Automate Interviews with n8n: Interview Scheduler Template
Use this n8n Interview Scheduler workflow template to automate interview coordination, centralize candidate data, and maintain an auditable log of every interaction. The automation combines a webhook trigger, text splitting, OpenAI embeddings, a Weaviate vector database, a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) agent, and structured logging in Google Sheets, with Slack alerts for operational errors.
This reference-style guide explains the workflow architecture, each node’s role, configuration details, and how data moves through the system so you can deploy, debug, and extend the template with confidence.
1. Workflow Overview
The Interview Scheduler workflow is designed to:
- Accept interview requests via an HTTP POST webhook.
- Extract and split free-text content into manageable chunks.
- Generate semantic embeddings with OpenAI and store them in Weaviate.
- Use a RAG-style agent to interpret candidate constraints and propose next steps.
- Persist all outcomes to Google Sheets for reporting and auditability.
- Send Slack alerts if any error occurs during processing.
The result is a reusable, API-driven interview scheduling automation that can sit behind your forms, ATS, or custom front-end.
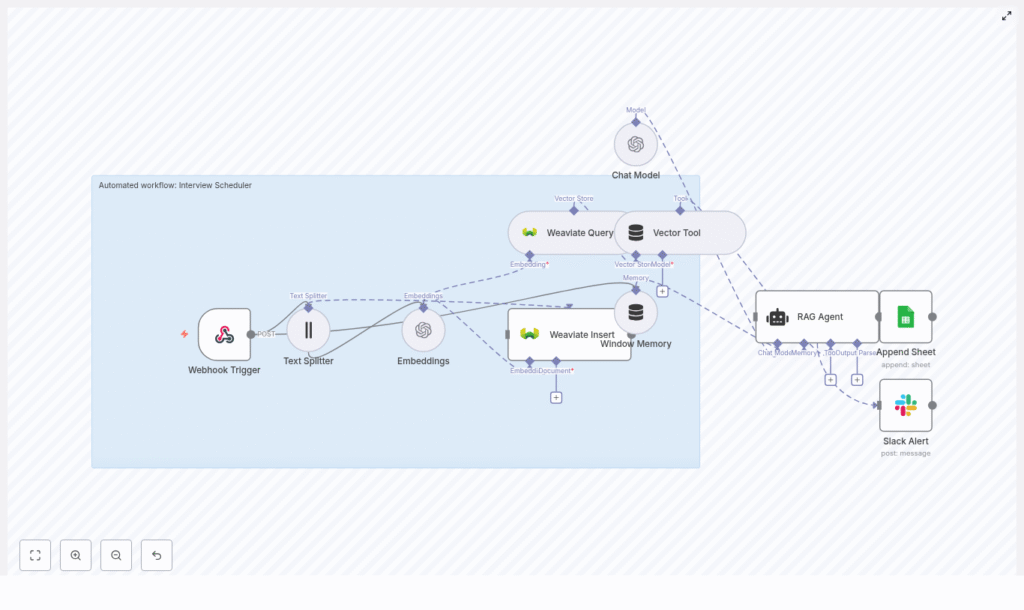
2. Architecture & Data Flow
The workflow is composed of the following logical stages:
- Webhook Trigger – Receives interview request payloads via HTTP POST.
- Text Splitting – Splits long notes or email threads into chunks.
- Embeddings (OpenAI) – Converts chunks into vector representations.
- Weaviate Insert – Stores embeddings into the
interview_schedulerindex. - Weaviate Query – Retrieves contextually relevant records for the current request.
- Vector Tool – Exposes Weaviate query as a tool for the RAG agent.
- RAG Agent – Uses OpenAI Chat Model, vector tool, and window memory to generate a scheduling decision or response.
- Window Memory – Maintains short-term conversational state across steps.
- Google Sheets Append – Logs each processed request and agent status.
- Slack Alert (onError) – Sends notifications to a Slack channel if the workflow fails.
Data flows linearly from the webhook through embedding and retrieval into the agent, then into logging. An error branch handles failures and triggers Slack alerts.
3. Node-by-Node Breakdown
3.1 Webhook Trigger
Node type: Webhook
Purpose: Entry point for external systems to submit interview requests.
