Automate Google Trends to Google Sheets with n8n & Jina.ai
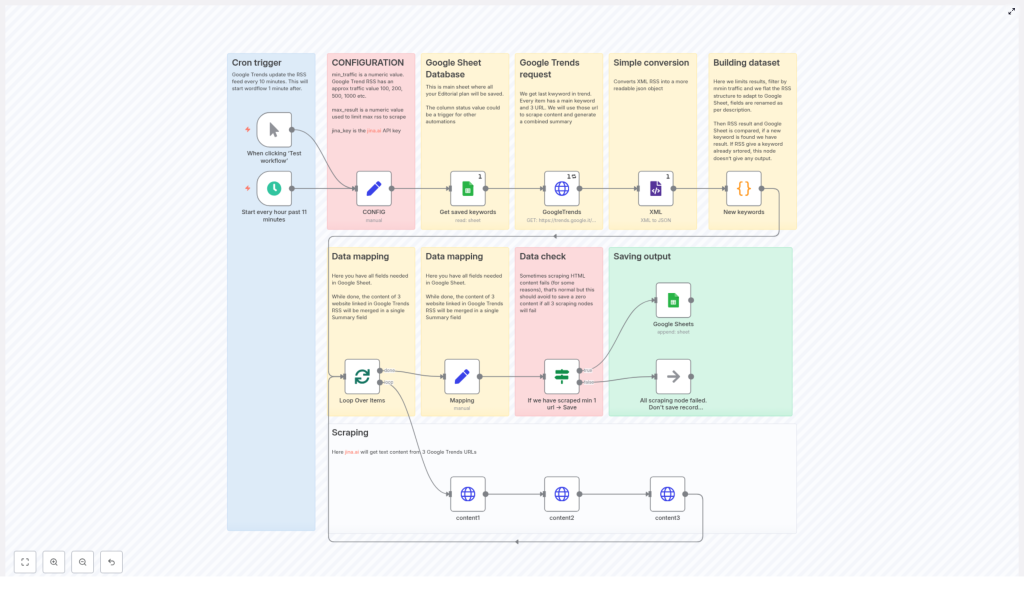
This reference-style guide documents an n8n workflow that turns Google Trends RSS topics into a structured editorial backlog in Google Sheets. The automation retrieves Google Trends RSS items, converts the XML feed to JSON, normalizes and filters the data in a Code node, scrapes the related news URLs through Jina.ai, deduplicates against an existing Google Sheet, and finally appends only vetted, non-duplicate entries to your editorial sheet.
The content below explains the overall architecture, each node’s role, configuration parameters, and practical considerations for running this workflow in production.
1. Workflow overview
1.1 Purpose and use cases
The workflow is designed for content teams, newsrooms, and growth marketers who want to:
- Continuously monitor Google Trends topics without manual RSS checks
- Automatically extract and summarize related news content from trend items
- Filter topics by estimated search interest using
approx_traffic - Prevent duplicate topics in an existing editorial Google Sheet
- Maintain a structured, always-on editorial idea pipeline
1.2 High-level data flow
At a high level, the workflow executes the following pipeline on a schedule or manual trigger:
- Trigger: Cron-based schedule or manual trigger for testing
- Configuration: A Set node that stores
min_traffic,max_results, and the Jina.ai API key - Existing data: Google Sheets Read node that fetches existing editorial entries and their
trending_keywordvalues - Source feed: HTTP Request node that retrieves the Google Trends RSS feed, followed by an XML node that converts it to JSON
- Normalization & filtering: Code node that flattens the RSS feed, parses
approx_traffic, filters by traffic and duplicates, and limits results - Per-item processing: SplitInBatches (or equivalent) to iterate over each new trending keyword individually
- Scraping: Up to three HTTP calls to
r.jina.aifor each item’s related news URLs, collecting plain text content - Validation: If node that checks whether enough content was scraped to justify saving
- Persistence: Google Sheets Append node that writes curated items to the editorial sheet
2. Architecture & node sequence
2.1 Trigger layer
- scheduleTrigger: Cron-based execution (e.g. every hour at minute 11)
- manualTrigger: Optional node used for ad-hoc runs and debugging
The cron schedule should be configured with awareness of Google Trends update frequency (roughly every 10 minutes) and external API rate limits. Hourly or less frequent runs are typically sufficient.
2.2 Configuration layer
- CONFIG (Set node): Central place to store runtime constants:
min_traffic– minimumapprox_trafficvalue required for a trend to be considered (for example 500)max_results– maximum number of trends to process and save per runjina_key– API key for the Jina.air.jina.aiendpoint
Keeping these values in a Set node (or environment variables) allows non-technical users to adjust thresholds without editing the Code node.
2.3 Existing data layer (Google Sheets read)
- Get saved keywords (Google Sheets):
- Reads the editorial Google Sheet that stores existing trend-derived ideas
- Extracts the
trending_keywordcolumn - Provides a reference list for deduplication in the Code node
If a trend’s keyword is already present in this sheet, the workflow will skip it to avoid repeated ideas.
2.4 Source feed ingestion layer
- GoogleTrends (HTTP Request):
- Performs an HTTP GET request to the Google Trends RSS endpoint, for example:
https://trends.google.it/trending/rss?geo=IT - Returns the raw XML RSS feed
- Performs an HTTP GET request to the Google Trends RSS endpoint, for example:
- XML node:
- Converts the XML RSS response into JSON
- Makes fields such as
title,pubDate, andapprox_trafficaccessible to downstream nodes
The XML node is essential because the subsequent Code node expects a JSON representation of each RSS item and its nested related news entries.
