Automate Slack Message Summaries with n8n and Claude AI
Overview
This guide describes a production-ready n8n workflow template that summarizes Slack channel activity on demand using a Slack slash command and Claude AI. The automation retrieves recent messages from a specified Slack channel, prepares a structured prompt for Claude, receives a concise summary with suggested replies, and returns the result to Slack as an ephemeral message visible only to the requesting user.
The reference is written for users already familiar with n8n, Slack APIs, and basic HTTP-based integrations. It focuses on node configuration, data flow, and integration details so you can confidently deploy, audit, and extend the workflow.
Solution Architecture
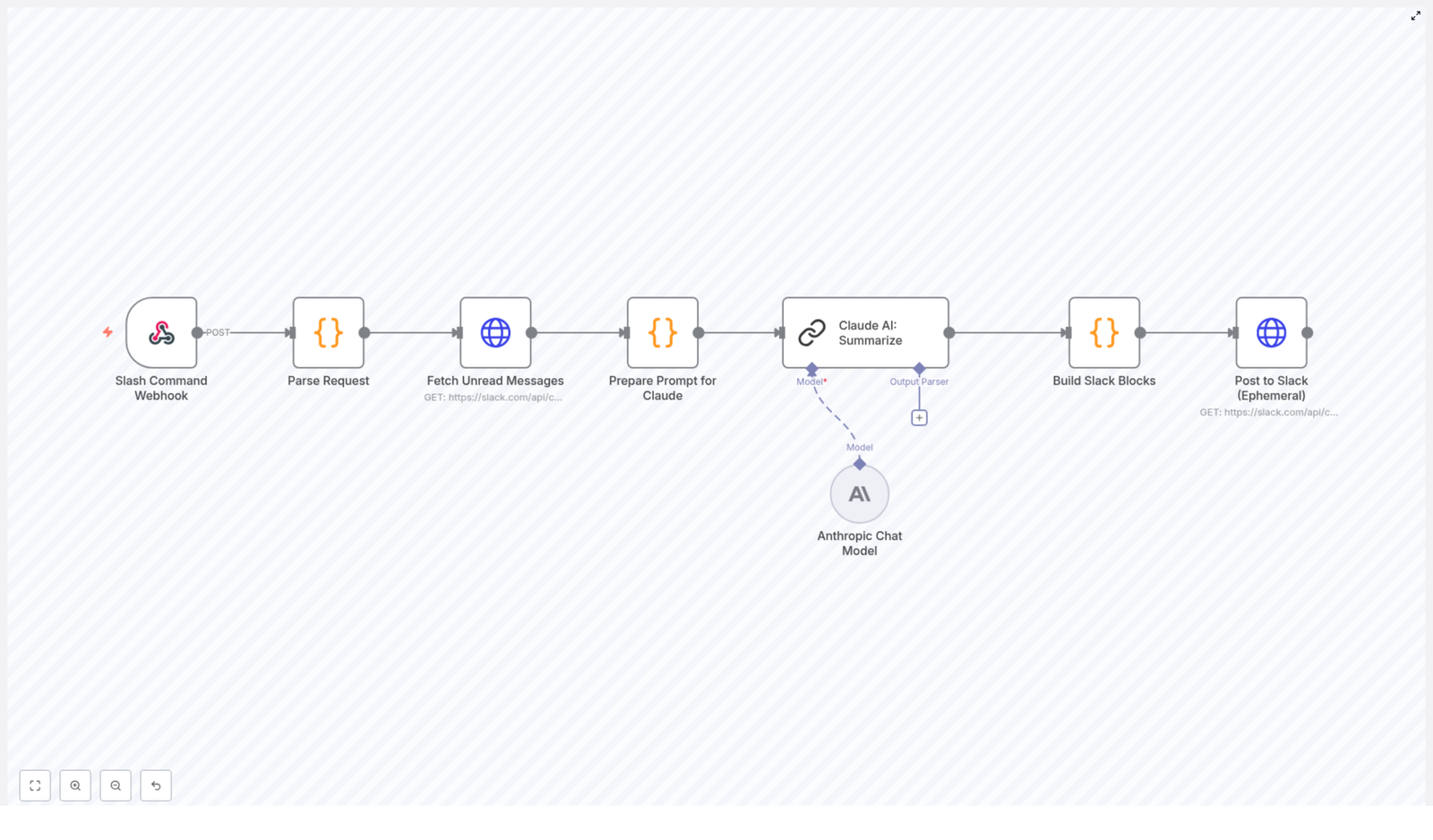
The workflow is event-driven and starts when a user invokes a custom Slack slash command, for example /summarize. The command triggers a webhook in n8n, which then orchestrates the following sequence:
- Receive and validate the incoming Slack slash command payload via webhook.
