Automate Google Search Console Reports with an n8n Workflow
Managing SEO at scale requires reliable, repeatable access to high quality Search Console data. Manually exporting reports is slow, prone to error, and rarely integrated into existing analytics or task management systems. This article presents a reusable n8n workflow template that automates key Google Search Console (GSC) API operations, including URL inspection, performance queries, keyword diagnostics, cannibalization detection, content gap discovery, and performance drop monitoring.
The goal is to transform raw GSC data into structured, prioritized SEO actions that can be consumed by analysts, SEOs, and product teams, using a maintainable, modular n8n setup.
Why automate Google Search Console with n8n?
For organizations handling large websites or multiple properties, automation is essential. Using n8n as an orchestration layer for the Google Search Console API provides several strategic advantages:
- Operational efficiency – Replace manual exports with scheduled, reproducible workflows.
- Data reliability – Reduce human error in filtering, segmenting, and aggregating GSC data.
- Early issue detection – Surface cannibalization, content gaps, and performance drops before they become critical.
- Actionable output – Translate metrics into clear action items such as rewriting titles, consolidating content, or creating new pages.
- Integrated reporting – Push results directly into Slack, Google Sheets, BI tools, or ticketing systems.
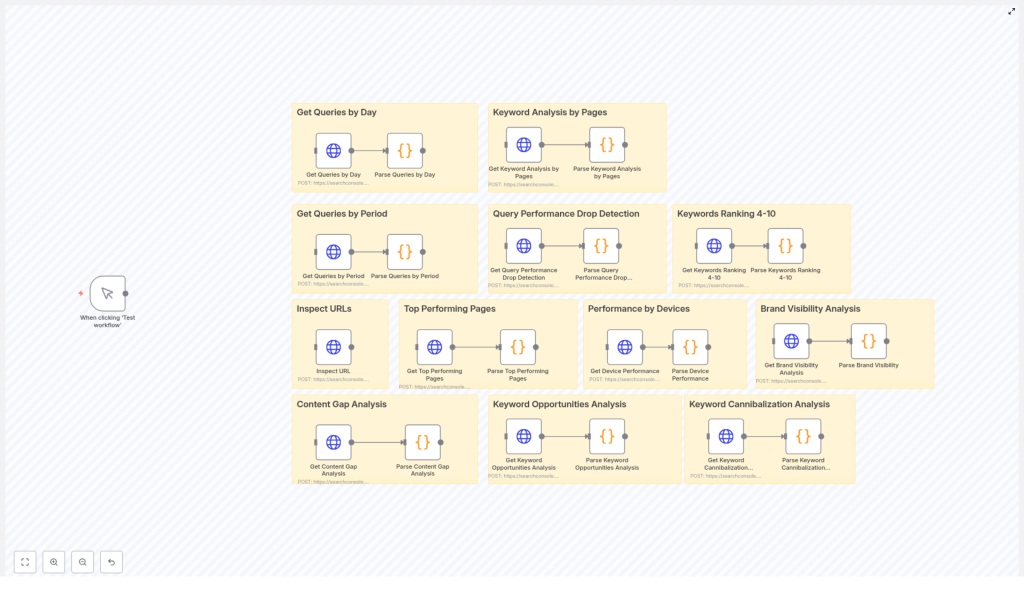
The workflow template, titled “Product – Google Search Console API Examples”, is designed as a modular toolkit that SEO and data teams can adapt to their own context.
Architecture of the n8n GSC workflow
The workflow is organized into functional groups, each focusing on a specific SEO analysis or monitoring task. These groups share common building blocks such as HTTP Request nodes (for GSC API calls), JavaScript Code nodes (for parsing and enrichment), and optional output nodes (for reporting and notifications).
Core functional modules
- Inspect URL Uses the Google Search Console URL Inspection API to return indexing, coverage, and status details for a single URL. Ideal for monitoring critical landing pages or troubleshooting indexation issues.
- Top Performing Pages Queries
searchAnalyticsby page to compute clicks, impressions, CTR, and average position, then classifies pages and recommends optimization actions. - Performance by Devices Breaks down performance by device type (desktop, mobile, tablet) and calculates relative shares of clicks and impressions to support device-specific optimization strategies.
