send all required call details and assistant variables in a POST request
- Poll the call status until the conversation ends
- Store the AI assistant’s final summary for later use
- Apply best practices around security, error handling, and scaling
Why Automate Phone Calls with n8n and VAPI.ai?
Automated phone calls are useful for reminders, outreach, appointment confirmations, follow-ups, and basic customer support. When you combine:
- n8n for workflow orchestration and integrations, and
- VAPI.ai for conversational voice AI and telephony,
you get a flexible system that can run personalized calls at scale, without building your own phone infrastructure.
Conceptual Overview of the Workflow
The template uses a simple control loop:
- A trigger in n8n starts the workflow and passes in call parameters.
- n8n sends a POST request to VAPI.ai to create an outbound call.
- n8n receives a call ID from VAPI.ai.
- Using that call ID, n8n periodically checks the call status.
- As long as the call is not finished, n8n waits for a short delay and checks again.
- When the call ends, n8n extracts the assistant’s analysis summary and stores it for downstream steps.
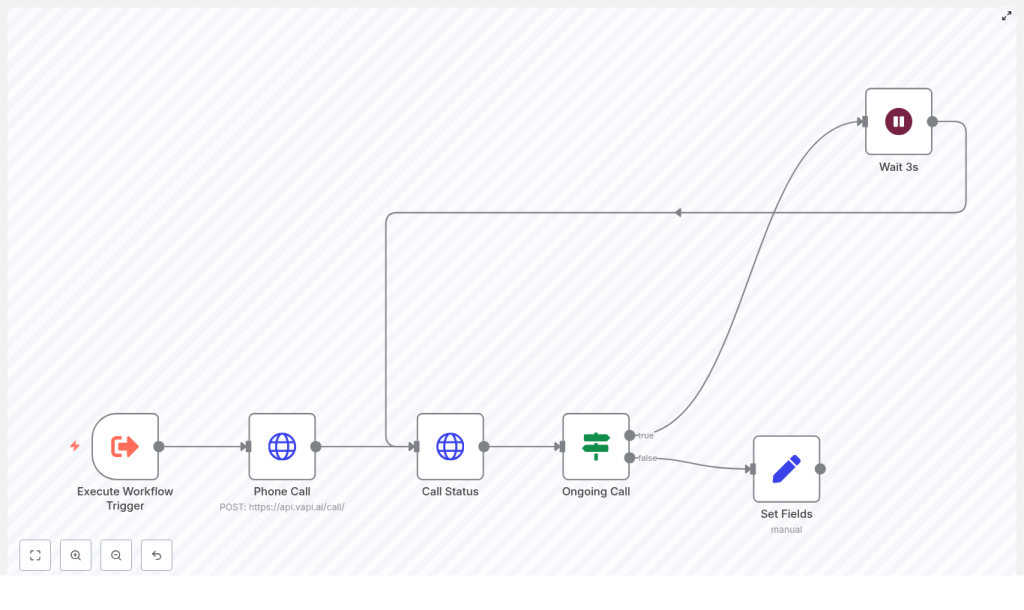
At a high level, the template includes these core nodes:
- Execute Workflow Trigger – starts the automation and provides call inputs.
- Phone Call (HTTP Request) – tells VAPI.ai to start the call.
- Call Status (HTTP Request) – checks the current state of the call.
- Ongoing Call (If node) – decides whether to keep polling or exit the loop.
- Wait 3s – pauses between polls to avoid hammering the API.
- Set Fields – stores the call summary when everything is done.
Preparing Your Inputs
The workflow expects certain call details to be present in the trigger data. These values are later passed to VAPI.ai through assistantOverrides.variableValues and the customer object.
Key Input Fields
Make sure your trigger provides the following fields (for example in a webhook’s query or body):
phone_numberfirst_nametypeinstructionscall_purposeresponse_styletonepause_between_sentencesfallback_response
These values allow you to customize how the assistant speaks and behaves on a per-call basis.
