Rank Tracker Postgres Template for n8n: Turn SEO Data Into Daily Momentum
From Manual Checks To A Calm, Automated SEO Rhythm
If you have ever spent your morning clicking through rank trackers, exporting CSVs, and stitching together reports, you know how quickly SEO work can turn into busywork. The more keywords you care about, the more time you spend checking them instead of acting on them.
The Rank Tracker Postgres template for n8n is built to change that rhythm. It takes the repetitive part of rank tracking off your plate and replaces it with a reliable, daily pipeline that quietly runs in the background while you focus on strategy, content, and experiments.
At its core, this template connects BigQuery (for search impressions and rankings) with PostgreSQL (for long term storage and analysis), then uses n8n to orchestrate everything. The result is a lean, automated system that:
- Tracks rankings for a curated list of keywords in a
tracked_keywordstable - Stores daily ranking metrics in
rank_tracking_by_keywords - Surfaces top ranking keyword opportunities in
top_ranking_keywords
Instead of checking rankings manually, you get a steady flow of fresh, structured data ready to query, visualize, and act on.
Shifting Your Mindset: From Reactive Reporting To Proactive Growth
Automation is not just about saving time. It is about creating the space to think, plan, and make better decisions. When rank tracking runs itself, you can:
- Spot quick wins where you already rank in Top 3, Top 10, or Top 20 but have not fully optimized yet
- Build a consistent historical dataset that reveals trends, seasonality, and the impact of your experiments
- Free your team from repetitive checks so they can invest energy in content, CRO, and technical improvements
This template is ideal if you want a repeatable, cost aware SEO pipeline that quietly powers your dashboards and decision making, without the overhead of a heavy enterprise tool.
What This n8n Rank Tracker Template Actually Does
Here is the high level journey your data takes through the workflow:
- n8n loops through a list of domains and BigQuery tables you define.
- It checks the last date you collected data so it only pulls new rows from BigQuery.
- It reads your tracked keywords from Postgres and builds a filtered query.
- BigQuery aggregates clicks, impressions, position, and CTR per date, keyword, URL, and device.
- n8n upserts those metrics into Postgres tables so you keep a clean, deduplicated history.
- A second BigQuery query finds keyword opportunities and stores them in a dedicated table.
From there, you can plug your Postgres data into Looker, Data Studio, Metabase, or any BI tool and start exploring.
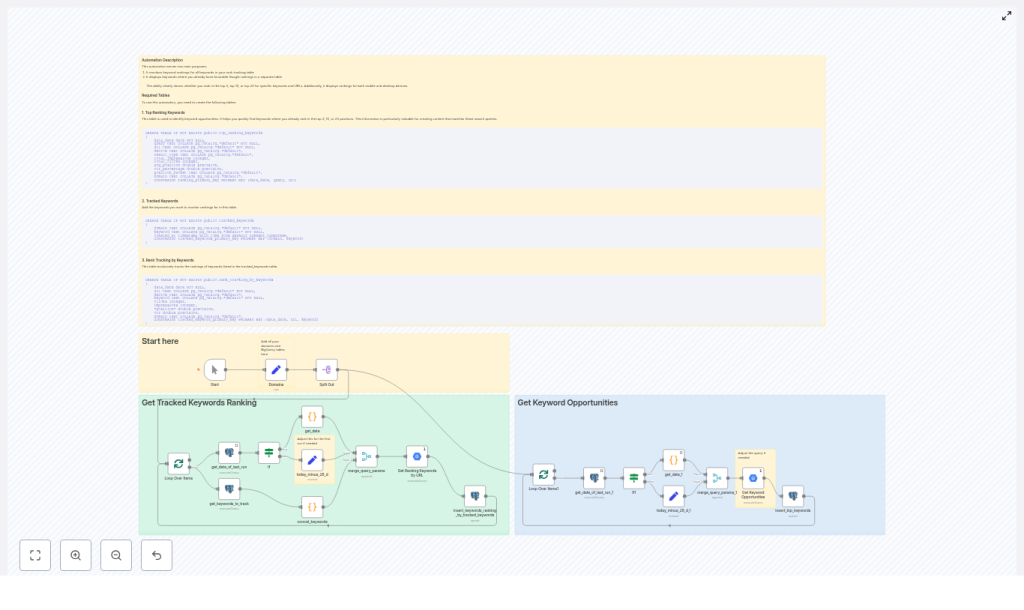
Designing The Foundation: Required Postgres Tables
Before the workflow can become part of your daily stack, you need a solid storage layer. The template uses three Postgres tables to organize your data and keep it query friendly.
