Automate Notion Updates with n8n & Supabase
Imagine this: you are copying text out of Notion, pasting it into some other tool, checking context, updating a status, logging it somewhere else, then doing it all again for the next page. And the next. And the next. By the fifth time, you are questioning your life choices.
This workflow template is here to rescue you from that copy-paste purgatory. With n8n, Supabase, LangChain, OpenAI embeddings, and Anthropic chat, you can turn Notion-related chaos into a sensible, automated pipeline that actually understands context instead of just blindly moving text around.
In this guide, you will see how the template:
- Listens for incoming events through a webhook
- Splits and embeds your Notion content
- Stores and retrieves vectors in Supabase
- Uses a RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) Agent to generate smart, context-aware responses
- Logs everything neatly in Google Sheets and warns you in Slack if something breaks
By the end, you will know exactly what this “Notion API Update” workflow does, how it works, and how to set it up without losing your sanity.
What this n8n workflow actually does (in human terms)
The workflow is called Notion API Update, but it is more than just a basic sync. It is a production-ready automation that:
- Receives incoming POST requests via a webhook
- Splits big chunks of Notion content into smaller, embedding-friendly pieces
- Turns those pieces into vector embeddings using OpenAI’s
text-embedding-3-small - Saves those vectors in a Supabase vector index named
notion_api_update - Queries that index later to pull relevant context for new events
- Gives that context to a RAG Agent powered by Anthropic chat
- Lets the agent generate a final output that actually respects your previous content
- Logs the result in Google Sheets and sends Slack alerts if something fails
In short, it is a context-aware Notion automation that knows what has happened before, can “remember” related content via Supabase vectors, and uses that to produce smarter updates and logs.
Why bother automating Notion updates like this?
If you are already tired of repetitive manual updates, you probably know the answer. This workflow helps you:
- Trigger updates in real time with webhook-driven events instead of periodic manual sweeps
- Make your content searchable by meaning using text splitting and embeddings, not just keyword search
- Use Supabase as a vector database so you can fetch the most relevant context in milliseconds
- Leverage a RAG agent that combines stored context with a chat model to produce smart, grounded outputs
- Stay informed using Google Sheets logging and Slack alerts so failures do not hide quietly in the background
Instead of juggling multiple tools and tabs, you get one pipeline that listens, understands, responds, and logs. You just get to look clever while it runs.
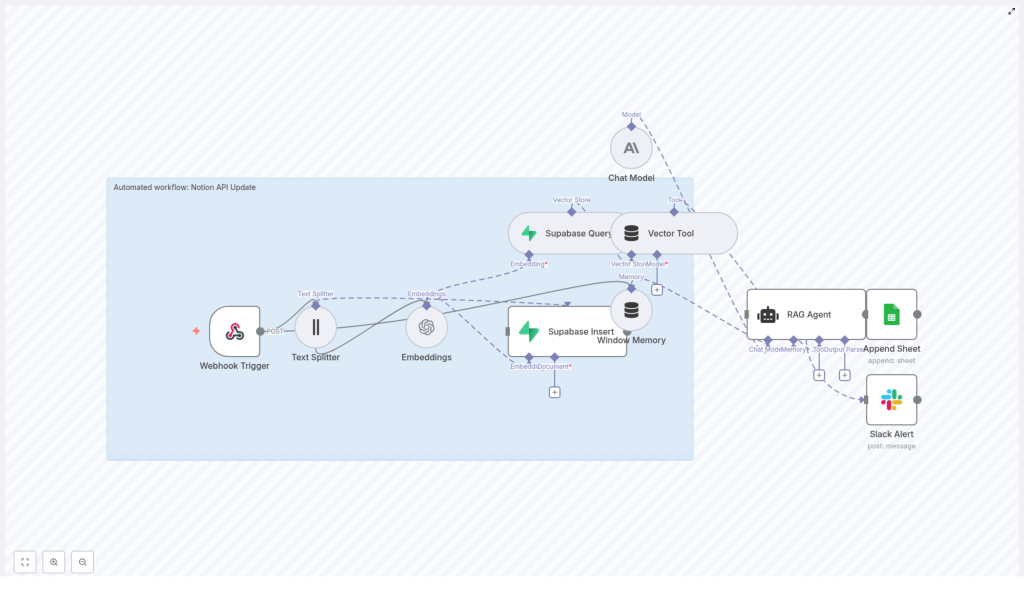
High-level architecture: how the pieces fit together
Here is the big picture of the Notion API Update workflow in n8n:
- Webhook Trigger receives a POST payload from Notion, another app, or your own script.