Step-by-Step: Building the n8n Workflow
Step 1: Configure the Execute Workflow Trigger
The first node simply starts the workflow. It can be:
- An HTTP Webhook that receives call details from another system
- A scheduled trigger that runs at specific times
- Any other n8n trigger that fits your use case
Ensure that the trigger passes the input fields listed above. In the example template, these values are accessed with expressions such as {{$json.query.query.first_name}}, which assumes the data is coming in via query parameters on a webhook.
Step 2: Start the Phone Call with an HTTP Request
Next, you create the outbound phone call in VAPI.ai using an HTTP Request node in n8n.
Basic HTTP Request Configuration
- Method:
POST - URL:
https://api.vapi.ai/call/ - Headers:
Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_API_KEY>
- Body: JSON payload with assistant ID, overrides, customer info, and phone number ID
Example JSON Body (using n8n expressions)
{ "assistantId": "6acda9bc-ef39-4a4c-84a3-0fdd38f2ab88", "assistantOverrides": { "variableValues": { "first_name": "{{ $json.query.query.first_name }}", "type": "{{ $json.query.query.type }}", "instructions": "{{ $json.query.query.instructions }}", "call_purpose": "{{ $json.query.query.call_purpose }}", "response_style": "{{ $json.query.query.response_style }}", "tone": "{{ $json.query.query.tone }}", "pause_between_sentences": "{{ $json.query.query.pause_between_sentences }}", "fallback_response": "{{ $json.query.query.fallback_response }}" } }, "customer": { "number": "{{ $json.query.query.phone_number }}", "name": "{{ $json.query.query.first_name }}" }, "phoneNumberId": "75207c9a-a7c0-474f-b638-87838b5639bc"
}
Replace assistantId, phoneNumberId, and the API key with your own values. The expressions in double curly braces pull data from the trigger node.
When this request succeeds, VAPI.ai returns a response that includes a unique call ID. You will use that ID in the next step to track the call.
Step 3: Poll the Call Status with a GET Request
Once the call is created, you need to know when it has finished. The template uses another HTTP Request node to fetch the current status of the call.
Call Status Node Configuration
- Method:
GET - URL: something like
https://api.vapi.ai/call/{{ $json.id }} - Headers:
Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_API_KEY>
The expression {{ $json.id }} refers to the ID returned by the previous Phone Call node. This GET request returns a payload that includes a status field, which indicates whether the call is still ongoing or has ended.
Step 4: Check If the Call Is Still Ongoing
The workflow uses an If node to inspect the status value from the Call Status response. The goal is to loop while the call is active and exit once it is complete.
Ongoing Call (If Node) Condition
- leftValue:
{{$json.status}} - operator:
notEquals - rightValue:
ended
This means:
- If
statusis notended, the call is still in progress and the workflow should wait and check again. - If
statusisended, the call is finished and the workflow should proceed to capture the summary.
Step 5: Wait Between Polls to Avoid Rate Limits
If the If node determines that the call is still ongoing, the workflow moves to a Wait node.
Wait 3s node: This node pauses the workflow for 3 seconds before looping back to the Call Status node.
You can adjust this delay depending on your needs. Shorter intervals will detect call completion faster but increase API usage. Longer intervals reduce API calls but may delay downstream actions slightly.
Step 6: Store the Assistant’s Summary When the Call Ends
When the If node detects that status = ended, the workflow goes to a Set node to capture the analysis summary from the VAPI.ai response.
Set Fields Node Mapping
In the template, the Set node creates a field called response and assigns it the assistant’s summary:
response = {{ $json.analysis.summary }}After this step, you have the call summary stored in the workflow data. You can then:
- Log it to a database such as MySQL, Postgres, or Airtable
- Attach it to a contact in a CRM such as HubSpot or Salesforce
- Send it to a Slack channel or email for your team
Example: Where the Assistant Summary Comes From
When a call is completed, VAPI.ai typically returns an analysis object that contains:
summary– a condensed description of the conversation- Other metadata or insights (depending on your VAPI.ai configuration)
The template assumes this structure and uses $json.analysis.summary as the source for the response field. If your payload structure is slightly different, adjust the expression accordingly.
