Automate GitHub with n8n: Push Files & Updates Easily
From Manual Git Pushes To A Smoother, Automated Flow
If you work with GitHub regularly, you know how quickly small tasks add up. Editing a single file, committing changes, pushing updates, keeping everything in sync – it can quietly consume a surprising amount of your time and attention.
What if those repetitive GitHub updates could run in the background while you focus on higher value work? That is exactly where n8n comes in. With the right workflow, you can turn manual Git operations into a simple, repeatable automation that keeps your repository fresh without constant hands-on effort.
This article walks you through an n8n workflow template that does just that. You will see how to:
- Update a single file directly in your GitHub repo using native GitHub nodes
- Push all local changes, including new files and edits, using Git commands inside n8n
Think of this template as a stepping stone. It is a practical starting point that you can customize, extend, and connect to other automations as your workflows evolve.
Shifting Your Mindset: From Reactive To Proactive Automation
Before we dive into the technical steps, it helps to see this workflow as more than just a convenience. Automating GitHub updates is a mindset shift. Instead of reacting to every small change, you design a system that takes care of them for you.
With n8n, you are not just saving a few clicks. You are:
- Reducing context switching between coding, documentation, and Git operations
- Creating consistent, reliable update routines that do not depend on memory or mood
- Building a foundation you can plug into CI, reporting, documentation, or release workflows later
Once you have one reliable automation in place, it becomes easier to imagine and build the next one. This GitHub workflow can be that first tangible win that gets you thinking in systems instead of single actions.
How The n8n GitHub Automation Workflow Works
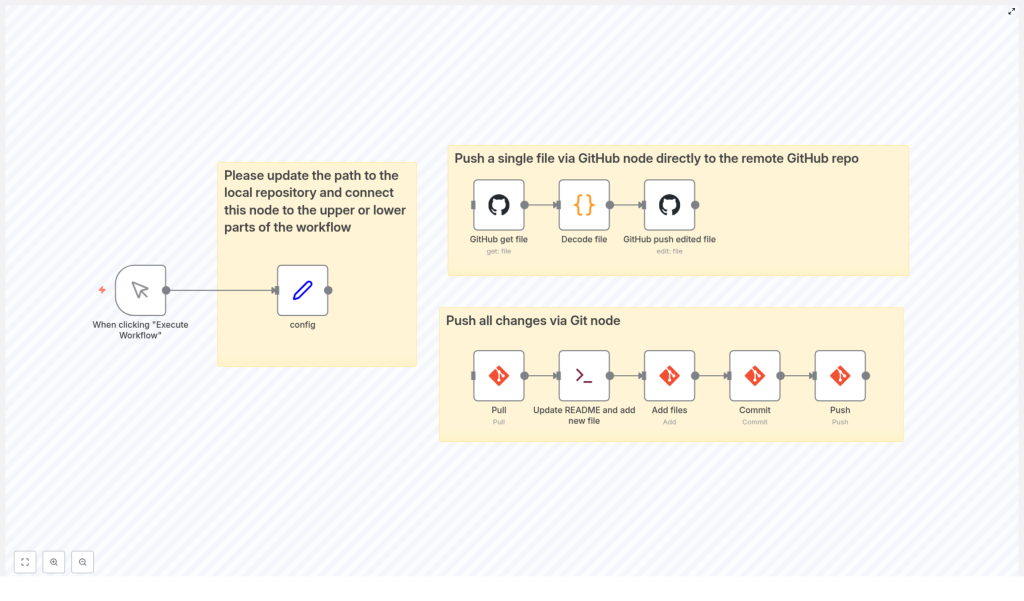
The workflow starts with a manual trigger, then branches into two paths. Each path solves a different kind of update:
- Path 1 – Update a single file (for example,
README.md) directly on GitHub using the GitHub API - Path 2 – Pull, stage, commit, and push all local changes using Git commands inside n8n
You can use one path or both, depending on what fits your current process. Over time, you can extend these branches or connect them to other triggers like webhooks, schedules, or form submissions.
Path 1: Update A Single File With GitHub Nodes
This branch is ideal when you want to automate small, focused updates to a specific file. For example, you might keep your README.md in sync with a changelog, a report, or a status update generated elsewhere.