- Text Splitter breaks large content into smaller chunks with a configurable size and overlap.
- Embeddings (OpenAI) converts each chunk into a semantic vector using
text-embedding-3-small. - Supabase Insert stores those vectors plus metadata in the
notion_api_updateindex. - Supabase Query later retrieves similar vectors when context is needed.
- Vector Tool + Window Memory expose vector search and recent interaction history to the RAG Agent.
- RAG Agent (LangChain) with Anthropic chat uses that context to generate the final response.
- Append Sheet + Slack Alert log results to Google Sheets and send Slack alerts on failure.
Think of it as a pipeline that turns raw Notion events into structured, context-aware answers, then writes everything down so you can track what happened.
Quick setup guide: from zero to automated Notion updates
You do not need to be a full-time ML engineer to get this running. Here is how to wire it up in n8n, step by step.
1. Webhook Trigger – your front door for events
Start with a Webhook node in n8n and configure it to accept POST requests at a path like:
/notion-api-update
Any external system that can send HTTP requests can now feed this workflow. That includes:
- Notion-related services
- Other automation tools
- Custom scripts or internal tools
For security, do not leave the door wide open. Protect the webhook URL with authentication, IP allowlisting, or a private network setup. Treat it like an API endpoint, not a public suggestion box.
2. Text Splitter – breaking big content into smart chunks
Large Notion pages are not ideal for embeddings as a single blob. The Text Splitter node chops content into smaller segments so the embedding model can focus and your vector search stays sharp.
Template defaults:
chunkSize: 400chunkOverlap: 40
You can adjust these if your content is usually shorter or longer, or if your embedding model has specific token limits. Smaller chunks tend to improve recall but also increase the number of vectors stored and queried.
3. Embeddings (OpenAI) – turning text into vectors
Each chunk from the Text Splitter goes into an Embeddings node using OpenAI’s text-embedding-3-small model. The output is a vector for each chunk, which becomes the backbone of semantic search in Supabase.
Make sure you:
- Store your OpenAI API key securely using n8n credentials
- Monitor token usage and cost if you process a lot of content
The better your embeddings, the better your context retrieval and RAG responses will be.
4. Supabase Insert – building your Notion vector store
Next, the workflow uses a Supabase Insert node to store embeddings in a vector index called notion_api_update. Each record can include metadata such as:
- Notion page ID
- Block ID
- Timestamp
- Original text snippet
This metadata is what lets you trace results back to the exact Notion content they came from. It is incredibly useful when you are debugging or explaining why the RAG Agent produced a particular answer.
5. Supabase Query + Vector Tool – retrieving context on demand
When a new event comes in and the agent needs context, the workflow uses:
- Supabase Query to pull the most similar vectors from
notion_api_update - Vector Tool to expose that vector store as a usable tool for the RAG Agent
This is the “R” in RAG: Retrieval. Instead of the chat model guessing based on vibes, it gets real, stored context from your previous Notion content.
6. Window Memory – giving the agent short-term memory
The Window Memory node keeps a short history of recent interactions. When multiple updates arrive for the same Notion page or topic, the agent can look back at what it did or decided earlier.
This helps avoid responses that sound like the agent has amnesia every time a new event comes in.
7. Chat Model and RAG Agent – the brain of the operation
The RAG Agent node uses LangChain with an Anthropic chat model to combine:
- Retrieved vectors from Supabase
- Conversation history from Window Memory
- Tools like the Vector Tool
You can configure the agent with a system message such as:
You are an assistant for Notion API Update
The agent then turns everything it knows about the incoming event plus stored context into a final, contextualized output. That might be a status message, a content summary, or another structured result suitable for logging or further updates.
8. Append Sheet and Slack Alert – logging and visibility
Finally, the workflow handles outcomes in two ways:
- Append Sheet writes successful results into a Google Sheet, including a column named
Statusthat stores the agent output for historical tracking and audits. - Slack Alert catches failures and sends them to a Slack channel so you can spot and fix issues in real time, instead of discovering them three weeks later.
