Build an n8n Telegram AI Agent with OpenAI, Airtable & LangChain
Imagine having a smart study buddy or support assistant right inside Telegram, ready to understand both your texts and your voice notes. That is exactly what this n8n workflow template gives you: a Telegram AI agent that can listen, think, remember, and respond like a helpful assistant.
In this guide, we will walk through how the template works, when you might want to use it, and how to set it up step by step. We will keep all the technical bits accurate, but explain them in a friendly, practical way so you can actually ship this into your own Telegram chats.
What this n8n Telegram AI agent actually does
Let us start with the big picture. This n8n workflow connects Telegram, OpenAI, Airtable, and a LangChain-style agent so your bot can:
- Accept both text and voice messages from Telegram users
- Transcribe voice notes into text using OpenAI audio models (speech-to-text)
- Store and recall memory in Airtable, both short-term and persistent
- Use tools like a calculator, Wikipedia, and a content creator through a LangChain-style agent
- Reply directly back to the user in the same Telegram chat
So whether you want a study assistant, a lightweight support bot, or a personal AI helper, this pattern gives you a solid, flexible starting point.
When should you use this workflow?
This template is a great fit if you:
- Want a conversational Telegram bot that can handle both typing and voice notes
- Need your bot to remember things between messages, like preferences or previous questions
- Like the idea of an AI agent that can call tools such as a calculator or Wikipedia instead of trying to do everything in its head
- Prefer using n8n as the central place to orchestrate APIs, logic, and data
If that sounds like your use case, let us look at how the whole thing is wired together.
How the architecture fits together
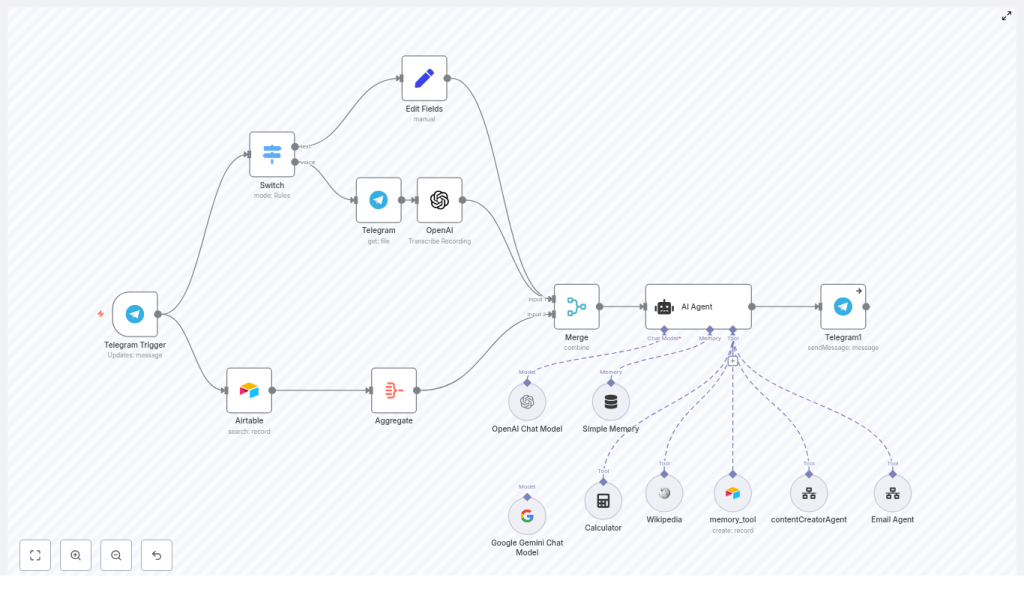
Here is the high-level flow of the n8n Telegram AI agent workflow:
- Telegram Trigger – Starts every time a new Telegram message arrives, text or voice
- Switch node – Checks if the message is text or a voice note and routes it accordingly
- Telegram (get file) + OpenAI transcription – If it is a voice note, downloads the file and converts it to text
- Set / Edit Fields – Normalizes everything into a single text field so the agent has one consistent input
- Airtable + Aggregate + Merge – Pulls relevant memory from Airtable and merges it with the incoming message
- AI Agent node (LangChain-style) – Uses tools, memory, and the message to decide what to say
- Telegram sendMessage – Sends the AI’s reply back to the user in the same chat
Let us break this down into steps you can follow in n8n.
Step-by-step: building the Telegram AI agent in n8n
1. Set up your Telegram bot and trigger
First, you need a Telegram bot that n8n can talk to.
- Open Telegram and chat with @BotFather
- Create a new bot and copy the bot token BotFather gives you
- In n8n, create Telegram credentials using that token
- Add a Telegram Trigger node and configure it to receive Updates: message
From now on, whenever someone messages your bot, n8n will receive that message and kick off the workflow.
2. Use a Switch node to separate text and voice
Next, you want to treat text and voice messages slightly differently. That is where the Switch node comes in.
Configure the Switch node with rules that look for:
message.textfor plain text messagesmessage.voice.file_idfor voice messages
This way, text messages can go straight to the agent pipeline, while voice messages get routed through a download and transcription step first.
3. Download and transcribe Telegram voice messages
When the Switch detects a voice message, you will:
- Add a Telegram node with resource: file to download the audio using the
file_id - Pass that audio file into an OpenAI transcription node (or another speech-to-text provider if you prefer)
The transcription node returns text, so by the end of this branch you have a clear text version of what the user said in their voice note. That text will be used just like a normal text message.
4. Normalize the input and attach memory
Now you want to give the AI agent a clean, consistent input, no matter how the user contacted you.
