Automate Form Translation with n8n and RAG
Managing multilingual form submissions and turning them into translated, searchable records can quickly become a bottleneck. This reference guide describes a production-ready n8n workflow that automates the entire pipeline using webhooks, OpenAI embeddings, Supabase vector storage, a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) agent, Google Sheets for logging, and Slack alerts for error notifications.
The workflow is available as the “Translate Form Submissions” n8n template. This article reorganizes the original walkthrough into a more technical, documentation-style format so you can deploy, understand, and extend the template with confidence.
1. Workflow Overview
This n8n workflow is designed for product, operations, and data teams that need to:
- Automatically translate and normalize free-text form submissions.
- Index submissions semantically for search and analytics using embeddings and a vector store.
- Maintain a structured, auditable log of every processed submission in Google Sheets.
- Receive Slack alerts whenever processing fails or an exceptional condition is detected.
Core technologies used:
- n8n as the low-code automation and orchestration engine.
- OpenAI embeddings to convert text chunks into vectors.
- Supabase vector store to persist embeddings and support semantic search.
- RAG agent that combines a chat model, vector tool, and memory for context-aware translation and normalization.
- Google Sheets for logging and downstream reporting.
- Slack for proactive error alerts.
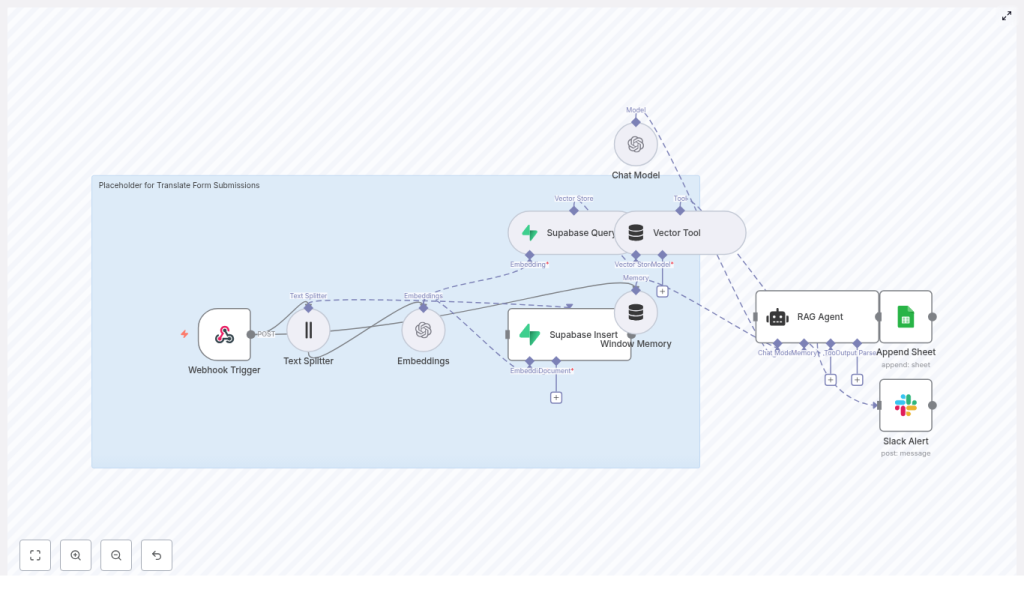
2. Architecture & Data Flow
The template implements a linear but robust pipeline that starts with an HTTP webhook and ends with logged results and optional alerts. At a high level, the workflow performs the following steps:
- Webhook Trigger receives a POST request containing the form submission payload.
- Text Splitter splits long submissions into overlapping chunks to optimize embedding quality and cost.
- OpenAI Embeddings converts each chunk into a numeric vector representation.
- Supabase Insert writes vectors and metadata into a Supabase vector index (
translate_form_submissions). - Supabase Query + Vector Tool exposes the vector index as a tool that can be called by the RAG agent for semantic retrieval.
- Window Memory retains short-term context across the agent interaction.