Think of this as your “black box recorder” plus a friendly alarm system.
Configuration tips and best practices
To keep your Notion automation stable and maintainable, keep these guidelines in mind:
- Use n8n credentials for all secrets Configure OpenAI, Supabase, Google Sheets, and Slack credentials in n8n. Avoid hard-coding API keys in the workflow itself.
- Tune chunk size thoughtfully Start with
chunkSize: 400andchunkOverlap: 40. Smaller chunks improve recall but increase the number of vectors and query time. Iterate based on your content patterns. - Store rich metadata Include Notion IDs, timestamps, and any useful identifiers in each vector record. This makes reverse lookups and traceability much easier later.
- Maintain your index If your Notion content changes frequently, plan periodic pruning or reindexing of older vectors so your retrieval stays relevant.
- Handle errors explicitly Use the RAG Agent’s
onErrorpath to trigger Slack alerts. Silent failures are the worst kind of automation bug.
Security and compliance considerations
Automation is fun until sensitive data leaks. Keep things safe by:
- Restricting webhook access with IP allowlists, shared secrets, or private network rules
- Controlling who can access Supabase and Google Sheets where your data and logs live
- Encrypting data at rest and anonymizing content before creating embeddings if your Notion workspace holds sensitive information
- Reviewing the privacy policies of OpenAI and Anthropic, especially if you are processing PII in embeddings or chat prompts
With a bit of planning, you can have both powerful automation and a compliance team that still speaks to you.
Testing and debugging your Notion automation
Before pointing this at production data, run a few safe experiments.
- Start with sample payloads Use Postman or
curlto send test POST requests to the webhook. This helps you iterate quickly without touching real Notion pages. - Inspect intermediate nodes Check outputs from the Text Splitter and Embeddings nodes. Confirm that chunking looks reasonable and that vector shapes and metadata are correct.
- Query Supabase directly Verify that vectors are stored in the
notion_api_updateindex with the expected metadata. Make sure the index name is consistent everywhere. - Use the logging spreadsheet The Google Sheet populated by the Append Sheet node acts as a running history of agent behavior. It is great for spotting patterns or weird outputs over time.
Scaling and cost: keeping your bill under control
Most of the cost in this setup comes from embeddings and chat model usage. To keep things efficient:
- Cache embeddings for identical content so you are not re-embedding the same text repeatedly.
- Batch smaller updates where possible to reduce per-request overhead.
- Use smaller embedding models for high-volume, non-critical text where ultra-precision is not required.
With a bit of tuning, you can scale this workflow without your finance team staging an intervention.
Example webhook payload
Here is a sample payload you might send into the Webhook Trigger to test the workflow:
{ "pageId": "notion-page-123", "content": "Complete release notes and changelog for v1.2...", "updatedBy": "jane@company.com", "timestamp": "2025-10-01T15:03:00Z"
}
You can adjust these fields to match your own event format, as long as the workflow knows where to find the content it needs to split and embed.
Wrap-up: what you get from this Notion API Update workflow
With this n8n-based Notion automation in place, you get:
- An extensible workflow that listens for events and updates intelligently
- A searchable, semantic memory of your Notion content in Supabase
- A RAG Agent that produces context-aware, explainable outputs instead of opaque, rule-based reactions
- Structured logs and alerts so you can trust what is happening behind the scenes
It is a big upgrade from simple “if X then Y” rules, especially when your content and context actually matter.
Next steps to take this further
- Customize the RAG Agent’s system message and prompt templates so it speaks your domain language.
- Extend the workflow to write directly back to Notion via the Notion API, creating or updating pages and blocks automatically.
- Add role-based access controls and auditing around your automation to satisfy organizational security requirements.
Call to action: make your Notion updates less painful
If you want a copy of this n8n template or help adapting it to your own Notion workspace, reach out to our automation team or subscribe to our newsletter for more templates and tutorials.
Ready to escape repetitive Notion updates?
- Deploy the webhook in n8n
- Connect your OpenAI, Supabase, Google Sheets, and Slack credentials
- Send a test payload and watch the workflow do the tedious parts for you
Your Notion updates can be smarter, faster, and mostly hands-off in just a few minutes.