Mailing List Analysis with n8n Automation
Systematic analysis of mailing lists is essential for identifying B2B opportunities, prioritizing outreach, and maintaining clean subscriber data. Doing this manually does not scale. In this article, you will learn how to use an n8n workflow template to fully automate mailing list analysis: from retrieving subscribers in MailerLite, through domain and website enrichment, to AI-driven classification and final storage in Google Sheets.
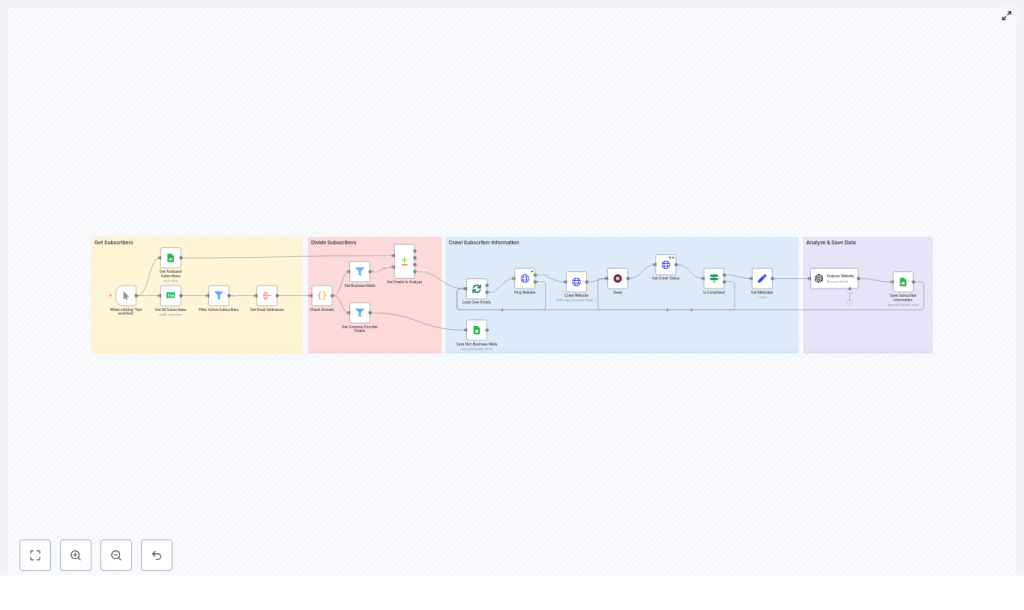
The workflow described here is based on the “Mailing List Analysis” template and is designed for automation engineers, growth teams, and data professionals who want a robust, repeatable process.
Business case and automation goals
Manual review of large subscriber lists is slow, inconsistent, and often misses valuable signals. By orchestrating this process in n8n, you can:
- Quickly distinguish business emails from consumer email providers to surface B2B leads.
- Enrich email domains with website metadata that reveals company focus, services, and market segment.
- Feed AI models with structured content to classify website niche and offerings.
- Persist enriched records in Google Sheets or downstream CRMs for segmentation and sales workflows.
Automation also improves repeatability. Once configured, the workflow can run on a schedule, continuously updating your lead intelligence without manual intervention.
High-level workflow architecture
The n8n template implements a multi-stage pipeline that can be summarized as follows:
- Retrieve subscribers from MailerLite and filter to active contacts.
- Extract and aggregate email addresses for downstream processing.
- Classify each email as consumer vs business (custom domain).
- Persist consumer emails for reference and route business domains to enrichment.
- Ping and crawl each business domain using an external crawler (for example, crawl4ai).
- Extract website metadata and content needed for analysis.
- Use an AI model (OpenAI via LangChain or similar) to infer niche and services.
- Write enriched subscriber data into Google Sheets for ongoing use.
The following sections walk through the main components of this workflow, along with configuration considerations and best practices for production deployments.
Triggers and list acquisition
Workflow trigger strategy
The template ships with a Manual Trigger node so you can run and debug the workflow interactively. For production environments, it is recommended to replace or complement this with a scheduled trigger, such as a Cron node, to execute the pipeline on a recurring basis (for example hourly or nightly). This keeps your mailing list intelligence continuously up to date.
