AI Visa Requirement Checker with n8n & Weaviate
This reference guide documents the Visa Requirement Checker n8n template, which automates visa eligibility checks using Cohere embeddings, a Weaviate vector database, and an Anthropic-powered agent. It explains the overall architecture, node-by-node behavior, configuration details, and operational considerations so you can deploy, audit, and customize the workflow with confidence.
1. Solution Overview
The Visa Requirement Checker workflow turns unstructured visa rules and immigration guidance into a searchable knowledge base that can be queried using natural language. It is designed for use cases such as travel agencies, internal compliance tools, or customer-facing visa guidance assistants.
1.1 Key capabilities
- Semantic search over large visa and immigration documents using vector embeddings.
- Natural-language query handling via an HTTP webhook or chat-style front end.
- Context-aware reasoning with Anthropic Chat and an n8n Agent node.
- Structured logging of interactions to Google Sheets for auditing and workflow integration.
- Incremental updates by adding or refreshing documents in the Weaviate vector store.
1.2 Typical data flow
- A client system (web app, chatbot, internal tool) sends a POST request to the n8n Webhook node with traveler details and a free-text question.
- The workflow retrieves relevant visa rules from Weaviate using Cohere embeddings and a semantic search query.
- The Anthropic Chat node, orchestrated by an Agent, reasons over the retrieved snippets and the conversation history.
- The Agent returns a concise, actionable answer and logs the interaction to Google Sheets for traceability.
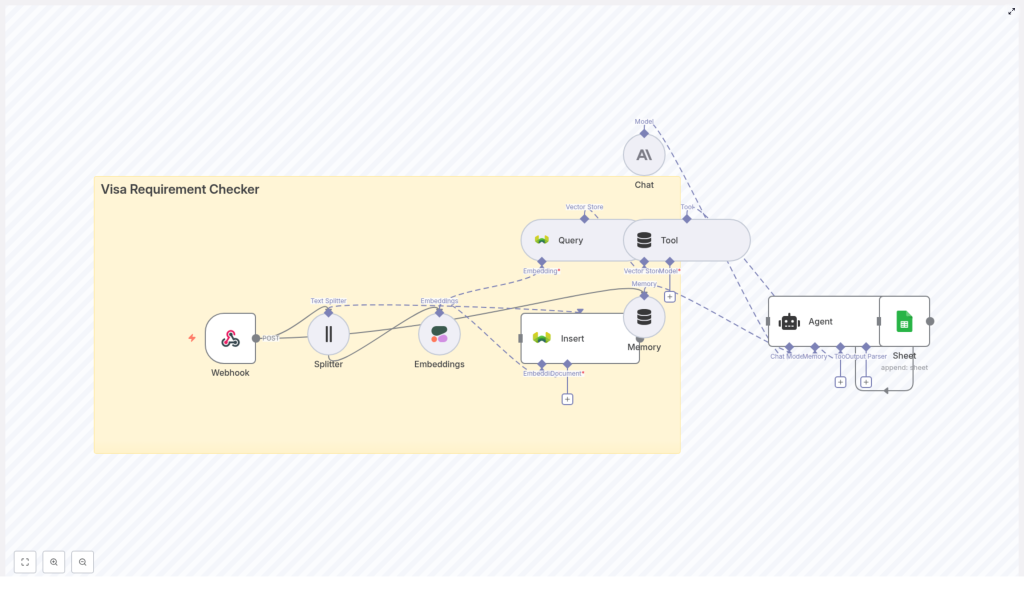
2. Architecture & Components
The workflow is structured around several core components:
- Webhook node for inbound visa queries.
- Text Splitter node for preprocessing source documents.
- Embeddings node (Cohere) to generate vector representations.
- Weaviate Insert and Query nodes for vector storage and retrieval.
- Tool node to expose Weaviate search as a tool to the Agent.
- Memory (Buffer Window) node to persist recent conversation context.
- Chat (Anthropic) node and Agent for reasoning and response generation.
- Google Sheets integration (within the Agent flow) for logging.
The vector index is typically named visa_requirement_checker and stores both embeddings and metadata so that the LLM can ground its answers in authoritative sources.