1. top_ranking_keywords – Your Opportunity Radar
This table stores aggregated keyword opportunities, including impressions, clicks, average position, and position buckets such as Top 3, Top 10, or Top 20.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS public.top_ranking_keywords
( data_date date NOT NULL, query text NOT NULL, url text NOT NULL, device text, result_type text, total_impressions integer, total_clicks integer, avg_position double precision, ctr_percentage double precision, position_bucket text, domain text, CONSTRAINT ranking_primary_key PRIMARY KEY (data_date, query, url)
)
2. tracked_keywords – The Keywords You Care About Most
This table defines the curated list of keywords you want to follow. Keeping this list focused helps you stay aligned with business goals.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS public.tracked_keywords
( domain text NOT NULL, keyword text NOT NULL, created_at timestamp with time zone DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, CONSTRAINT tracked_keywords_primary_key PRIMARY KEY (domain, keyword)
)
3. rank_tracking_by_keywords – Your Daily Rank History
This table holds the daily performance snapshot for each keyword, URL, and device. It becomes the backbone of your trend analysis and reporting.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS public.rank_tracking_by_keywords
( data_date date NOT NULL, url text NOT NULL, device text, keyword text NOT NULL, clicks integer, impressions integer, "position" double precision, ctr double precision, domain text, CONSTRAINT tracked_keyword_primary_key PRIMARY KEY (data_date, url, keyword)
)
Inside The Workflow: How The n8n Template Flows
Once your tables exist, the n8n workflow takes over the daily heavy lifting. The template is built around two primary flows on the n8n canvas: Get Tracked Keywords Ranking and Get Keyword Opportunities. Together, they keep your rank tracking loop running with minimal manual touch.
Flow 1: Get Tracked Keywords Ranking
- Start / Domains / Split Out – You provide a list of domains and their associated BigQuery tables. The workflow loops through each domain so you can scale across multiple sites without rewriting anything.
- get_date_of_last_run – This node queries Postgres to find the most recent
data_datealready stored. That date becomes your lower bound, which keeps BigQuery costs in check by only pulling new data. - get_keywords_to_track – Here, n8n reads from the
tracked_keywordstable and builds a keyword list for the SQLWHEREclause. You are in full control of what gets tracked. - Get Ranking Keywords by URL – A BigQuery node that aggregates clicks, impressions, position, and CTR for each date, keyword, URL, and device. It filters the dataset by your tracked keywords and the new date range.
- insert_keywords_ranking_by_tracked_keywords – Finally, n8n upserts the results into
rank_tracking_by_keywordsin Postgres, keyed bydata_date,url, andkeyword. This keeps your history clean and consistent.
Flow 2: Get Keyword Opportunities
- Get Keyword Opportunities – A separate BigQuery node focuses on discovering opportunity queries. It aggregates performance, calculates average position, and buckets queries into ranges such as Top 3, Top 10, or Top 20.
- Those aggregated rows are then upserted into
top_ranking_keywords, giving you a dedicated table to mine for quick wins.
Together, these flows turn raw search impression data into a living rank tracking system that supports both daily monitoring and long term insights.
Step By Step: Turning The Template Into Your Daily Workflow
You do not need to rebuild anything from scratch. Follow these steps and you will have a working automated rank tracker that runs on its own schedule.
- Provision Postgres
Create the three tables shown above in your Postgres instance. This is where your rankings, tracked keywords, and opportunities will live. - Configure BigQuery Access
Make sure the BigQuery project and tables that store your search impressions and sum_position data are accessible from the n8n service account. Proper permissions here are essential for smooth automation. - Import The Template Into n8n
Download the JSON workflow and import it into your n8n instance. The entire pipeline, including both flows, will appear on your canvas ready for configuration. - Set Credentials
In n8n, add your Postgres and Google BigQuery credentials. Assign these credentials to the corresponding nodes in the workflow so n8n can read and write data securely. - Populate The Domains Node
In the Domains node, define each domain you want to track along with the BigQuery table paths, for example:searchdata_url_impressionsearchdata_site_impression
This is what allows the workflow to scale across multiple sites with one template.