Subscriber retrieval from MailerLite
The Get All Subscribers (MailerLite) node is responsible for fetching subscribers from your MailerLite account. You must configure your MailerLite API credentials in n8n before this node can operate.
Once subscribers are retrieved, the workflow applies a filter:
- Filter Active Subscribers – only records where
status == "active"are passed downstream. This avoids processing unsubscribed, bounced, or inactive contacts, which would waste crawler and API capacity.
After filtering, an Aggregate (Get Email Addresses) node collects email values into a structured list. This aggregation enables batch processing and simplifies later logic in the code and batch nodes.
Email classification and routing logic
Domain inspection with custom JavaScript
The workflow uses a Code node to classify email domains. This node runs custom JavaScript that inspects each email, extracts the domain, and determines whether it belongs to a common consumer provider or a custom/business domain.
The logic relies on a predefined list of consumer providers such as Gmail, Yahoo, Outlook, and similar services. Domains not in this list are treated as potential business domains and routed to the enrichment path.
// Simplified example used in the Code node
const commonDomains = ['gmail','yahoo','outlook','hotmail','aol','icloud','protonmail','zoho','yandex','live','msn','gmx'];
const result = [];
for (const item of $input.all()) { for (const email of item.json.email) { const domain = email.split('@')[1].toLowerCase(); const baseDomain = domain.split('.')[0]; result.push({ email, isCustomDomain: !commonDomains.includes(baseDomain) }); }
}
return result;In production, you can expand this list or connect a domain intelligence API to improve classification quality. Some teams also add MX record checks or WHOIS lookups for additional signals.
Branching paths for consumer vs business emails
After classification, the workflow splits into two main branches:
- Business emails (custom domains) – routed to a sequence of nodes that ping the associated domain, trigger a crawl, and perform AI analysis of the website.
- Common provider emails – stored directly in Google Sheets (or another datastore) for record keeping. These are typically excluded from web crawling and AI analysis because they rarely map directly to a company website.
This routing ensures that expensive operations such as crawling and AI inference are reserved for high-value business leads.
Controlled processing with batching and rate management
SplitInBatches for concurrency control
The SplitInBatches node is central to managing throughput. It processes a configurable number of items at a time, which allows you to:
- Respect rate limits imposed by crawlers and third-party APIs.
- Prevent overloading your infrastructure or external services.
- Tune performance by adjusting batch sizes as your data volume grows.
For larger lists, it is common to combine SplitInBatches with Wait or Sleep nodes to introduce pauses between batches and to avoid burst traffic to external services.
Domain validation, crawling, and content extraction
Domain ping and crawl initiation
For each business domain, the workflow performs a validation and crawl sequence. Typical nodes in this segment include:
- Ping Website – checks whether the domain is reachable before initiating a full crawl.
- Crawl Website – triggers an external crawler, such as crawl4ai, to fetch the site content.
- Get Crawl Status – polls the crawler API until the crawl completes.
A combination of Wait/Sleep nodes and status checks ensures that the workflow does not proceed to analysis before the crawler has finished. This pattern is important for long-running or asynchronous crawls.
Metadata extraction for downstream analysis
Once the crawl is complete, a Set node (Get Metadata) structures the relevant information from the crawler response. Typical fields include:
- Page title.
- Meta description.
og:locale(or equivalent locale information).- Scraped markdown or HTML content that will be fed into the AI model.
By standardizing these outputs, you simplify the prompt and schema expected by the AI node and ensure consistent data going into your enrichment layer.
AI-driven website analysis
Using OpenAI or LangChain for classification
The Analyze Website step uses an AI model to transform raw website content into structured insights. The template uses an OpenAI model (optionally orchestrated through LangChain) to process the metadata and content captured from the crawler.
The AI node typically receives a prompt that asks it to return a JSON object describing:
- What the website is about (short description).
- The primary niche or industry.
- The key services or products offered.
The AI response is parsed into fields such as about, niche, and services. These attributes are then attached to the corresponding email or domain record and passed to the storage layer.
