Automate News Summaries: AI-Powered Slack Posting
Introduction
Monitoring relevant industry news is essential for informed decision-making, yet manually reviewing multiple sources every day is inefficient and error-prone. By combining n8n, AI summarization, and Slack, you can implement a reliable, fully automated news briefing that keeps your team aligned without adding to anyone’s workload.
This article presents an n8n workflow template that aggregates news from Hacker News based on configurable keywords, generates concise AI summaries in Japanese, and posts the results directly into a chosen Slack channel on a defined schedule. It is designed for automation professionals who want a repeatable, configurable system rather than an ad hoc process.
Use Case Overview
The workflow implements an end-to-end news monitoring pipeline:
- Scheduled execution at a defined time (default: daily at 9:00)
- Configurable keywords to filter relevant Hacker News articles
- Retrieval of matching articles using n8n’s Get many items capability
- AI-based summarization of each article using an OpenRouter Chat Model
- Formatting of summaries into a Slack-optimized message structure
- Automated posting of the summaries into a specified Slack channel
The result is a daily, AI-powered news digest tailored to your topics of interest, delivered where your team already collaborates.
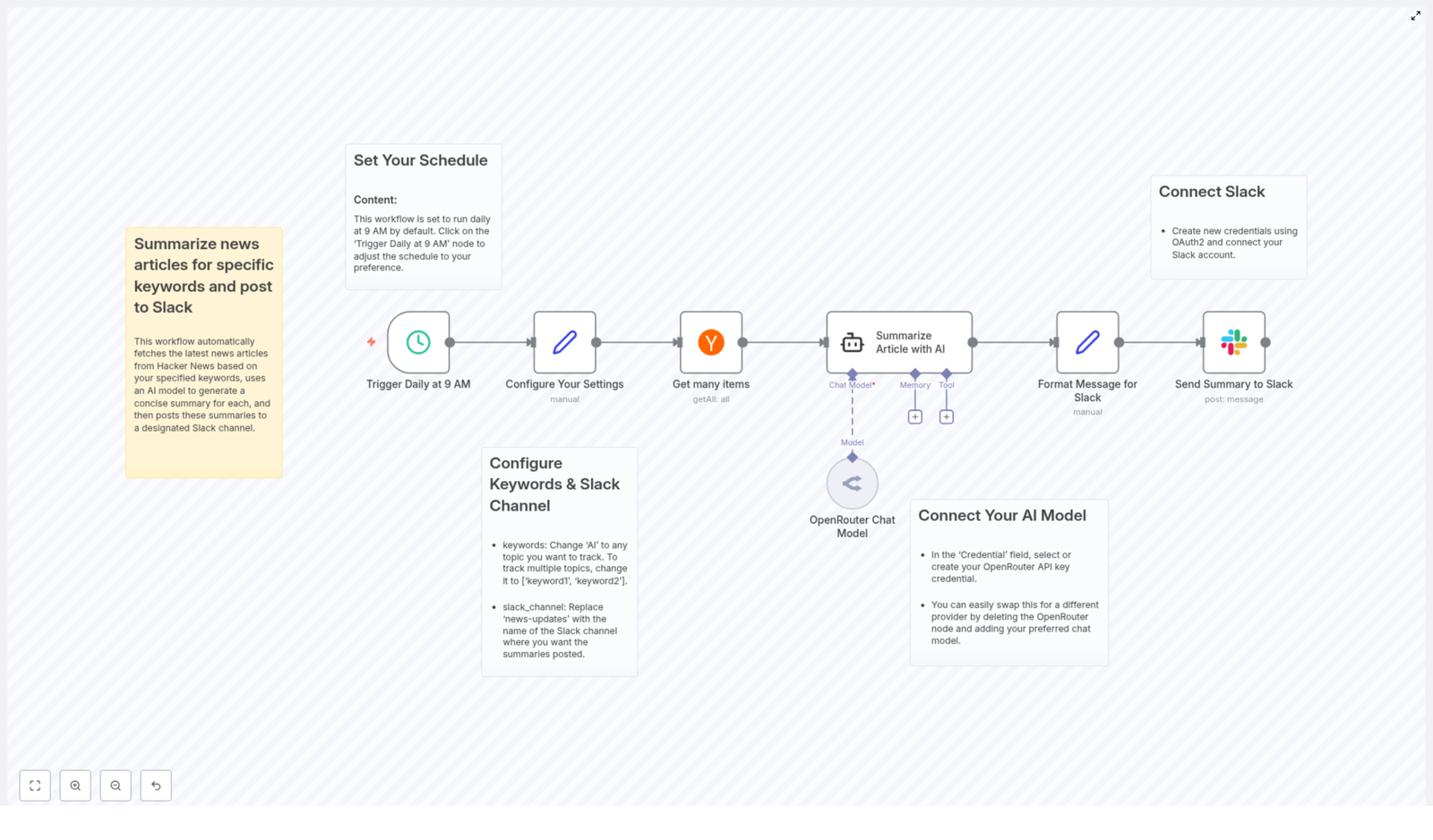
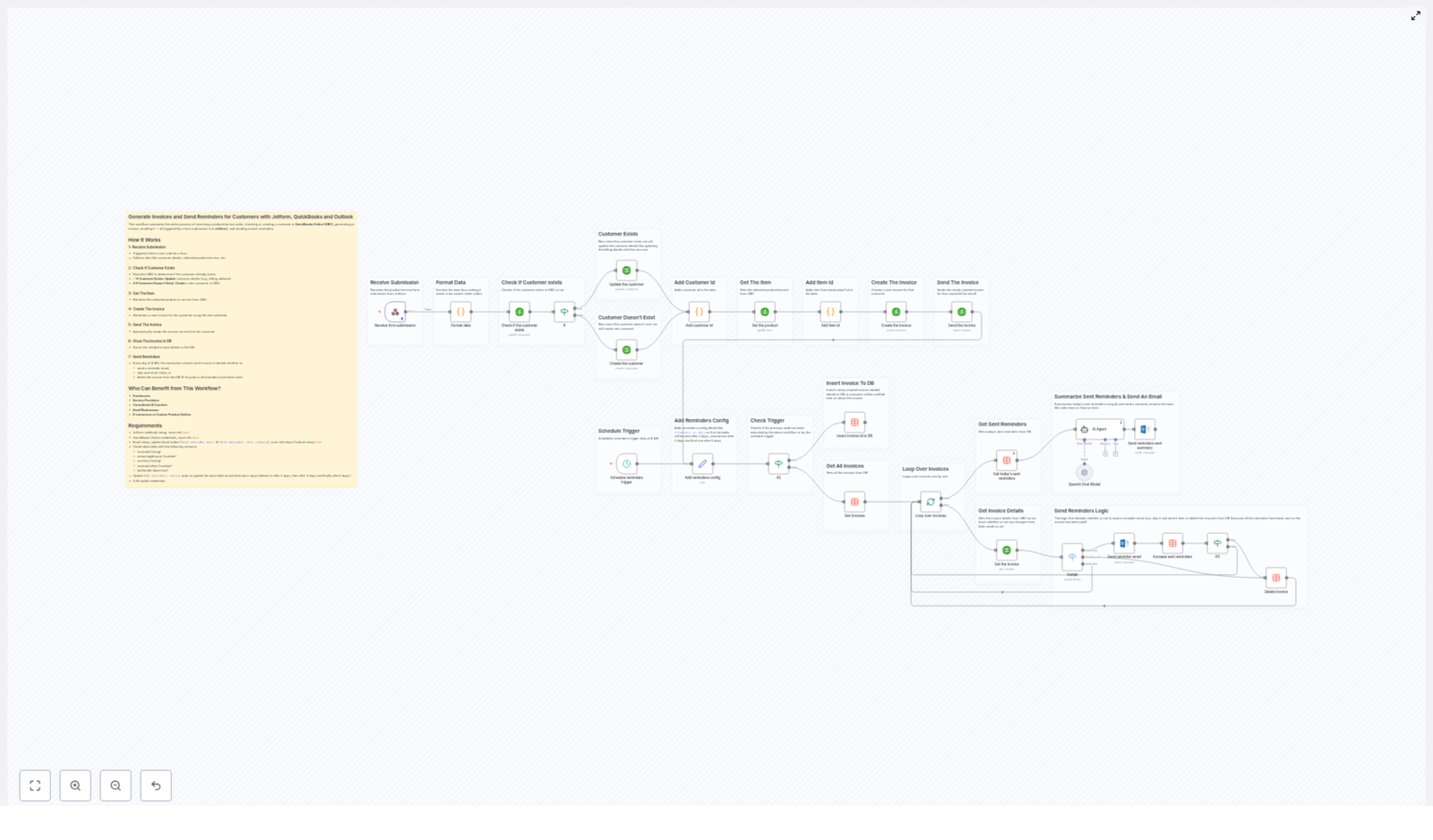
Core Workflow Architecture
The template is structured around a set of clearly defined nodes, each responsible for a distinct part of the automation. At a high level, the workflow consists of:
- Trigger node for scheduling execution
- Configuration node for keywords and Slack channel settings
- Data retrieval node to fetch Hacker News articles
- AI summarization node powered by OpenRouter
- Message formatting node to prepare Slack-ready content
- Slack node to deliver the summaries to your workspace
Step-by-Step Workflow Breakdown
1. Scheduling the Automation
The workflow uses a time-based trigger to run automatically. By default, the Trigger Daily at 9 AM node is configured to execute once per day at 09:00.