Use a Set or Edit Fields node to create a unified payload, for example:
{ text: "…user message or transcript…"
}
At the same time, you can pull in memory from Airtable:
- Use an Airtable node to look up stored facts or short history for the current user or chat
- Use Aggregate to combine or summarize any retrieved rows
- Use a Merge node to combine the user’s current message with the relevant memory context
The goal is simple: when the AI agent runs, it sees both the latest user message and any useful background information.
5. Configure the LangChain-style AI Agent node
The heart of the workflow is the AI Agent node, which behaves like a LangChain-style agent inside n8n. This is where you tell the AI who it is, what tools it can use, and how it should respond.
Set up the AI Agent node with:
- System message and role instructions Define the agent’s role, such as a study assistant or helpful mentor. Describe:
- What it is good at
- Which tools it can call
- The tone and format of its responses
- Language model credentials Connect your OpenAI credentials. You can also plug in a Gemini model if your setup supports it.
- Tool connectors Add tools the agent can call, such as:
- Calculator
- Wikipedia
- Airtable memory creator
contentCreatorAgent- Email Agent
These tools are exposed to the agent so it can decide when to use them.
- Memory buffer Configure a memory buffer keyed by the Telegram chat id. This keeps conversations coherent across multiple messages for each user.
The result is an AI agent that does not just respond blindly, but can think with context, call tools when needed, and remember what was said before.
6. Send the AI’s reply back to Telegram
Finally, take the output from the AI Agent node and connect it to a Telegram sendMessage node.
- Map the agent’s reply text to the
textfield - Map the correct chat id from the incoming Telegram message so the reply shows up in the right conversation
Once this is wired up, you can message your bot on Telegram and watch it answer using the tools and memory you configured.
Prompt engineering and configuration tips
To get the most out of this Telegram AI agent workflow, a few configuration details make a big difference.
- System message Be explicit about the agent’s role. For example, if it is a study assistant, tell it:
- How to explain concepts
- When to use tools like the calculator or Wikipedia
- What tone to use (friendly, concise, detailed, etc.)
- Memory size Keep Airtable memory entries short, ideally one-liners. Use:
- The agent’s internal memory buffer for short-term session context
- Airtable for long-term facts or preferences that should persist
- Tool access rules Consider when the agent should call external tools. If it calls them too often, you might:
- Increase latency for users
- Increase your API costs
You can shape this behavior in the system prompt.
- Session key Use the Telegram chat id as the key for memory entries. This makes sure user A never sees user B’s context or history.
Security, privacy, and cost considerations
Security & privacy
Because this workflow touches user messages and external APIs, it is worth tightening up a few basics.
- Store all API keys, such as OpenAI, Airtable, and Telegram, in n8n credentials. Avoid hardcoding secrets directly inside nodes.
- Be careful with personally identifiable information (PII) in Airtable. If you must store sensitive data, consider encryption or avoid saving it altogether.
- If you do not want the bot open to everyone, add a simple whitelist check in the workflow so only specific user ids can interact with it.
Costs
LLM and transcription calls are powerful, but they are not free. To keep costs under control:
- Be mindful of how often you call transcription or the language model, especially for long or non-critical messages
- Monitor token usage and consider summarizing or compressing long histories before sending them to the model
- Use conditional logic in n8n to skip heavy operations when they are not needed
Troubleshooting common issues
If something does not work the first time, here are a few places to check.
- Audio files not downloading Verify:
- Your Telegram node credentials are correct
- The audio file size is within Telegram’s limits and supported by your transcription provider
- Poor transcription quality Confirm the audio format is supported and, if possible, pre-process audio:
- Normalize volume levels
- Reduce background noise
- Mapping or data errors Use the n8n Execution log to inspect each node’s input and output. This is very helpful for catching wrong JSON paths, such as an incorrect reference to the Telegram
chat id. - Too many or slow LLM calls Add conditions to throttle calls. For quick, low-stakes answers, you might:
- Use simpler prompt templates
- Cache common responses
Scaling and production deployment
Once your Telegram AI agent works nicely for a few users, you might want to move it into a more robust setup.
For production use, consider:
- Running n8n in a managed environment or container with persistent storage
- Using a queue or worker pattern for heavy tasks like transcription so they do not block other flows
- Enabling retries and dead-letter handling for temporary API failures
- Adding monitoring and alerts for failed executions so you can catch issues early
Advanced ideas to upgrade your Telegram AI agent
Once the basic workflow is live, you can gradually layer on more capabilities.
- Add a simple authentication or permission model so only certain users can run specific commands
- Introduce text-to-speech (TTS) so the bot can respond with voice messages as well as text
- Schedule periodic summarization of long chat histories and store condensed notes in Airtable to save tokens
- Integrate more tools, such as:
- Calendar or scheduling APIs
- Knowledge bases or documentation search
- CRMs or ticketing systems for support workflows
Wrapping up
This n8n Telegram AI agent template gives you a practical, extensible blueprint for building a smart bot that:
- Understands both text and voice messages
- Uses OpenAI to transcribe and respond intelligently
- Stores memory in Airtable to keep conversations coherent
- Calls tools like calculators, Wikipedia, and content creators through a LangChain-style agent
Whether you are building a study companion, a lightweight support bot, or a personal AI helper, this workflow lets you move from idea to working prototype quickly, and then scale it as you go.
Ready to try it? Export the n8n workflow, connect your Telegram, OpenAI, and Airtable credentials, and send a few messages to your bot. Start simple, then iterate on prompts, tools, and memory as you see how users interact.
Call to action
If this guide helped you understand how to build a Telegram AI agent in n8n, consider subscribing for more tutorials on n8n automation and AI integrations. Need help implementing or customizing this workflow for your own use case? Reach out for a consultation or a professional setup, and we can help you get from idea to production.
Keywords: n8n, Telegram bot, OpenAI transcription, LangChain, Airtable memory, workflow automation, voice messages, Telegram AI agent, n8n templates.