- Add Tracked Keywords
Insert the keywords you care about into thetracked_keywordsPostgres table for each domain. This is your chance to focus the system on terms that matter most for revenue, leads, or strategic topics. - Run A Test
Start with a single domain and run the workflow manually. Confirm that:- BigQuery queries run without errors
- Credentials are valid
- Data is correctly upserted into
rank_tracking_by_keywordsandtop_ranking_keywords
This quick test gives you confidence before you scale.
- Schedule For Daily Automation
Once everything looks good, enable a schedule in n8n. A daily run is recommended so you always have a fresh, up to date view of your rankings and opportunities.
Smart SQL Choices: How The Template Keeps Data Useful And Costs Controlled
The BigQuery nodes in this template are written with performance and practicality in mind. They use a filtered approach so you get the data you need without unnecessary cost.
- Date based filtering – Only queries newer than the last stored
data_dateare pulled, which keeps each run incremental. - Data quality filters – Only non anonymized queries and rows with impressions above a minimum threshold are considered, so you focus on meaningful traffic.
- Position handling – Position is derived and rounded to make trend analysis and reporting easier.
You can adjust thresholds such as minimum impressions or maximum position to match your own data quality standards and reporting goals.
Best Practices To Get The Most From Your Automated Rank Tracker
Once the template is running, a few intentional choices will help you turn raw data into consistent growth.
- Stay focused with tracked_keywords
Do not track everything. Keeptracked_keywordslimited to queries that map directly to your business goals or key content clusters. - Monitor BigQuery costs
The incremental date filter already helps, but you can further manage costs by tightening impression thresholds or limiting the scope of domains and tables. - Lean on batching
The workflow uses splitInBatches so it can scale per domain without overwhelming Postgres or BigQuery. This makes it safer to grow the number of domains or keywords over time. - Backfill with intention
If you want historical data, run controlled backfills by date range instead of a single massive query. This keeps costs and runtime predictable. - Tag by device
Use the device field (mobile, desktop) to spot platform specific differences. Often, mobile and desktop rankings behave differently, and this view can uncover new optimization angles.
Troubleshooting: Turning Roadblocks Into Learning Moments
Every automation journey includes a bit of debugging. Here are some common issues and how to resolve them so you can keep moving forward quickly.
- Missing credentials
If nodes fail due to authentication, double check your BigQuery and Postgres credentials in n8n. Re run a single domain test once they are fixed. - SQL syntax errors
Verify that the BigQuery table paths and column names in the template match your actual dataset, especially fields likesum_positionandimpressions. - Duplicate keys on upsert
Ensure that thematchingColumnssettings in the Postgres upsert nodes align with your primary keys, for example(data_date, query, url)or(data_date, url, keyword). - Slow performance on large datasets
Tighten filters, reduce batch sizes, or increase BigQuery compute slots. A few small adjustments can dramatically improve speed and reliability.
Going Further: Extend The Template To Fit Your Stack
Once your core rank tracking loop is stable, you can turn this template into a central piece of your SEO automation system.
- Notify your team in real time
Add a Slack or email node to alert stakeholders whenever new Top 3 keyword opportunities appear. This keeps everyone aligned and ready to act. - Build live dashboards
Connect your Postgres tables to tools like Looker, Data Studio, or Metabase. Visualize trends by keyword, URL, device, or domain and share them across your organization. - Enhance result_type insights
Join your data with schema that identifies FAQ, HowTo, or review result types per URL. This can help you understand how rich results are affecting visibility and CTR.
Each small extension compounds the value of your automated pipeline and brings you closer to a fully integrated SEO data environment.
Your Next Step: Turn This Template Into A Daily Habit
The Rank Tracker Postgres template for n8n gives you a practical, cost aware path to daily keyword rank tracking. With a short one time setup, you unlock a long term asset:
- Automated rank collection for your most important keywords
- A clean historical dataset for trend and impact analysis
- A dedicated opportunity table that highlights near term wins
You do not have to overhaul your entire stack to start. Begin with a single domain, a focused keyword list, and a daily schedule. As the workflow proves itself, you can expand, refine, and build additional automations on top of it.
Ready to put your rank tracking on autopilot?
- Import the template into n8n
- Create the Postgres tables
- Configure credentials and run a test for one domain
From there, iterate. Adjust thresholds, refine keywords, plug in dashboards, and keep improving. Every small tweak makes your SEO process more scalable, more focused, and more resilient.