2.5 Normalization & filtering layer (Code node)
- New keywords (Code node):
- Flattens the nested RSS item structure into one object per trending topic
- Extracts and normalizes key fields:
trending_keyword(from RSS item title or equivalent)pubDateapprox_trafficparsed as an integer- Up to three related news entries per trend:
- URL
- Title
- Picture
- Source
- Parses traffic values, for example:
- Transforms strings like
"1,000+"into a numeric value1000
- Transforms strings like
- Filters out items that do not meet the configured criteria:
- Removes items where
approx_traffic < min_traffic - Removes items whose
trending_keywordalready exists in the Google Sheet
- Removes items where
- Sorts remaining items by traffic in descending order
- Applies
max_resultsto limit the number of items that proceed further
Centralizing this logic in a single Code node simplifies maintenance. Adjustments to thresholds, parsing rules, or how related news items are selected can be made in one place.
2.6 Per-item processing and mapping
- Loop Over Items (splitInBatches & mapping):
- splitInBatches: Iterates through each filtered trend item one at a time
- Mapping (Set node):
- Prepares a structured payload that will eventually be written to Google Sheets
- Defines the target fields such as:
status(e.g. default value"idea")trending_keywordpubDateapprox_traffic- Slots for up to three URLs, titles, pictures, and sources
abstract(to be filled with combined scraped content later)
This layer ensures each item is processed in isolation, which makes debugging and error handling more manageable.
2.7 Scraping & summarization with Jina.ai
- content1, content2, content3 (HTTP Request nodes):
- Each node targets one of the up to three related news URLs from the RSS item
- Uses the Jina.ai
r.jina.aiendpoint to:- Fetch the article HTML from the source URL
- Return a cleaned text representation of the page
- Includes headers that:
- Pass the
jina_keyfor authentication - May specify content preferences, such as removing certain selectors or limiting returned content length
- Pass the
The three scraping nodes are executed in sequence or conditionally depending on which URLs are present. Their outputs are later concatenated into a single summary string. This avoids maintaining a custom HTML parser and leverages Jina.ai’s text extraction capabilities.
2.8 Validation and conditional save
- If we have scraped min 1 url → Save (If node):
- Combines the text returned by
content1,content2, andcontent3 - Performs a length check on the combined summary, for example:
- Only passes the item forward if the summary length is greater than 100 characters
- If the condition is not met (no usable content or too short):
- Routes the item to a no-op branch, effectively skipping the save step
- Combines the text returned by
This prevents low-quality or empty summaries from polluting the editorial sheet, especially in cases where scraping fails or the target pages have minimal text.
2.9 Persistence layer (Google Sheets append)
- Google Sheets (append):
- Appends validated items as new rows to the configured Google Sheet
- Typical fields include:
status(e.g."idea")pubDateabstract(combined summary from scraped content)approx_traffic- Up to three:
- URL columns
- Title columns
- Picture columns
- Source columns
trending_keyword
From this sheet, you can trigger additional n8n workflows, such as Slack notifications, task creation, or content generation pipelines.
3. Detailed configuration notes
3.1 Credentials and keys
- Jina.ai API key (
jina_key):- Store this in n8n’s credential manager whenever possible
- Alternatively, reference it in the CONFIG node and ensure that workflow exports do not expose the key
- Pass the key in the headers of the Jina.ai HTTP Request nodes as required by the API
- Google Sheets credentials:
- Configure a Google Sheets credential in n8n with appropriate access to the target spreadsheet
- Use the same credential for both read and append operations
3.2 Traffic thresholds and limits
min_traffic:- Controls the minimum interest level a trend must have to be considered
- Google Trends uses approximate bands such as 100, 200, 500, 1000+
- Choose a value that fits your market or niche. For example:
- Smaller markets:
min_trafficmight be 100 or 200 - Larger markets: start at 500 or 1000
- Smaller markets:
max_results:- Limits how many new trends are processed and appended per run
- Helps control editorial workload and API usage
3.3 Scheduling strategy
- Google Trends updates frequently, but not necessarily every minute
- Hourly schedules are a good starting point to balance freshness and API consumption
- Adjust frequency based on:
- Available Jina.ai quota and rate limits
- Google Sheets write limits
- Your editorial team’s capacity to handle new ideas
3.4 Sheet structure expectations
The workflow assumes a Google Sheet with columns that can store at least:
statustrending_keywordpubDateapprox_trafficabstract- Columns for up to three:
- URL fields
- Title fields
- Picture fields
- Source fields
The exact column order and naming must match the configuration of your Google Sheets Append node. The deduplication logic relies on a consistent trending_keyword column.
4. Edge cases, error handling & best practices
4.1 Rate limits and quotas
- Jina.ai:
- Each run can trigger up to three scraping requests per trend item
- Use
max_resultsand scheduling to keep total requests within your plan limits
- Google APIs:
- Google Sheets Read and Append operations count against API quotas
- Batch runs and moderate scheduling reduce the risk of hitting limits
4.2 Handling empty or low-quality scraping results
- Some URLs may:
- Block scraping
- Return very short content
- Use heavy client-side rendering that yields little text
- The If node’s length check (e.g. summary length > 100 characters) helps:
- Skip items where no meaningful content was returned
- Avoid cluttering the sheet with empty abstracts
- If you consistently see empty results for certain domains, consider:
- Adjusting Jina.ai parameters (such as selectors) if applicable
- Using a different scraping approach for those domains in a separate branch
4.3 Data validation enhancements
Beyond the built-in traffic and length checks, you can add extra validation steps, for example:
- Language detection to keep only content in your target language
- Additional duplicate checks, such as:
- Recent time window deduplication
- Comparisons on URL rather than only on
trending_keyword
- Minimum number of distinct URLs successfully scraped
4.4 n8n error handling patterns
- Enable retryOnFail where appropriate for transient HTTP failures