- Chat Model + RAG Agent uses the retrieved context and memory to generate a translated and normalized output.
- Google Sheets Append logs the outcome for auditing and analytics. If an error occurs, a Slack Alert is sent via the agent’s
onErrorbranch.
The workflow is designed so that each node is responsible for one clear function: ingestion, transformation, storage, retrieval, reasoning, logging, or alerting. This separation simplifies debugging and future extension.
3. Node-by-Node Breakdown
3.1 Webhook Trigger
Role: Entry point for external form submissions.
- Node type: Webhook
- HTTP Method:
POST - Path:
translate-form-submissions(final URL is typically/webhook/translate-form-submissionsdepending on your n8n deployment) - Expected payload: JSON body with one or more fields containing free-text form responses.
Typical sources: front-end forms, Typeform, Google Forms (via Apps Script or middleware), or any service that can send JSON via POST.
Implementation notes:
- Use the Webhook node’s Response configuration to return a clear, deterministic status (for example, HTTP 200 plus a short confirmation message) to the caller.
- For stricter validation, you can add a Function or Code node immediately after the webhook to:
- Check required properties (for example
submission_id,text). - Normalize or sanitize HTML, line breaks, or unwanted characters.
- Check required properties (for example
- Malformed or missing fields can be handled by short-circuiting to an error branch that logs the failure and optionally notifies Slack.
3.2 Text Splitter
Role: Break long submissions into smaller chunks that are more suitable for embedding and retrieval.
- Chunk size:
400characters - Chunk overlap:
40characters
Why chunking matters:
- Shorter segments reduce token usage per embedding call and therefore cost.
- Overlapping chunks preserve context across boundaries, which improves recall in semantic search.
Edge considerations:
- Very short submissions may result in only one chunk, which is expected and does not affect correctness.
- Extremely long submissions will generate multiple chunks; ensure your OpenAI usage limits and Supabase index can handle the volume.
3.3 OpenAI Embeddings Node
Role: Convert each text chunk into a vector representation using an OpenAI embedding model.
- Node type: OpenAI Embeddings
- Model:
text-embedding-3-small - Credentials: OpenAI API key configured in n8n credentials.
Configuration notes:
- Ensure the node is configured to iterate over all incoming items from the Text Splitter node so each chunk is embedded.
- Where possible, let n8n batch items to reduce HTTP overhead and latency. Exact batching behavior depends on your node configuration and n8n version.
Error handling:
- API rate limits or temporary failures can be handled by enabling retries at the workflow or node level.
- For persistent failures, route the error to the
onErrorbranch so the Slack Alert node can notify your team.
3.4 Supabase Insert (Vector Store)
Role: Persist embeddings into a Supabase vector index so that they can be queried later via semantic search.
- Node type: Supabase (Vector Store)
- Mode:
insert - Index name:
translate_form_submissions
Recommended metadata fields:
- Original submission ID (for example
submission_id). - Timestamp of the submission.
- Detected or declared language, if available.
- Source or channel (for example
form_typeorproduct_area).
Storing metadata alongside vectors enables more precise filtering when running queries. For instance, you can later restrict retrieval to a specific product line or language.
3.5 Supabase Query + Vector Tool
Role: Provide the RAG agent with a semantic retrieval mechanism over the Supabase vector index.
- Node types: Supabase Query, Vector Tool
- Usage: The Vector Tool exposes semantic search as a callable tool for the agent, backed by the Supabase index.
Configuration notes:
- Configure the query to use the same index (
translate_form_submissions) that the Insert node writes to. - Set the number of results (k) to return per query and, where supported, a similarity threshold to reduce noise.
- Optionally filter by metadata (for example language or form type) to narrow the context the agent receives.
This retrieval layer is what makes the workflow a RAG pipeline instead of a simple translation script. The agent can pull in semantically similar past submissions or contextual documents to inform its output.
3.6 Window Memory
Role: Maintain short-term memory for the RAG agent so it can reason over multiple retrieved chunks and maintain continuity within the current interaction.