- Keyword Analysis by Pages Maps queries to landing pages to identify top-performing keywords per URL, highlight underutilized terms, and suggest on-page optimization opportunities.
- Keyword Cannibalization Detection Groups data by query to identify cases where multiple pages are competing for the same keyword. Provides guidance on consolidation, canonicalization, or restructuring.
- Content Gap Analysis Identifies high-impression queries with weak rankings, signaling opportunities for new or significantly expanded content.
- Keyword Opportunities & Emerging Keywords Detects queries ranking between positions 10 and 50, especially those with rising impressions, and assigns priority levels for content or optimization work.
- Query Performance Drop Detection Compares performance across time periods to flag statistically significant drops in clicks, impressions, or average position for important queries.
- Keywords Ranking 4-10 Extracts queries where URLs are close to the top of page 1, highlighting “quick win” opportunities where minor adjustments can yield notable gains.
- Brand Visibility Analysis Segments queries into brand and non-brand groups, then compares CTR and average position. Useful for understanding branded search strength and incremental non-brand opportunity.
Key n8n components and how they work
1. HTTP Request nodes for Search Console queries
The backbone of the workflow is a set of HTTP Request nodes that call the Google Search Console searchAnalytics/query endpoint using POST requests. Each request is configured with a JSON payload that defines:
startDateandendDatefor the reporting windowdimensionssuch asquery,page,device, ordaterowLimitto control the maximum number of rows returned
Example payload for a page-level analysis:
{ "startDate": "2025-02-26", "endDate": "2025-03-26", "dimensions": ["page"], "rowLimit": 5000
}Authentication uses Google OAuth2 credentials configured within n8n. To ensure stable access:
- Enable the Search Console API in your Google Cloud project.
- Grant the OAuth client the appropriate scopes for Search Console.
- Confirm that the authenticated Google account has access to the relevant property in Search Console (for example,
sc-domain:your-domain.com).
2. JavaScript Code nodes for parsing and prioritization
Raw GSC API responses are not directly actionable. The workflow uses Code nodes to normalize, enrich, and categorize the data. Typical operations include:
- Mapping rows into explicit fields such as
page,query,clicks,impressions,ctr, andposition. - Calculating derived metrics such as
clickShareandimpressionShareacross segments. - Classifying performance into categories like Star Performer, CTR Opportunity, or Ranking Opportunity based on configurable thresholds.
- Generating structured recommendations, for example:
- “Rewrite title tag” for URLs with strong positions but weak CTR.
- “Content optimization” where rankings are moderate but impressions are high.
- “Merge similar pages” where cannibalization is detected.
- Detecting cannibalization by grouping rows by query, then assessing click distribution and variation in average position across competing URLs.
Thresholds and classification logic are intentionally simple to customize, so teams can adapt them to different traffic scales and business priorities.
3. Pagination and aggregation of large result sets
For larger sites, individual queries can return up to tens of thousands of rows. The workflow supports pagination for requests with high rowLimit values (up to 25,000). Paginated responses are combined before analysis so that:
- Aggregated metrics remain accurate.
- Cannibalization and content gap calculations are based on complete data rather than partial samples.
- Severity and prioritization scoring reflects the full query set.
This pattern is particularly important for enterprise environments or properties with extensive long-tail traffic.
Configuration guide
To deploy this n8n GSC workflow template, follow these configuration steps:
- Create and configure a Google Cloud project
- Create a project in the Google Cloud Console.
- Enable the Google Search Console API.
- Set up OAuth 2.0 credentials
- Create OAuth 2.0 client credentials (typically a Web application).
- Add your n8n instance’s redirect URI to the OAuth configuration.
- Add Google OAuth credentials in n8n
- In n8n, create a new Google OAuth2 credential.
- Use the client ID and client secret from the Google Cloud project.
- Authorize access with a Google account that has the relevant Search Console property rights.
- Customize HTTP Request nodes
- Update all instances of the property identifier, for example replace
sc-domain:your-domain.comwith your actual domain or URL prefix property. - Adjust
startDateandendDateto match your analysis windows (daily, weekly, monthly, or custom ranges). - Review and adjust
rowLimitvalues according to your data volume and resource constraints.