Best Practices and Design Considerations
Use Webhooks When Available
The polling approach in this template is simple and easy to understand. However, it is not always the most efficient. If VAPI.ai supports webhooks for call updates or completion events, consider:
- Configuring a webhook in VAPI.ai that points to an n8n Webhook node
- Letting VAPI.ai notify n8n when the call status changes instead of continuously polling
This reduces API usage and improves scalability, especially at higher call volumes.
Handle Errors and Retries
Network issues, invalid inputs, or API errors can occur at any step. To make your workflow more robust:
- Use n8n’s On Fail workflows or error workflows to catch failures
- Implement retries with backoff for transient errors in HTTP Request nodes
- Log error details to a database or monitoring channel for later analysis
Secure Your Secrets
Never hard-code sensitive data like API keys or IDs directly in the node configuration. Instead:
- Store your VAPI.ai API key and other secrets in n8n credentials or environment variables
- Restrict permissions in your VAPI.ai account to the minimum required
- Rotate keys on a regular schedule
Rate Limits and Cost Management
Automated calling can generate significant traffic and cost if not carefully managed. To stay in control:
- Review VAPI.ai rate limits and pricing
- Keep polling intervals reasonable to avoid unnecessary requests
- Log call counts, durations, and statuses for auditing and forecasting
Idempotency and Duplicate Prevention
If your workflow is triggered by external systems or webhooks, it is possible to receive duplicate events. To avoid placing the same call multiple times:
- Use an external request or event ID to detect duplicates
- Store processed IDs in a database or in workflow metadata
- Skip call creation if a given ID has already been handled
Testing and Debugging Your Workflow
Before moving to production, thoroughly test the workflow in a safe environment.
- Use a staging or test assistant in VAPI.ai and a phone number you personally control.
- Enable logging of raw request and response bodies in the Phone Call and Call Status nodes so you can inspect what is being sent and received.
- Simulate edge cases:
- Call failures or rejected calls
- Very short calls and very long calls
- Unexpected status values
- If VAPI.ai offers sandbox or mock endpoints, use them to avoid real calls during early development.
Security, Privacy, and Compliance
Automated phone calls often involve personal data and sometimes call recording. To stay compliant:
- Check local laws and regulations around consent and call recording
- Only store personally identifiable information (PII) when necessary
- Ensure that any stored data is encrypted at rest and in transit
Advanced Enhancements and Ideas
- Dynamic assistantOverrides: Adjust tone, instructions, and response style based on customer segment, language, or call purpose.
- Event-driven callbacks: Replace polling with event-based webhooks from VAPI.ai if available for better scalability.
- Sentiment and follow-ups: Run sentiment analysis on the summary or transcript, then trigger follow-up workflows based on keywords or sentiment scores.
- Monitoring dashboard: Build a dashboard that tracks active calls, completion rates, and costs using n8n plus your preferred database or BI tool.
Production Readiness Checklist
Before you rely on this workflow in production, verify the following items:
- All placeholder values such as
assistantId,phoneNumberId, and API keys are replaced with correct production values. - Secrets are stored in n8n credentials or environment variables, not in plain text.
- The phone number associated with
phoneNumberIdis provisioned and allowed to make outbound calls to your target regions. - Error handling, logging, and retry policies are configured and tested.
- Legal and compliance checks for consent and recording are completed for each region you call.
Recap
This n8n and VAPI.ai workflow template gives you a solid foundation for automated, AI-powered phone calls. You learned how to:
- Trigger calls and pass in personalized variables
- Start a call via an HTTP POST to VAPI.ai
- Poll the call status in a controlled loop until it ends
- Capture and store the assistant’s summary for follow-up actions
With improvements such as webhooks, robust error handling, and secure secret management, you can turn this template into a production-grade voice automation system.
FAQ
Can I change how the assistant speaks on each call?
Yes. The assistantOverrides.variableValues object