Automation best practice is to align this schedule with your team’s working patterns. For example, a morning summary can support daily standups, while an evening run might serve as a recap. You can modify the cron or schedule settings in this trigger node to adjust:
- Execution time (for example, 8:30 instead of 9:00)
- Execution frequency (daily, weekdays only, or at multiple intervals)
2. Central Configuration: Keywords and Slack Channel
To make the workflow easily maintainable, key parameters are consolidated in the Configure Your Settings node. This node typically uses static data or expressions to define:
- Keywords to track: An array of terms that will be used to filter Hacker News articles. For example:
['AI', 'machine learning', 'LLM']Providing a single keyword such as “AI” will restrict the search to that term. Multiple topics can be monitored simultaneously by extending this array.
- Target Slack channel: The channel name or channel ID where the summaries will be posted. This value is referenced later by the Slack node when sending messages.
Storing these values centrally simplifies future adjustments and supports reuse of the template across different teams or topics.
3. Retrieving Articles from Hacker News
Once the schedule and configuration are in place, the workflow proceeds to data collection. The Get many items node is used to query Hacker News for the latest articles that match the configured keywords.
Key aspects of this step:
- The node filters articles based on the keywords defined in the configuration node.
- You can limit the number of returned items to control volume and avoid overwhelming users with too many links.
- The output of this node typically includes article titles, URLs, and other metadata, which are passed downstream for summarization.
From an automation perspective, it is advisable to start with a conservative limit on article count, then expand as needed once you confirm the signal-to-noise ratio is acceptable.
4. AI-Powered Summarization Using OpenRouter
For each retrieved article, the workflow invokes an AI summarization step that leverages an OpenRouter Chat Model. The article URL and relevant metadata are provided as input to the model, which then generates a concise summary tailored to a specific format.
The summarization behavior in this template is defined as follows:
- Output language: Japanese
- Structure: three bullet points
- Style: Focused on key facts and essential information
- No introductory or closing phrases, only the bullet points themselves
This structured approach ensures consistency across all summaries and makes them easy to scan in Slack. You can further refine the prompt inside the OpenRouter node to adjust tone, detail level, or formatting, as long as you preserve the core logic of the workflow.
5. Formatting Messages for Slack Delivery
After the AI model produces the summary, the workflow prepares the final message that will appear in Slack. A dedicated formatting step combines:
- The article title
- The article URL
- The AI-generated bullet point summary in Japanese
This node applies Slack-friendly formatting so that messages are both readable and visually structured. Typical techniques include clear separation between title, link, and summary, and the use of bullet lists that render well in Slack clients.
Maintaining a consistent message format is important for downstream consumption. Teams can quickly scan the channel, identify relevant items, and click through to the full article when necessary.
6. Posting Summaries to Slack
In the final step, the workflow uses an authenticated Slack node to send the formatted message to the configured channel. This node relies on your Slack OAuth2 credentials to post securely into the selected workspace.
Once configured, each run of the workflow will automatically publish the latest news summaries. Team members receive timely updates without needing to leave Slack or manually check external news sites.
Connecting External Services
AI Model Integration (OpenRouter)
- In the OpenRouter Chat Model node, select or create an OpenRouter API key credential.
- Use this credential to authenticate requests and enable AI summarization within the workflow.
- If you prefer a different AI provider, you can replace the OpenRouter node with another compatible model node, preserving the same input and output structure.
This abstraction allows you to change providers or models without redesigning the entire workflow.
Slack Workspace Authentication
- Create and configure OAuth2 credentials for Slack within n8n.
- Grant the required permissions so the workflow can post messages to channels in your workspace.
- Reference these credentials in the Slack node used for sending the summaries.
Using OAuth2 ensures secure and controlled access, which is a best practice for production-grade automation that interacts with collaboration platforms.
Customization and Optimization Options
The template is intentionally flexible, allowing automation professionals to adapt it to different environments and requirements. Common customization patterns include:
- Keyword strategy: Modify the keywords array in the configuration node to focus on specific technologies, vendors, or domains. For example, you might track:
- General topics such as
['AI', 'cloud', 'security'] - Product-specific terms for competitive monitoring
- General topics such as
- Scheduling: Adjust the trigger node so the workflow runs:
- Multiple times per day for high-volume topics
- Only on weekdays to align with business hours
- At different times for different teams or regions
- Summary style and language: Update the AI prompt to:
- Change the level of detail in the bullet points
- Switch to another language if needed
- Apply a more formal or more conversational tone
- Alternative destinations: While the template targets Slack, the same pattern can be extended to other channels by adding or replacing the final node with email, other chat tools, or internal dashboards.
Operational Benefits and Next Steps
By implementing this n8n workflow, you transform unstructured news consumption into a consistent, automated process. The key benefits include:
- Reduced time spent on manual news monitoring
- Centralized, topic-specific updates delivered directly into Slack
- Higher situational awareness across teams without additional effort
- Scalable configuration for multiple topics, teams, or workspaces
To get started, import the template, connect your OpenRouter and Slack credentials, configure your keywords and channel, then tune the schedule and summary style to match your team’s needs.
Call to action: Deploy this workflow in your n8n instance to establish an AI-driven news briefing system that keeps your organization informed and focused, without manual overhead.