Automate Proxmox with n8n + AI Agent
On a quiet Tuesday evening, Mia stared at her Proxmox dashboard for what felt like the hundredth time that day. She was the lone DevOps engineer at a fast-growing startup, and every new feature launch meant another wave of virtual machines to create, resize, migrate, or delete. None of it was hard, but all of it was constant.
Slack messages like “Can you spin up a test VM with 4GB RAM?” or “Please delete VM 105 on psb1” pinged her at all hours. She knew Proxmox had a powerful REST API, and she had heard about n8n and AI agents, but connecting all three into something reliable felt like another project she did not have time for.
Then one day she came across an n8n workflow template that promised exactly what she needed: an AI agent powered by Google Gemini, wired directly into the Proxmox REST API, wrapped in a safe, structured, and auditable automation layer.
This is the story of how Mia went from manual VM babysitting to conversational, API-driven automation with n8n, Proxmox, and an AI agent.
The pain: repetitive VM management and fragile scripts
Mia’s problems were not dramatic, just relentless:
- Endless repetitive VM lifecycle tasks like creating, cloning, starting, and deleting VMs
- Hand-written curl scripts that broke whenever parameters changed
- Colleagues who could not use the Proxmox UI safely but still needed VMs on demand
- Fear of making a typo in a critical API call and impacting production
She wanted something better. Ideally, her teammates could simply type natural-language requests like “Create a VM with 2 cores and 4GB RAM on psb1” and an automated system would handle the rest. It needed to be:
- Flexible enough to understand human language
- Strict enough to never send malformed or dangerous API calls
- Auditable, so she could see exactly what had been done and by whom
That is when she decided to try the n8n Proxmox AI agent template.
The discovery: an n8n workflow that speaks Proxmox and human
The template description sounded almost too good to be true. It combined:
- n8n for low-code automation and routing
- Proxmox REST API for full control over VM lifecycle
- Google Gemini as an AI agent to translate natural language into structured API commands
Instead of Mia writing complex logic for every possible VM operation, the workflow used an AI agent to interpret plain text and then enforced a strict JSON schema before anything touched Proxmox.
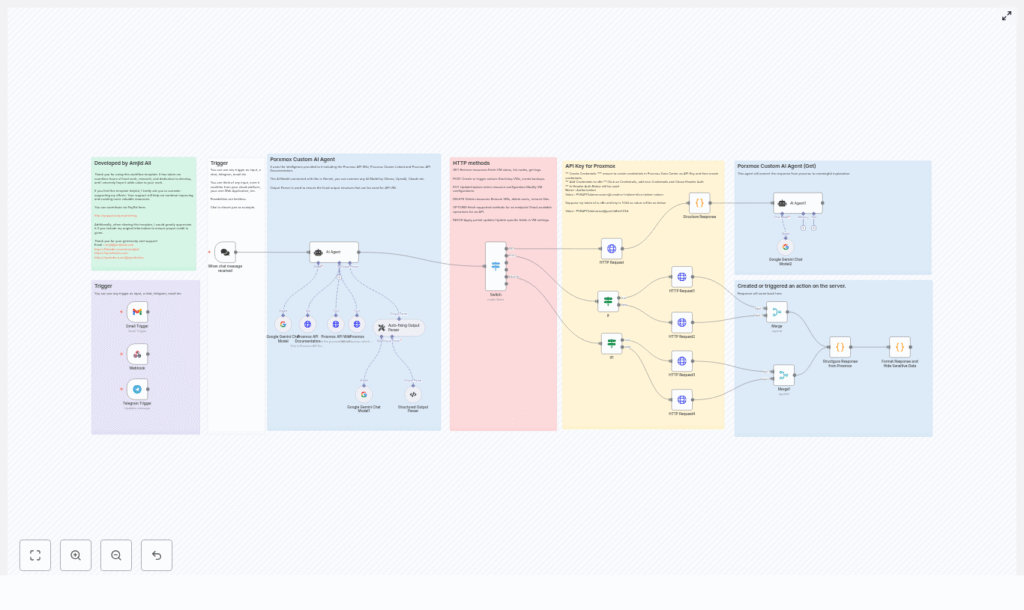
How the architecture clicked for Mia
As Mia explored the template in n8n, she realized it followed a clear architecture that mapped perfectly to her needs. The workflow was broken into logical sections:
- Triggers to capture user intent from chat, Telegram, Gmail, or webhooks
- AI Agent (Gemini) to understand the request and generate a structured command
- Structured output and auto-fixing parsers to enforce valid JSON
- Switch and If nodes to route by HTTP method and payload presence
- HTTP Request nodes to talk directly to the Proxmox API
- Response formatting to redact secrets and return human-friendly results
Instead of a typical “click here, then there” tutorial, she began to see a story: user intent flows in, the AI interprets it, the workflow validates it, and only then does Proxmox get a clean, safe API call.