3. Node-by-Node Breakdown
3.1 Webhook node
The Webhook node is the entry point for all user queries. It accepts HTTP POST requests and can be integrated with:
- Web or mobile front ends.
- Chat interfaces or bots.
- Backend services that need automated visa checks.
A typical JSON payload includes structured traveler attributes and can also include a free-text question. For example:
{ "nationality": "India", "destination": "Germany", "passportType": "Ordinary", "purpose": "Tourism", "departureDate": "2025-05-20", "returnDate": "2025-05-30"
}In production, it is recommended to:
- Secure the webhook with a secret token, IP allowlist, or both.
- Validate the incoming JSON schema to avoid malformed payloads.
- Return appropriate HTTP status codes (for example 400 for invalid input, 200 for success) from the workflow.
3.2 Text Splitter node
The Text Splitter node processes long visa or immigration documents before they are embedded. It divides each document into smaller chunks, which:
- Improves embedding efficiency and retrieval performance.
- Helps preserve local context while avoiding overly large vector payloads.
Typical configuration:
- Chunk size: around 400 characters.
- Chunk overlap: around 40 characters.
This overlap is important so that clauses or sentences that cross chunk boundaries still have enough shared context. For very long legal texts, you can slightly increase overlap to reduce the chance of splitting critical sentences mid-way. Avoid extremely small chunk sizes, which can fragment the rules and reduce semantic coherence.
3.3 Embeddings node (Cohere)
The Embeddings node uses Cohere to transform text chunks and user queries into high-dimensional vectors. These embeddings are then stored in, or used to query, the Weaviate vector index.
Core responsibilities:
- Generate embeddings for each chunk of the source documents during ingestion.
- Generate an embedding for each incoming user query at runtime.
Configuration considerations:
- Credentials: set a valid Cohere API key in n8n credentials.
- Model selection: choose a model that balances latency, cost, and semantic accuracy for your document set.
- Error handling: monitor for rate-limit or authentication errors and handle them gracefully in n8n (for example, by using error workflows or retries where appropriate).
3.4 Weaviate Insert node (vector store)
The Weaviate Insert node populates the vector store with document chunks and their associated metadata. Each record typically includes:
- The embedding vector generated by Cohere.
- The original text chunk.
- Metadata fields such as:
countrydoc_titleeffective_datesource_url
The template uses a Weaviate class or index named visa_requirement_checker. Before inserting data:
- Ensure the Weaviate instance is reachable (self-hosted or managed).
- Define the schema with the required properties and vectorization settings.
- Verify that authentication and any TLS settings are correctly configured in the n8n Weaviate credentials.
3.5 Weaviate Query node & Tool node
At query time, the workflow uses the Weaviate Query node to perform semantic search against the visa_requirement_checker index using the embedding of the user question.
The retrieved snippets are then exposed to the Agent via a Tool node:
- The Weaviate Query node returns the most similar chunks along with their metadata.
- The Tool node wraps this retrieval capability so that the Anthropic-based agent can invoke it as needed.
If the query returns no results, typical causes include:
- No documents were inserted into Weaviate.
- Embeddings were not generated or stored correctly.
- Schema or index name mismatches between Insert and Query nodes.
3.6 Memory (Buffer Window) node
The Memory node maintains a rolling context window of recent messages. This enables multi-turn interactions such as:
- Agent follow-up questions about missing details (for example, passport type, travel dates).
- User clarifications or corrections.
Configuration usually involves:
- Choosing the number of past messages to retain.
- Defining which fields are treated as user messages vs. assistant messages.
Keep the window size within the token limits of the Anthropic model you are using. Oversized memory windows can increase latency and cost, and may push out the most relevant parts of the context.
3.7 Chat (Anthropic) node & Agent
The Anthropic Chat node provides the language model that interprets the user question, reasons over the retrieved visa rules, and generates the final answer. The n8n Agent orchestrates:
- Tool usage (Weaviate search).
- Memory integration (Buffer Window).
- Prompting and response formatting.
Typical configuration steps:
- Set Anthropic API credentials in n8n.