- Update all instances of the property identifier, for example replace
- Tune thresholds in Code nodes
- Modify impression, CTR, and position thresholds to reflect your site scale. For example, increase an impressions threshold from 100 to 500 or more for large enterprise domains.
- Adjust logic for what constitutes a “drop” in performance, such as minimum percentage decline or absolute change in clicks or position.
- Connect outputs to your preferred destinations
- Send summarized results to Google Sheets for stakeholder reporting.
- Post alerts to Slack channels for real-time monitoring.
- Write to a database or data warehouse for long-term storage and BI integration.
- Push action items into Jira, Asana, or other project management tools.
Practical automation scenarios
Once configured, the workflow can support a variety of recurring SEO processes.
- Daily performance monitoring Run the Query Performance Drop Detection segment each morning. If significant declines are identified, automatically notify a Slack channel with key details and recommended next steps.
- Weekly SEO reporting Schedule exports of Top Performing Pages and Keyword Opportunities & Emerging Keywords to a Google Sheet. This creates a consistent weekly snapshot for stakeholders, including product, content, and leadership teams.
- Automated SEO action queue Convert generated CTAs such as “Rewrite title tag – very low CTR” or “Merge similar pages” into tasks in Jira or Asana. This ensures that insights from GSC are directly translated into execution work for content and development teams.
- URL health and indexation monitoring Use the Inspect URL module on a recurring schedule for high value pages. If coverage or indexation issues are detected, trigger alerts for engineering or SEO ops teams.
Best practices for robust GSC automation
To operate this workflow reliably at scale, consider the following best practices:
- Optimize API usage Combine dimensions where appropriate to reduce the number of API calls. For example, request
["page", "query"]together when you need both dimensions instead of running separate queries. - Use appropriate row limits and pagination Set
rowLimitin line with your expected data volume and available runtime. For very large properties, consider chunking by date range or segment to stay within time and quota limits. - Align thresholds with your domain profile Tailor CTR, impression, and position thresholds to your domain authority, market, and traffic level. What is “high impression” or “low CTR” will vary significantly between sites.
- Persist processed data Store enriched outputs (including classifications and action items) in a database or data warehouse. This avoids reprocessing the same time windows, supports trend analysis, and enables more advanced BI reporting.
Troubleshooting common issues
If you encounter problems while running the workflow, the following checks typically resolve them:
- 401 or 403 errors
- Verify that the OAuth token has the necessary scopes.
- Confirm that the authenticated Google account has access to the Search Console property.
- Check that the property identifier (for example
sc-domain:example.com) is correct.
- Empty or missing rows
- Ensure that the selected date range actually contains data.
- Confirm that the dimensions are valid for the chosen endpoint and property.
- Test a shorter, recent date range to verify that the integration is working.
- Slow or long-running executions
- Reduce
rowLimitor split requests into smaller date ranges. - Segment by device or country to limit per-call volume.
- Review n8n execution limits and schedule heavy jobs during off-peak times.
- Reduce
Extending the workflow template
The template is intentionally modular so that teams can build on top of it as their analytics capabilities mature. Potential extensions include:
- Predictive modeling Integrate a machine learning model that estimates traffic lift from specific content or on-page changes, informed by historical GSC performance.
- BigQuery or data warehouse integration Pipe normalized GSC data into BigQuery or another warehouse for large scale historical analysis, cohort studies, and advanced dashboards.
- Content quality and duplication checks Combine GSC data with content metadata or CMS exports to detect duplicate, thin, or overlapping content that contributes to cannibalization and weak performance.
Conclusion
Automating Google Search Console reporting with n8n moves your SEO practice from reactive reporting to proactive, data-driven optimization. By operationalizing URL inspection, performance segmentation, cannibalization detection, and opportunity identification, this workflow template turns raw API output into a prioritized backlog of SEO tasks that teams can execute consistently.
Next steps
Import the template into your n8n instance, connect your Google OAuth credential, and configure the property and thresholds for your domain. Once scheduled, the workflow will continuously surface insights and action items without manual intervention.
If you require support in tailoring thresholds, setting up Slack alerts, or integrating with Google Sheets and project management tools, reach out to your internal automation team or SEO operations lead to extend and customize the workflow for your specific environment.