The workflow is triggered via an HTTP POST webhook named interview-scheduler. n8n exposes a unique URL for this webhook, which you can integrate with:
- Web forms (e.g. application or scheduling forms).
- Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) that support webhooks.
- Custom front-ends or backend services.
Expected payload fields (example):
candidate_namecontact_info(email, phone, or both)preferred_times(free text or structured JSON)notes(optional, may include email threads or recruiter comments)
Configuration notes:
- Method should be set to
POST. - Ensure the n8n instance is accessible via a public endpoint if used from external systems.
- Consider adding authentication or IP allowlists to restrict access to the webhook.
3.2 Text Splitter
Node type: Text Splitter
Purpose: Break long text into smaller segments suitable for embedding and retrieval.
Candidate notes or email threads can be lengthy. The Text Splitter node processes the relevant text fields and divides them into overlapping chunks, for example:
chunkSize = 400charactersoverlap = 40characters
This configuration preserves context across boundaries and improves retrieval accuracy. Overlap ensures that important information near the end of a chunk is still visible at the beginning of the next chunk.
Edge considerations:
- If the text is shorter than the configured
chunkSize, it will pass through as a single chunk. - Verify that only relevant fields (for example
notesorpreferred_times) are passed to the splitter to avoid unnecessary token usage later.
3.3 Embeddings (OpenAI)
Node type: OpenAI Embeddings
Purpose: Transform text chunks into numerical vectors for semantic search.
The workflow uses an OpenAI embeddings model such as text-embedding-3-small to convert each text chunk into a vector. These embeddings are later stored in Weaviate and used for similarity search.
Typical configuration:
- Model:
text-embedding-3-small(or another compatible OpenAI embedding model) - Input: Array of chunked text from the Text Splitter node
- Credentials: OpenAI API key configured in n8n credentials
Operational notes:
- Monitor your OpenAI usage limits and costs, especially if processing high volumes.
- Batching chunks into a single embeddings request where possible can reduce API overhead.
- If the node fails, check API key validity, model name, and account rate limits.
3.4 Weaviate Insert & Query
Node types: Weaviate Insert, Weaviate Query
Purpose: Persist embeddings and retrieve relevant context for each new request.
3.4.1 Weaviate Insert
The Insert node stores each embedding vector along with its associated metadata in a Weaviate index. The template assumes an index (class) named interview_scheduler.
Key configuration elements:
- Weaviate instance: Cloud or self-hosted, reachable from n8n.
- Index name (class):
interview_scheduler. - Schema: Should support fields such as text content, candidate identifiers, timestamps, and any other metadata you include.
Schema validation:
- Ensure the schema is created in Weaviate before running the workflow.
- Match property names in the node configuration with the Weaviate schema fields.
3.4.2 Weaviate Query
The Query node performs a similarity search against the interview_scheduler index using the current request’s embeddings. This returns the most relevant passages or records to be used as context by the RAG agent.
Usage in the workflow:
- The query uses the embedding of the current request to retrieve similar historical notes or constraints.
- Returned results are passed to the Vector Tool node, which exposes them to the agent.
Failure handling:
- If the query fails, verify network connectivity to the Weaviate instance and index name spelling.
- Check that the Weaviate API key or auth configuration is correctly set in n8n credentials.
3.5 Vector Tool & RAG Agent
3.5.1 Vector Tool
Node type: Vector Tool (LangChain-style tool wrapper)
Purpose: Wrap Weaviate query capabilities as a callable tool for the agent.
The Vector Tool node takes the Weaviate Query configuration and exposes it as a function-like tool that the agent can invoke when it needs additional context. This keeps the RAG logic modular and allows the agent to decide when to query the vector store.
3.5.2 RAG Agent
Node type: Agent (RAG / tool-using agent)
Purpose: Combine candidate data, vector store context, and a chat model to generate scheduling decisions.
The RAG Agent node uses an OpenAI Chat Model together with:
- The Vector Tool for retrieving context from Weaviate.
- Window Memory for short-term conversational history.
Key configuration aspects:
- Model: An OpenAI chat model configured in n8n (for example a GPT-based model).
- System prompt: Instructs the agent to act as an Interview Scheduler assistant, guiding it to:
- Interpret candidate availability and constraints.
- Identify conflicts or missing information.
- Propose suggested interview times or next steps.