Data persistence and downstream integration
Storing enriched records in Google Sheets
The final step in the template writes all relevant information into a Google Sheet using the Google Sheets node. Typical fields include:
- Email address.
- Flag indicating
isCustomDomain. - Website description (
about). - Niche or industry classification.
- List of services or offerings.
The sheet effectively becomes your canonical dataset for segmentation, outreach planning, or further processing in a CRM. You can also use this sheet later for deduplication and caching to avoid reprocessing already analyzed domains.
Credential configuration requirements
Before running the workflow, ensure that the following credentials are configured in n8n:
- MailerLite API credentials – used by the Get All Subscribers node.
- Google Sheets OAuth2 credentials – required to write and update rows in your spreadsheet.
- Crawler authentication – for example, HTTP header authentication for crawl4ai or any other crawler you use.
- OpenAI API credentials – needed for AI analysis if you use OpenAI-based nodes or LangChain integrations.
Review access scopes and key rotation policies to align with your organization’s security standards.
Operational best practices
Throttling and rate control
Combine SplitInBatches with Sleep/Wait nodes to keep API usage within allowed limits. Adjust batch sizes and delays based on:
- Limits defined by MailerLite, your crawler, and OpenAI.
- Expected list size and desired throughput.
- Infrastructure capacity on your n8n instance.
Deduplication and caching
To optimize cost and performance, avoid reprocessing subscribers or domains you have already analyzed. A common pattern is to:
- Use a CompareDatasets node to compare newly fetched emails against rows stored in Google Sheets.
- Skip emails or domains that already exist in your enriched dataset.
- Cache website analysis results and reuse them if the domain appears again.
Improving domain classification
The initial consumer domain list is intentionally simple. For more reliable classification:
- Maintain an up-to-date list of public email providers.
- Integrate a third-party enrichment API to get company vs personal signals.
- Use DNS queries (MX records) or WHOIS information to identify corporate domains.
Email deliverability checks
Integrating an email verification provider early in the workflow can significantly improve data quality. Consider connecting services such as ZeroBounce or Mailgun’s verification API to:
- Remove invalid or risky addresses before crawling and AI analysis.
- Reduce bounce rates in subsequent campaigns.
Error handling and observability
Production workflows should handle failures gracefully. In n8n, you can:
- Use retryOnFail options on nodes that depend on external APIs.
- Implement onError branches to capture failed crawls, unreachable domains, or AI timeouts.
- Log errors to a separate Google Sheet or notify your team via Slack or email.
This approach gives you visibility into issues without interrupting the entire pipeline.
Security, privacy, and compliance
Mailing list analysis involves handling personally identifiable information, especially email addresses. To remain compliant with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA, keep the following checklist in mind:
- Restrict access to the Google Sheet or any datastore containing PII.
- Use secure credential management in n8n and rotate API keys regularly.
- Mask or hash email addresses if you generate public reports or dashboards.
- Document which external services (crawlers, AI providers) receive subscriber data and under what legal basis.
- Ensure that your data processing agreements cover the use of AI and crawling services for this purpose.
Scaling and cost optimization
As your mailing list grows, so do crawl and AI inference costs. To scale efficiently:
- Prioritize high-value domains such as those with recent engagement or strong lead scoring signals.
- Sample large lists when first rolling out the workflow, then expand coverage as you validate ROI.
- Store concise metadata and AI summaries rather than full page content to reduce storage needs.
- Leverage caching so that domains are crawled and analyzed only when necessary.
Next steps: deploying and customizing the template
To put this workflow into practice:
- Import the Mailing List Analysis n8n template and configure the required credentials (MailerLite, Google Sheets, crawler, OpenAI).
- Run the workflow on a small subset of subscribers to validate outputs in your Google Sheet.
- Iterate on:
- Domain classification logic and consumer domain lists.
- Crawl depth and allowed paths for your crawler.
- AI prompts and output schema to better match your target industries and service categories.
Once validated, schedule the workflow and integrate the enriched data with your CRM or marketing automation platform to operationalize lead scoring and segmentation.
Import the workflow in n8n, connect your services, and start generating structured insights from your mailing list with minimal manual effort.