- Node type: Window Memory
Behavior:
- Stores a configurable number of recent messages or turns so the agent has access to immediate context without persisting long-term history.
- Useful if a single form submission results in multiple agent calls or if you enrich the interaction with additional system or tool messages.
3.7 Chat Model + RAG Agent
Role: Execute the core reasoning, translation, and normalization logic using a chat model augmented by the vector tool and memory.
- Components: Chat Model node, RAG Agent node, Vector Tool, Window Memory.
- System message:
You are an assistant for Translate Form Submissions
Capabilities:
- Calls the Vector Tool to retrieve relevant context from Supabase.
- Uses Window Memory to keep track of recent messages.
- Generates a normalized, translated representation of the submission.
Prompt and output format:
- Define a strict, structured output format in the system or user prompt, for example:
- JSON object with fields such as
original_text,language,translation,tags,status.
- JSON object with fields such as
- Deterministic output is crucial if you plan to parse the agent output in downstream nodes (Google Sheets, databases, or other APIs).
Error behavior:
- If the agent or underlying chat model request fails, the workflow should route to an
onErrorbranch where the Slack Alert node is connected. - You can also choose to log failed attempts to a separate sheet or table for later inspection.
3.8 Google Sheets Append (Audit Log)
Role: Persist a structured log of each processed submission, including status and key attributes.
- Node type: Google Sheets
- Operation:
append - Document ID: your
SHEET_ID(store securely, for example via credentials or environment variables) - Sheet name:
Log
Typical columns:
Status(for examplesuccessorerror).Submission ID.Timestamp.Language.- Optional
Tagsor other classification fields produced by the agent.
This log can feed dashboards, reporting pipelines, or manual review workflows. Since it is append-only, it also serves as an audit trail for compliance and debugging.
3.9 Slack Alert
Role: Notify your team when the RAG agent or another critical node encounters an error or exceptional condition.
- Node type: Slack
- Channel: for example
#alerts - Message template:
Translate Form Submissions error: {$json.error.message}
Usage pattern:
- Connect the Slack node to the
onErrorbranch of the RAG agent or other key nodes. - Include enough context in the message (submission ID, environment, timestamp) to make triage easier.
4. Step-by-Step Configuration Guide
- Create the workflow and Webhook Trigger:
- Create a new workflow in n8n.
- Add a Webhook node with method
POSTand pathtranslate-form-submissions. - Save and activate (or test in manual mode) to obtain the full webhook URL.
- Add the Text Splitter:
- Insert a Text Splitter node after the Webhook.
- Set chunkSize to
400and chunkOverlap to40. - Map the form text field from the webhook payload to the Text Splitter input.
- Configure OpenAI Embeddings:
- Add an OpenAI Embeddings node connected to the Text Splitter.
- Select the
text-embedding-3-smallmodel. - Configure your OpenAI API credentials in n8n and link them to this node.
- Insert vectors into Supabase:
- Add a Supabase (Vector Store) node in insert mode.
- Configure Supabase credentials (URL, API key) in n8n.
- Set the index name to
translate_form_submissions. - Map embeddings and any relevant metadata (submission ID, timestamp, language) to the appropriate fields.
- Set up Supabase Query and Vector Tool:
- Add a Supabase Query node that targets the same index.
- Expose this query via a Vector Tool node so the RAG agent can call it for contextual retrieval.
- Configure parameters like the number of results and any filters you need.
- Configure Window Memory, Chat Model, and RAG Agent:
- Add a Window Memory node to store recent context.
- Add a Chat Model node using your OpenAI chat model credentials.
- Add a RAG Agent node that:
- Uses the Chat Model node as its language model.
- Has access to the Vector Tool for retrieval.
- Uses Window Memory to maintain short-term context.
- Includes a clear system prompt, for example:
You are an assistant for Translate Form Submissions. Always return JSON with fields: original_text, language, translation, tags, status.