Automate AI Video Creation & Multi-Platform Publishing with n8n
Overview
This reference guide describes an n8n workflow template that automates the complete lifecycle of short-form video content: from AI-based video generation to multi-platform publishing across nine social networks. The automation integrates Telegram, Blotato, Piapi, GPT-4, Cloudinary, and Google Sheets to create, enrich, store, and distribute videos with minimal manual intervention.
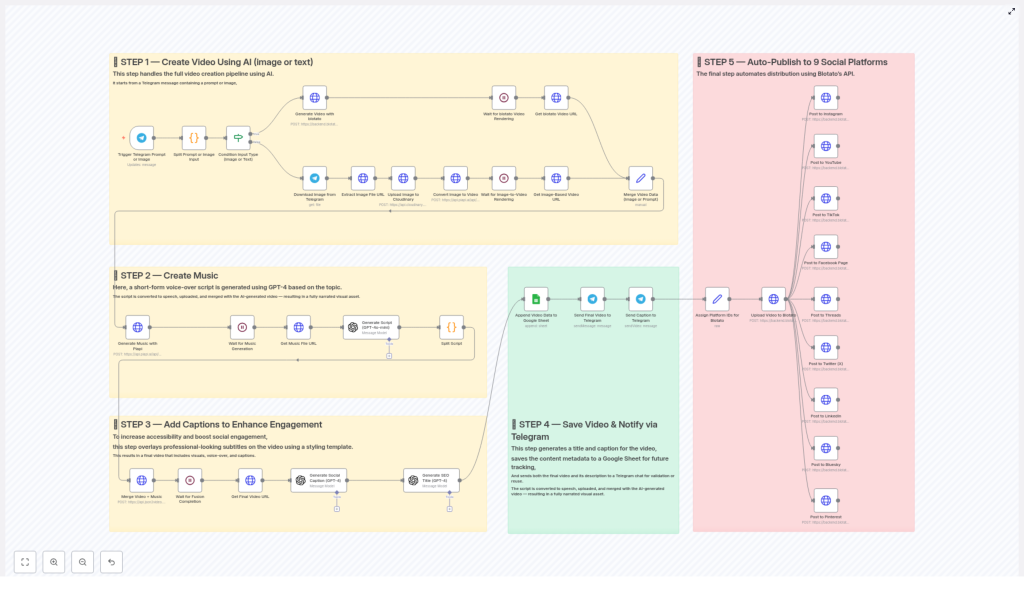
The workflow is organized into five major stages:
- AI video generation from text or image input
- Automatic music and voice-over creation
- Caption overlay and video enhancement
- Metadata storage and Telegram notification
- Automated publishing to nine social platforms
This documentation-style rewrite focuses on the technical behavior of the template, including data flow, node responsibilities, and configuration considerations for advanced users of n8n and API-based automation.
Architecture & Data Flow
At a high level, the workflow is triggered by a Telegram interaction and then branches based on whether the user submits text or an image. Both branches ultimately converge into a unified video asset that is enriched with audio, captions, and metadata, then published to multiple social channels.
Core Integrations
- Telegram – Input channel for prompts or images and final notification endpoint.
- Blotato API – AI video generation from text prompts and multi-platform publishing orchestration.
- Piapi API – Image-to-video conversion and text-to-audio generation.
- GPT-4 – Script generation, caption text creation, and SEO-friendly titles.
- Cloudinary – Media storage for uploaded images used in video generation.
- Google Sheets – Persistent storage of video metadata for tracking and analytics.
Execution Stages
- Input & Video Generation – Accepts either text or image from Telegram, then generates an AI video via Blotato or Piapi.
- Audio & Music Creation – Uses GPT-4 to generate a voice-over style script and Piapi to render it as audio.
- Caption & Overlay Processing – Combines video and audio, applies a caption style template, and adds hook/payoff text overlays.
- Storage & Notification – Writes metadata to Google Sheets and returns the final video and details to Telegram.
- Multi-Platform Publishing – Distributes the final video and caption to nine social platforms via Blotato.
Stage 1 – AI Video Creation from Text or Image
Trigger & Input Handling
The workflow begins when a user interacts via Telegram. The trigger node (for example, a Telegram Trigger node) receives either:
- A text prompt describing the desired video, or
- An image uploaded to the chat, optionally with a caption.