Rising action: Mia wires up the first trigger
Mia started simple. She configured a single n8n webhook trigger that her teammates could hit from a chat integration. The idea was straightforward:
Someone would send a message like:
“Create a VM with 2 cores, 4GB RAM, and 40GB disk on psb1 using virtio.”
The trigger would forward that text to the AI agent node inside n8n. The template already supported multiple triggers, including:
- Chat messages
- Telegram
- Gmail
- Plain n8n webhooks
She liked that she could add more channels later without touching the core logic.
The AI agent: translating human requests into strict JSON
The heart of the workflow was the AI agent node using Google Gemini. It was configured with clear instructions:
- Interpret natural-language input like “Start VM 202 on psb1”
- Reference Proxmox API documentation and wiki tools embedded in the workflow
- Always return a strict JSON object with
response_type,url, anddetails
When Mia tested her first request, the agent produced output like this:
{ "response_type": "POST", "url": "/nodes/psb1/qemu", "details": { "vmid": 201, "cores": 2, "memory": 4096, "net0": "virtio,bridge=vmbr0", "disk0": "local:32,format=qcow2", "sockets": 1 }
}
It was exactly what she wanted: human intent on one side, clean Proxmox API parameters on the other.
The turning point: enforcing structure so nothing breaks
Mia had used AI tools before and knew they could occasionally hallucinate or format JSON incorrectly. The template anticipated that problem.
Structured Output Parser and Auto-fixing Parser
Right after the AI agent, the workflow passed the JSON through two critical nodes:
- Structured Output Parser to enforce the exact schema
- Auto-fixing Output Parser to re-prompt or correct the AI if the schema was violated
If the AI ever produced malformed JSON or missed required fields, these nodes would catch it and fix or retry before n8n attempted any Proxmox call. That meant fewer broken executions and a much lower chance of sending a bad request to the API.
For Mia, this was the turning point. The workflow did not just “use AI,” it wrapped the AI in strict validation. That combination of flexibility and safety was what made her comfortable moving toward production usage.
Routing logic: from JSON command to the right Proxmox call
Once the JSON command passed validation, the workflow used n8n’s routing nodes to decide what to do next.
Switch and If nodes in action
The response_type field from the AI output told n8n which HTTP method to use. The Switch node checked whether it was:
GETPOSTPUTDELETEOPTIONS- or
Invalid
From there, If nodes checked whether a details payload existed. If it did, the workflow attached it as a JSON body. If not, it called endpoints that did not require a payload.
This routing layer turned the AI’s structured output into a deterministic, auditable set of HTTP Request nodes, each mapped to specific Proxmox API endpoints.
Talking to Proxmox: HTTP Request nodes that do the real work
At the bottom of the workflow, Mia found the HTTP Request nodes that actually spoke to Proxmox. They handled:
- Header-based authentication using a
PVEAPITokenin theAuthorizationheader - The
allowUnauthorizedCertsflag for self-signed TLS certificates (used cautiously) - Setting the HTTP method and attaching a JSON body when needed
Because the AI and parsers had already enforced the structure, these nodes could focus on one job: send a clean request to the right Proxmox endpoint and return the response.
Default behaviors that made Mia’s life easier
As Mia experimented, she discovered a few default behaviors built into the template that removed even more friction:
- If no node was specified in the request, the system defaulted to psb1.
- The AI agent could query Proxmox to find the next available
vmidby checking the highest existing ID, so users did not have to supply it. - Optional fields that users omitted were stripped out, allowing Proxmox to apply its own defaults cleanly.
These conveniences meant her teammates could be less precise in their wording while still getting correct, safe behavior.
Security: Mia’s non-negotiable requirement
Before she let anyone else touch the system, Mia walked through the template’s security recommendations and added her own checks.
Security and best practices she followed
- Stored API tokens in n8n Credentials using Header Auth, never hard-coded in nodes or messages
- Created a dedicated PVE API token in Proxmox with only the permissions the automation needed
- Confirmed that sensitive values were redacted in the response-formatting node before being sent back to users
- Preferred valid TLS certificates on Proxmox and only used
allowUnauthorizedCertsfor tightly controlled internal workflows - Monitored API activity using both Proxmox logs and n8n execution history
With these in place, she felt confident the workflow would not leak secrets or overstep its privileges.