- Tools: The Vector Tool is attached so the agent can fetch context as needed.
Output: The agent produces a structured status message that typically includes:
- Recommended interview slots or actions.
- Any detected conflicts or issues.
- Summary notes for logging.
Prompt design tips:
- Define a clear output format (for example JSON fields or bullet points) to simplify downstream parsing and logging.
- Explicitly instruct the agent on how to handle ambiguous or incomplete availability information.
3.6 Window Memory
Node type: Window Memory
Purpose: Maintain a limited sliding window of conversation history for the agent.
Window Memory stores the most recent messages in the interaction so the agent can maintain context across multiple steps. This is particularly useful for:
- Follow-up questions about availability.
- Clarifications on constraints or preferences.
- Multi-turn interactions where the agent refines its suggestion.
Configuration note: The memory window size should be set to a reasonable number of turns to balance context retention with token usage and performance.
3.7 Append to Google Sheets
Node type: Google Sheets – Append
Purpose: Persist a log of each processed request and the agent result.
After the RAG Agent generates the final status, the workflow appends a new row to a Google Sheet. This sheet acts as a single source of truth and an audit log for interview scheduling operations.
Typical configuration:
- Spreadsheet ID: The target Google Sheets document ID (
SHEET_ID). - Sheet name:
Log.
Example fields to log:
- Timestamp of processing.
- Candidate name.
- Parsed availability or requested time slots.
- Agent decision or status message.
- Any error flags or notes.
Access control: Ensure the Google Sheets credentials used in n8n have write access to the specified spreadsheet and sheet.
3.8 Slack Alerts (Error Handling)
Node type: Slack – Send Message
Purpose: Notify the team when the workflow encounters an error.
The workflow includes an onError branch. If any upstream node fails (for example OpenAI, Weaviate, or Sheets), this branch sends a Slack alert to a configured channel such as #alerts.
Alert content (typical):
- Error message or stack trace (as available in n8n error data).
- Context about which node failed.
- Optional reference to the candidate or request ID if available.
Slack configuration:
- Slack app or bot token configured as credentials in n8n.
- Channel ID or name set in the node parameters (for example
#alerts).
4. Configuration & Deployment Checklist
Before enabling the Interview Scheduler in production, verify the following:
- n8n instance
- Hosted or self-hosted with a stable, public URL for the webhook.
- Environment variables and credentials stored securely in n8n.
- OpenAI
- OpenAI account with a valid API key.
- OpenAI credentials configured in n8n.
- Embedding model (for example
text-embedding-3-small) and chat model available in your account.
- Weaviate
- Cloud or self-hosted Weaviate instance reachable from n8n.
- Schema defined with an index (class) named
interview_scheduler. - Authentication and TLS configured according to your environment.
- Google Sheets
- Service account or OAuth credentials configured in n8n.
- Target spreadsheet ID (
SHEET_ID) accessible by those credentials. - Sheet named
Logcreated in the spreadsheet.
- Slack
- Slack app or bot with permission to post messages.
- Slack credentials configured in n8n.
- Alert channel (for example
#alerts) specified in the node.
5. Best Practices for Reliability & Cost Control
- Secure the webhook
- Use authentication headers, tokens, or IP allowlists to prevent unauthorized requests.
- Optimize text chunking
- Use chunk overlaps (for example 40 characters) to maintain context between chunks.
- Avoid embedding unnecessary fields to reduce token usage.
- Control embedding costs
- Monitor embedding volume and costs in OpenAI dashboards.
- Batch chunks where possible to reduce API overhead.
- Design robust prompts
- Provide a clear system message describing the agent’s role as an Interview Scheduler.
- Specify the expected output structure to make downstream parsing and logging easier.
- Minimize sensitive data in vectors
- Store only the necessary personal data in Weaviate.
- Use hashed identifiers where possible to align with privacy policies.
6. Security & Privacy Considerations
Interview workflows often handle personal and potentially sensitive information. Ensure that your implementation aligns with your organization’s security and compliance requirements.
- Encryption
- Use TLS for all connections to Weaviate and Google Sheets.
- Ensure n8n itself is served over HTTPS.
- Access control
- Restrict access to the Google Sheet and Weaviate index to necessary service accounts only.
- Limit who can view the n