A conditional node (such as an IF or Switch node) typically evaluates the Telegram payload to determine whether the incoming message contains text, an image, or both. Based on this evaluation, the workflow follows one of two paths.
Path A – Text-Based Video Generation with Blotato
When the user sends a text prompt, the workflow uses Blotato’s video generation API to produce a cinematic-style AI video.
Key Behavior
- The text prompt from Telegram is passed as the main input parameter to Blotato.
- A predefined cinematic style template is used to standardize the visual look and feel of generated videos.
- The Blotato node (typically an HTTP Request or dedicated Blotato node if available) sends the prompt and template identifier to the API.
- The API responds with a video asset reference, such as a rendered video URL or an ID that can be used to fetch the final video.
The result is a video object that will be merged later with other media and metadata in downstream nodes.
Path B – Image-to-Video Conversion with Piapi & Cloudinary
If the user provides an image, the workflow follows a separate branch that converts the image into a short AI-generated video.
Image Retrieval from Telegram
- The Telegram message payload is inspected to obtain the file ID or URL of the uploaded image.
- A follow-up call to Telegram’s API downloads the original image file.
Upload to Cloudinary
- The downloaded image is uploaded to Cloudinary using a configured Cloudinary node or HTTP Request node.
- Cloudinary returns a public image URL that is stable and accessible to external services.
Image-to-Video Generation with Piapi
- The Cloudinary image URL is passed to Piapi’s image-to-video endpoint.
- Piapi generates a short AI-based video using the image as the primary visual input.
- Once rendering is complete, the workflow retrieves the rendered video URL from Piapi’s response.
The output of this branch is a video asset derived from the original image, which is aligned with the text-based video output format so both branches can be merged consistently.
Convergence of Video Data
After the text and image branches complete, a merge node (for example, a Merge node in “Pass-through” or “Wait” mode) unifies the execution paths:
- Both branches are normalized to produce a standard structure containing at least a
videoUrlor equivalent identifier. - Any additional metadata, like the source type (text or image) or original prompt, can be preserved for logging or analytics.
From this point onward, the workflow processes a single video object regardless of the initial input type.
Stage 2 – Music & Voice-Over Creation
Script Generation with GPT-4
To create an engaging audio track, the workflow first generates a short-form voice-over script using GPT-4. The script is based on the video topic, original prompt, or caption idea.
Typical Parameters
- Input context – The original text prompt, Telegram caption, or derived topic description.
- Style constraints – Short-form, social-media-ready, concise, and optimized for spoken delivery.
- Output format – A single script string suitable for text-to-audio conversion.
The GPT-4 node returns a script that will be used as the text input for audio generation.
Text-to-Audio Conversion with Piapi
The generated script is then passed to Piapi’s text-to-audio capability to produce music or a voice-over track.
Node Behavior
- The Piapi node receives the script text and any required configuration, such as voice type or language, as parameters.
- Piapi starts rendering the audio file and returns either the final URL or a task identifier.
- The workflow waits until the audio rendering is complete before proceeding.
Waiting for Rendering Completion
Depending on Piapi’s API design, the workflow may:
- Use a direct response if the API returns the final audio URL immediately, or
- Implement a polling loop or delay if the API returns a job ID, checking periodically until the status indicates completion.
At the end of this stage, the workflow has a stable music or audio file URL that will be merged with the video in the next stage.
Stage 3 – Caption Overlay & Video Enhancement
Caption Strategy & Text Generation
To improve engagement and accessibility, the workflow overlays captions onto the video using a predefined styling template. GPT-4 is used again, this time to generate structured overlay text.
Hook and Payoff Lines
- The GPT-4 node is prompted to produce two distinct text segments:
- A hook line that captures attention at the beginning of the video.
- A payoff line that delivers the main value or conclusion.
- The output is formatted so that the hook and payoff can be mapped to specific caption regions or timestamps in the video.
Video & Audio Fusion with Captions
The workflow then merges the previously generated video and the audio track, and applies the caption overlay.
Processing Steps
- Inputs:
- Video asset from Stage 1.
- Audio file URL from Stage 2.
- Hook and payoff text from GPT-4.
- A caption or styling template is selected to ensure consistent typography, positioning, and effects.