Here is how this part of the workflow is structured:
1. GitHub get file
The workflow uses the GitHub get file node to retrieve the target file from your remote repository. In this example, that file is README.md.
GitHub returns the file content in base64 format, so the next steps focus on making it readable and editable.
2. Decode file
The Decode file node converts the base64-encoded file content into human readable text. Once decoded, you can modify the content however you want inside the workflow. For instance, you might:
- Append an update note or timestamp
- Insert generated metrics or summary text
- Replace specific sections programmatically
3. GitHub push edited file
After adjusting the content, the GitHub push edited file node sends the updated README.md back to your GitHub repository using the GitHub API.
The result is a clean, direct file update with no manual Git commands. You simply trigger the workflow and let n8n handle the API interaction for you.
Path 2: Push All Changes Using Git Commands In n8n
Sometimes you need more than a single file update. Maybe you have created new files, modified several existing ones, or made a series of local changes you want to push in one go. This second branch of the workflow uses Git command nodes to manage the full cycle.
Here is how it unfolds:
1. Pull the latest changes
The workflow starts with a Pull step that syncs your local repository with the remote one. This ensures you are working on top of the latest version and helps avoid conflicts.
2. Update README and add new file
Next, a shell command node runs custom commands in your local environment. In this template, it:
- Appends an update timestamp to
README.md - Creates a new file whose name is based on a unique timestamp
This is where the workflow starts to feel powerful. With simple shell commands, you can generate logs, reports, snapshots, or any other files you want to track in Git, all orchestrated by n8n.
3. Add files
The Add files step stages both the updated and newly created files in your local Git repository. It is the automated equivalent of running git add for the relevant paths.
4. Commit changes
The workflow then uses a Commit node to create a local commit with a clear, descriptive message. Consistent automated commits can become a valuable history of your generated updates, reports, or documentation.
5. Push to remote
Finally, the Push node sends the committed changes to your remote GitHub repository. With this, your local updates are fully synchronized, and the entire sequence has run from inside n8n.
Essential Configuration: Connecting n8n To Your GitHub Workflow
For this template to work smoothly, a few configuration details are important. Once you set them up, the workflow becomes a reliable part of your daily toolkit.
Set the correct local repository path
In the config node used by the Git command nodes, make sure you:
- Update the path to your local Git repository so n8n knows exactly where to run Git commands
This local path is what allows the workflow to pull, add, commit, and push files from the right project directory.
Authentication and credentials
The workflow uses two types of authentication:
- OAuth2 token for GitHub API calls in the GitHub nodes, which handle single file operations like getting and pushing
README.md - Git credentials for the Git command nodes, which may be a username and password or a token, depending on your Git setup
Once these are configured, you can trigger the workflow with confidence, knowing that every step has the right access to complete successfully.
Why This n8n GitHub Template Is A Powerful Starting Point
This workflow is more than a convenience script. It is a small, repeatable system that:
- Automates repetitive GitHub tasks so you can focus on creative and strategic work
- Handles both precise single file edits and broader bulk changes in one place
- Can be triggered manually today, then integrated into larger n8n automations tomorrow
You can connect it to scheduled triggers, form submissions, deployment processes, or internal tools. Over time, your GitHub repository becomes part of a larger automated ecosystem instead of a separate, manual chore.
Your Next Step: Experiment, Extend, And Make It Yours
The real value of this n8n workflow template appears when you start adapting it to your own needs. You might:
- Change which file is updated via the GitHub node
- Adjust the shell commands to generate custom reports or documentation
- Trigger the workflow from other automations, not just manual execution
Each small improvement brings you closer to a workflow where GitHub updates happen reliably, with less effort and more consistency. You are not just automating tasks, you are designing a smoother way of working.
If you are ready to simplify your GitHub maintenance, save time, and build momentum with automation, try replicating this workflow in your n8n instance today. Use it as a base, then iterate as you learn what works best for you and your team.
For more ideas on integrating GitHub with n8n and other automation tools, explore our blog for in-depth guides or subscribe to our newsletter to keep growing your automation skills.