- Extract key parameters such as
channel_id,user_id, and OAuthtoken. - Query the Slack
conversations.historyAPI to fetch up to 20 recent messages from the target channel. - Normalize and format the messages into a single prompt string for Claude AI, including timestamps and user attribution.
- Call Claude AI with a summarization prompt that requests grouped threads, concise summaries, and 2-3 suggested replies per thread.
- Transform Claude’s response into Slack Block Kit JSON suitable for a rich ephemeral message.
- Post the blocks back to Slack using
chat.postEphemeral, scoped to the user who issued the command.
The workflow is fully contained in n8n and uses a combination of Webhook, HTTP Request, Code, and Claude AI nodes (or equivalent custom HTTP nodes if you are calling Claude’s API directly).
Node-by-Node Breakdown
1. Webhook Trigger for Slack Slash Command
Node type: Webhook (Trigger)
Purpose: Entry point for the workflow. It receives the HTTP POST request that Slack sends when a user runs the configured slash command.
Key behaviors:
- Method:
POST - Expected payload: Standard Slack slash command payload including fields such as
token,team_id,channel_id,channel_name,user_id,user_name,command, andtext. - Security: Slack should be configured to call the public URL exposed by this webhook. Optionally, you can validate the Slack verification token or signing secret in a downstream node for additional integrity checks.
2. Parse Request Payload
Node type: Code or Function
Purpose: Extracts the fields needed for subsequent Slack API calls. This includes the channel where the command was invoked and the identity of the requesting user.
Typical extracted fields:
channel_id– used to scope the message history query and the ephemeral reply.user_id– used as the target user forchat.postEphemeral.token– OAuth access token that authorizes Slack API requests. This can be passed in the payload or mapped from stored Slack credentials in n8n.
If you are using n8n’s Slack credentials system, you may not need to forward the token directly from the payload. Instead, you can map the OAuth token from your credential configuration. The workflow as described, however, assumes the token is available and used in the HTTP headers for the Slack API calls.
3. Fetch Unread / Recent Messages
Node type: HTTP Request
API endpoint: https://slack.com/api/conversations.history
Purpose: Retrieve recent messages from the specified Slack channel. The workflow requests up to 20 of the latest messages to keep context manageable for Claude while still covering a meaningful time window.
Key configuration:
- HTTP method:
GETorPOSTwith appropriate query/body parameters. - Parameters:
channel: set from the parsedchannel_id.limit: typically set to20to cap the number of messages.
- Headers:
Authorization: Bearer <token>using the OAuth token extracted earlier or from n8n credentials.Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencodedorapplication/jsondepending on your request configuration.
Access scope: With a valid token and appropriate scopes (for example, channels:history, groups:history, im:history, or mpim:history), the node can retrieve messages from both public and private channels where the app is installed.
Edge cases:
- If the token does not have access to the channel, the API returns an error. You should handle this in a subsequent node by checking the
okfield in the response and returning a user-friendly error message to Slack. - If the channel has fewer than 20 messages, Slack simply returns all available messages.
4. Prepare Prompt for Claude AI
Node type: Code or Function
Purpose: Convert the raw Slack message list into a single structured prompt string suitable for Claude. Each message is formatted with a timestamp and user attribution so that the language model can infer conversation structure and context.
Typical processing steps:
- Iterate over the message array returned by
conversations.history. - Extract fields such as
user,text, andts(timestamp). - Optionally sort messages by timestamp to ensure chronological order.
- Build a human-readable transcript, for example:
[2024-01-01 10:15] @U12345: Message text [2024-01-01 10:16] @U67890: Reply text ...
The final output of this node is a single string containing the conversation context, which is passed as part of the prompt to the Claude AI node.
5. Claude AI Summarization
Node type: Claude AI (or HTTP Request to Claude API)
Purpose: Generate a structured summary of the Slack conversation. The workflow instructs Claude to group related messages into threads, produce short summaries for each thread, and suggest 2-3 replies per thread that the user could send back in Slack.
Prompt design:
- Include the formatted conversation transcript from the previous node.
- Provide clear instructions, for example:
- Group messages into logical threads.
- Provide a brief summary for each thread.
- Generate 2-3 concise, actionable reply suggestions per thread.