Real-world examples from Mia’s daily work
Within days, Mia had several everyday tasks fully automated through the template.
1. Creating a VM with natural language
A developer sent a request:
“Create a VM with 2 cores, 4GB RAM, and 40GB disk on psb1 using virtio.”
The AI agent produced:
{ "response_type": "POST", "url": "/nodes/psb1/qemu", "details": { "cores": 2, "memory": 4096, "disk0": "local:40,format=qcow2", "net0": "virtio,bridge=vmbr0" }
}
The workflow validated the JSON, routed it to the correct HTTP Request node, and Proxmox created the VM. The response was reformatted into a human-friendly confirmation message, with any sensitive fields redacted.
2. Deleting a VM safely
Another teammate asked:
“Delete VM 105 on psb1.”
The agent emitted a DELETE request with:
/nodes/psb1/qemu/105
Again, the routing logic handled the method, and the Proxmox API did the rest.
3. Starting and stopping VMs on demand
For operations like starting or stopping VMs, Mia saw clean mappings such as:
Input:
“Start VM 202 on psb1.”
Resulting call:
POST /nodes/psb1/qemu/202/status/start
Her team could now manage VM lifecycles conversationally without direct access to the Proxmox UI.
How Mia set it up: her personal checklist
Looking back, Mia realized that getting from “curious” to “fully working” followed a clear setup path. Here is the sequence she used:
- Create a PVE API token in Proxmox Data Center and assign only the necessary permissions.
- Add the token to n8n Credentials as Header Auth with:
- Header name:
Authorization - Value format:
PVEAPIToken=<user>@<realm>!<token-id>=<token-value>
- Header name:
- Install or enable the AI provider node (Gemini in the template) and configure its credentials.
- Import the workflow template and adjust the Proxmox base URLs if her cluster used different addresses.
- Run dry-run queries and inspect n8n execution logs before enabling production triggers.
This gave her the confidence that every part of the chain, from AI output to Proxmox response, behaved as expected.
When things went wrong: troubleshooting in the real world
Not everything worked perfectly on the first try, but the template included practical troubleshooting tips that saved her time.
- HTTP 401/403 Mia checked token correctness and privileges in Proxmox when she hit authentication errors.
- Blank or malformed JSON from the AI She inspected the Structured Output Parser and Auto-fixing Parser logs to see how the workflow re-prompted the agent.
- Self-signed certificate issues For internal environments, she temporarily enabled
allowUnauthorizedCertswhile planning a move to valid certificates. - Unexpected routing behavior When the AI returned
Invalidasresponse_type, the workflow responded with guidance to the user, and she refined the prompt instructions where needed.
Extending the workflow: Mia’s roadmap
Once the basics were stable, Mia started thinking about how to extend the automation further.
- Swap Gemini for other LLM providers like OpenAI, Ollama, or Claude by changing the chat model node and credentials.
- Add RBAC checks so that only certain users could trigger destructive operations like delete or reset.
- Log every executed command to an external system like Elastic, Splunk, Slack, or Microsoft Teams for audit trails and alerts.
- Support multiple tenants or workspaces by adding tenant context into the AI prompt and Proxmox requests.
The template gave her a solid foundation, and n8n’s modular design made these extensions feel approachable instead of overwhelming.
The resolution: from constant interruptions to controlled automation
A few weeks after adopting the n8n Proxmox AI agent template, Mia noticed something surprising. The constant Slack pings had dropped. Her teammates still got the VMs they needed, but now they sent natural-language requests that the workflow handled automatically.
She had:
- Turned chat and webhook inputs into valid Proxmox API requests
- Reduced mistakes using a strict JSON schema and auto-fixing parsers
- Enabled complex tasks like cloning, resizing, and migrating VMs via natural language
- Audited and formatted responses before they reached users
Most importantly, she reclaimed focus time for higher-value work while her automation quietly managed VM lifecycles in the background.
Try the same journey with your own Proxmox cluster
This n8n template is more than a quick integration. It is a reusable, structured foundation for conversational and automated control over Proxmox using the REST API, AI agents, and safe routing logic.
Get started in your environment:
- Import the workflow into your n8n instance.
- Add your Proxmox API token to Credentials using Header Auth.
- Run a simple test like: “List all VMs on psb1.”
If you need help customizing the workflow, want a commercial integration, or prefer a walkthrough video, you can reach out via the author links in the template notes.
Call to action: Import the template, secure your credentials, and start automating routine Proxmox tasks today. Share your feedback or feature requests so this automation can keep evolving with real-world needs.