- The fusion process combines:
- The base video,
- The audio track as background music or voice-over, and
- Overlay text with the defined style.
Waiting for Final Video Rendering
The workflow waits for the video processing to complete. Similar to the audio step, this can involve:
- Using the final video URL directly if returned synchronously, or
- Polling for job completion if the processing is asynchronous.
Once completed, the workflow stores the final processed video URL, which now includes music and professional-looking captions.
Stage 4 – Metadata Storage & Telegram Notification
Title & Caption Generation with GPT-4
Before storing and distributing the video, the workflow generates optimized metadata for social media.
SEO-Friendly Title
- GPT-4 is prompted to create a concise, descriptive video title.
- The title is designed to be both SEO-friendly and suitable for platforms like YouTube and Pinterest.
Engaging Social Caption
- A separate or combined GPT-4 call generates an engaging social media caption.
- The caption is tailored for short-form platforms and can incorporate hooks, CTAs, and relevant keywords.
Persisting Video Metadata in Google Sheets
To track published content and support analytics, the workflow writes video metadata to a configured Google Sheet.
Typical Columns
- Video URL – Final processed video link from Stage 3.
- Title – SEO-optimized title from GPT-4.
- Caption – Social media caption text.
- Source – Optional field indicating whether the content originated from text or image input.
- Timestamp – Execution or creation date for tracking.
A Google Sheets node (such as “Append” mode) inserts a new row for each generated video, ensuring a persistent log of all content processed by the workflow.
Telegram Notification to the Originating Chat
After saving the metadata, the workflow sends the final result back to the Telegram chat that initiated the request.
Notification Content
- The final video (as a direct video file or a link, depending on Telegram configuration).
- The generated title and caption.
- Any additional contextual information, such as confirmation that the video is ready for publishing or reuse.
By maintaining this feedback loop, users can quickly validate the output, reuse captions, or share the content manually if needed.
Stage 5 – Automated Publishing to 9 Social Platforms
Blotato-Powered Multi-Platform Distribution
The final stage of the workflow automates publishing to multiple social networks using Blotato’s distribution capabilities. The same video asset and caption are syndicated across:
- YouTube
- TikTok
- Threads
- Twitter (X)
- Bluesky
Platform-Specific Account Mapping
Blotato’s API is configured with platform-specific account IDs so the same workflow can publish to multiple destinations without additional manual setup in n8n.
Typical Parameters Sent to Blotato
- Video URL – The final processed video from Stage 3.
- Caption – The social media caption text generated in Stage 4.
- Account IDs – Identifiers for specific profiles or pages on each platform.
The Blotato node handles the complexity of each platform’s API, while n8n focuses on orchestrating the overall process and passing the correct data payload.
Configuration Notes & Practical Considerations
Credentials & Authentication
- Telegram – Requires a bot token and proper webhook or polling configuration for the trigger node.
- Blotato – Needs an API key or token with permissions for video generation and publishing.
- Piapi – Requires credentials for both image-to-video and text-to-audio endpoints.
- Cloudinary – Needs API key, secret, and cloud name for authenticated uploads.
- Google Sheets – Uses OAuth or service account credentials to read/write the target spreadsheet.
- GPT-4 – Requires OpenAI-compatible credentials or equivalent provider access.
Error Handling & Edge Cases
When customizing this template, consider adding explicit error handling around:
- Missing or invalid Telegram input – For example, when neither a text prompt nor an image is provided.
- Failed uploads to Cloudinary or failed downloads from Telegram.
- Timeouts or failed renders from Piapi or Blotato during video or audio generation.
- Rate limits or quota issues for GPT-4 and external APIs.
- Google Sheets write failures due to permission changes or sheet structure modifications.
In n8n, this can be addressed with Error Workflow configurations, IF nodes checking response status codes, or Try/Catch-style sub-workflows where supported.
Performance & Latency
- Video and audio rendering are typically the slowest steps. Consider using delays or polling intervals that balance responsiveness with API rate limits.
- For high throughput, you may want to limit concurrent executions or implement queuing logic within n8n.
Advanced Customization Ideas
Template & Style Variations
- Expose the cinematic style template as a variable so users can select between multiple visual styles.
- Allow different caption styles (font, color, position) by passing