Output: Claude returns a textual summary, often structured with headings or bullet points. The exact structure depends on the prompt design, but the workflow expects a format that can be parsed or directly embedded into Slack Block Kit sections.
6. Build Slack Block Kit Message
Node type: Code or Function
Purpose: Transform Claude’s response into a Slack Block Kit JSON payload suitable for an ephemeral message. This ensures the summary is rendered in a clear, readable layout inside Slack.
Typical structure:
blocksarray containing:sectionblocks for each thread summary.- Optional
dividerblocks between threads. - Text formatted with
mrkdwnfor bolding, lists, and inline formatting.
This node takes the raw text from Claude and either:
- Uses simple string concatenation and
mrkdwnformatting, or - Parses the output into a more structured representation before mapping it into Block Kit objects.
The result is a JSON object that the next node can pass directly to Slack’s chat.postEphemeral method.
7. Post Ephemeral Message Back to Slack
Node type: HTTP Request (or Slack node, if used)
API endpoint: https://slack.com/api/chat.postEphemeral
Purpose: Deliver the summary and suggested replies to the user who invoked the slash command, without exposing the content to the entire channel.
Key configuration:
- HTTP method:
POST - Body parameters:
channel: thechannel_idfrom the original request.user: theuser_idof the requesting user.blocks: JSON string of the Block Kit payload built in the previous node.
- Headers:
Authorization: Bearer <token>using the same Slack OAuth token.Content-Type: application/json
Behavior: The message appears only to the triggering user inside the target channel. This preserves privacy and avoids cluttering the channel with summaries that are primarily for individual consumption.
Configuration Notes
Slack Setup
- Create or configure a Slack app with the proper scopes to access channel history and post ephemeral messages.
- Define a slash command (for example
/summarize) and point its Request URL to the public URL of the n8n Webhook node. - Ensure your OAuth token has access to the channels where the command will be used, including private channels if necessary.
n8n Credentials and Security
- Store the Slack OAuth token in n8n credentials wherever possible rather than passing it directly in the payload.
- Optionally add validation logic in the Parse Request node to check Slack’s verification token or signing secret before proceeding.
- Limit access to the n8n instance and its webhook URL using HTTPS and appropriate network controls.
Claude AI Integration
- Configure your Claude API credentials in n8n or in the HTTP Request node used for the summarization call.
- Keep prompts deterministic and explicit so that the output is predictable enough to map into Slack blocks.
- Monitor token usage and rate limits on the Claude side, especially if the workflow is used heavily across teams.
Advanced Customization
Adjusting Message Volume and Context
The workflow currently fetches up to 20 recent messages. You can modify the limit parameter in the conversations.history request to increase or decrease the context window. Keep in mind that longer transcripts increase the prompt size and can affect Claude’s latency and cost.
Multi-Channel or Filtered Summaries
The template is designed around a single channel specified by channel_id from the slash command. Developers can extend the workflow to:
- Accept additional parameters via the slash command text to select different channels or time ranges.
- Filter messages in the Code node by user, keyword, or timestamp before building the prompt.
Error Handling and User Feedback
For a robust implementation, consider adding:
- Conditional checks after each Slack API call to handle
ok: falseresponses. - Fallback ephemeral messages that explain when the summary cannot be generated, for example due to missing permissions or empty conversations.
- Logging nodes to capture request and response metadata for debugging.
Benefits of This n8n + Claude Automation
- Time savings: Automatically condenses long Slack threads into concise summaries, reducing the need to manually scroll through conversations.
- Improved communication: Thread-based summaries help users quickly understand ongoing discussions and their current status.
- Actionable suggestions: Claude’s 2-3 suggested replies per thread accelerate response drafting and help maintain consistent communication tone.
- Privacy-preserving: Ephemeral messages ensure that only the requesting user sees the AI-generated summary and suggestions.
Getting Started
Integrate this workflow template into your Slack workspace via n8n to streamline how your team processes message-heavy channels. The template is straightforward to adapt for more advanced use cases, such as multi-channel reporting or experimenting with alternative AI models, while keeping the same core pattern of:
- Trigger via slash command.
- Fetch recent Slack messages.
- Summarize with Claude AI.
- Respond with an ephemeral Block Kit message.
Deploy the template and start transforming Slack message overload into clear, actionable insights.
Conclusion
By combining n8n’s flexible automation platform with Claude AI’s natural language processing capabilities, you can build a powerful Slack summarization workflow that fits neatly into existing collaboration patterns. This solution lets teams stay focused on high-value work while offloading the cognitive load of catching up on dense Slack conversations to an automated, AI-driven process.