- Configure the Chat node with the desired model and temperature settings.
- Define a system prompt that instructs the model to:
- Rely primarily on retrieved Weaviate sources.
- Cite source URLs and effective dates when available.
- Avoid speculating beyond the provided documents.
The Agent also typically appends a structured log entry to Google Sheets after each interaction. This log can contain:
- Input parameters (for example, nationality, destination, purpose).
- The final answer text.
- Timestamps and any relevant metadata.
4. Setup & Configuration Steps
4.1 Deploy the n8n workflow
- Import the provided workflow JSON into your n8n instance, or recreate the nodes manually following the template diagram.
- Enable the workflow and expose the Webhook node URL.
- Secure the webhook using a secret path segment, headers, or network-level controls.
4.2 Configure the embedding provider (Cohere)
- Obtain a Cohere API key and add it as an n8n credential.
- Select an embedding model suitable for your language and document characteristics.
- Run a small test set of documents and queries to verify embedding quality and latency.
4.3 Configure Weaviate
- Provision a Weaviate instance, either self-hosted or via a managed service.
- Create a class or index named
visa_requirement_checkerwith fields such as:countrydoc_titleeffective_datesource_url
- Connect n8n to Weaviate using the appropriate credentials and endpoint.
- Insert your initial corpus of visa and immigration documents using the Text Splitter, Embeddings, and Insert nodes.
4.4 Connect Anthropic
- Add your Anthropic API key to n8n credentials.
- Configure the Chat node with your preferred model and safety settings.
- Craft a system prompt that:
- Explains the tool’s purpose (visa requirement guidance).
- Instructs the model to ask for missing essential details.
- Requires citation of sources from Weaviate when possible.
5. Best Practices for Accuracy & Compliance
5.1 Source selection and versioning
For reliable visa guidance, only ingest:
- Official government immigration and consular websites.
- Embassy or consulate advisories.
- Other validated, authoritative immigration sources.
Always store metadata such as effective_date and source_url in Weaviate so that:
- The agent can surface how recent the information is.
- Users can click through to verify the original source.
5.2 Chunking and embedding strategy
Recommended baseline:
- Chunk size around 400 characters.
- Overlap around 40 characters.
For especially dense legal sections, increasing overlap slightly can help preserve context. Avoid overly large chunks which can dilute the semantic signal and make retrieval less precise.
5.3 Handling sensitive personal data
Traveler data can be sensitive. To reduce risk:
- Avoid storing personally identifiable information (PII) in plaintext in external services unless strictly necessary.
- If logging PII in Google Sheets or other systems, ensure:
- Data is encrypted at rest where possible.
- Access is restricted to authorized personnel.
- Consider hashing or pseudonymizing identifiers in logs.
6. Customization & Extensions
6.1 Front-end integration
- Embed a chat widget that sends user messages and traveler details to the webhook.
- Display the agent’s response along with cited source URLs and effective dates.
6.2 Multilingual support
To handle non-English queries:
- Add a language detection step before embedding.
- Translate non-English input into the language of your corpus prior to generating embeddings.
- Optionally translate the final answer back to the user’s original language.
6.3 Output formats and checklists
- Generate downloadable pre-travel checklists based on the agent’s recommendations, such as:
- Required documents.
- Vaccination requirements.
- Applicable fees or appointment steps.
6.4 Admin tooling
- Build an internal UI to upload or refresh source documents.
- Trigger re-indexing workflows that re-run the Text Splitter, Embeddings, and Weaviate Insert steps automatically.
7. Troubleshooting & Diagnostics
- Empty search results
Verify that:- Documents have been successfully inserted into Weaviate.
- Embeddings were generated and stored without errors.
- The class/index name in the Query node matches the Insert node configuration.
- Inaccurate or hallucinated answers
Check that:- The system prompt clearly instructs the model to rely on retrieved documents.
- The agent is required to cite sources and to avoid guessing when no relevant documents are found.
- Your underlying corpus is up to date and contains the jurisdictions in question.
- Slow performance
Investigate:- Embedding latency from Cohere.
- Weaviate instance sizing and query time.
- Anthropic model choice and context length