Automate Ticket Urgency Classification with n8n
Every support ticket that lands in your queue represents a customer waiting for help. The challenge is simple to describe yet hard to solve: which tickets deserve attention right now, and which can safely wait?
Manually scanning messages or juggling rigid rules can quickly become overwhelming. As your volume grows, the cost of misjudging urgency grows with it: delayed responses, stressed teams, and lost opportunities to delight your customers.
This is where automation becomes more than a convenience. It becomes a way to protect your focus, reclaim your time, and allow your team to work on the problems that truly need human judgment. In this guide, you will walk through an n8n workflow template that does exactly that: it automatically classifies ticket urgency, logs the results, and alerts you if anything goes wrong.
Along the way, you will see how embeddings, a Pinecone vector store, a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) agent, and lightweight memory come together to create a powerful, reliable automation. Think of this template as a starting point, a foundation you can build on as you automate more of your support operations.
From reactive triage to intentional focus
Many teams start with simple, rule-based filters. If the subject contains “urgent” or “ASAP”, mark it high priority. If it includes a certain product name, route it to a specific queue. These rules help at first, but they quickly hit a ceiling.
Real tickets are messy. Customers use different languages, informal phrasing, and unexpected descriptions. Critical issues may not contain any obvious “urgent” keywords at all. As a result, your rules either become too complex to maintain or too simplistic to trust.
An AI-powered urgency classifier changes this dynamic. Instead of matching exact words, it understands meaning. It can interpret nuance, context, and multilingual inputs, so you can classify tickets accurately without constantly tweaking rules.
Why an AI-powered urgency classifier is worth it
- Better accuracy on real-world language – Embeddings and vector search capture semantic meaning, so the system can handle varied phrasing, typos, and multilingual content.
- Adaptable over time – You can improve performance by adding more examples or retraining embeddings, rather than rewriting rules from scratch.
- Easy to integrate – The n8n template connects with tools you already use, such as Google Sheets, Slack, and your helpdesk platform.
Most importantly, this kind of automation frees your team from reactive triage. Instead of constantly firefighting, you can focus on resolving the issues that truly matter, faster and more consistently.
Adopting an automation mindset
Before diving into the technical steps, it helps to view this workflow not just as a one-off project, but as a stepping stone toward a more automated, focused way of working.
Automation in n8n does not have to be perfect on day one. You can start with a working template, test it on a small batch of tickets, and then gradually refine prompts, thresholds, and routing rules. Each improvement compounds over time.
Think of your support pipeline as a living system. As you learn more about your data and your customers, you can keep iterating. The template you are about to explore is designed to be modular, so you can extend it with feedback loops, auto-assignment, and multilingual support as your needs evolve.
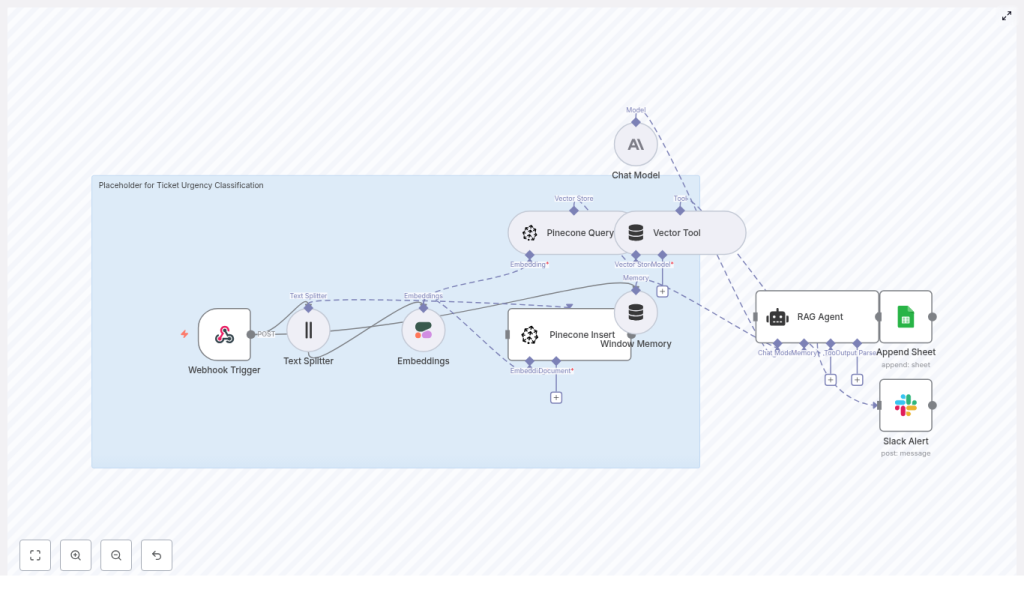
Meet the n8n template that classifies ticket urgency
The provided n8n workflow template orchestrates a complete AI-powered classification pipeline. It receives incoming tickets, processes their content into embeddings, stores and retrieves contextual information from Pinecone, uses an Anthropic-based RAG agent to decide urgency, and logs everything into Google Sheets. If anything fails, a Slack alert notifies your team.
Let us walk through this journey step by step so you can see how the pieces fit together and where you might customize the workflow for your own environment.
1. Webhook Trigger – your gateway for incoming tickets
The journey begins with a Webhook Trigger node in n8n. This node listens for incoming HTTP POST requests from your helpdesk system or any other source that can send ticket data.
Your ticket payload should include at least:
- Ticket ID
- Subject
- Description or message body
- Metadata such as customer, current priority (if any), or tags
Once configured, every new ticket automatically flows into your classification pipeline without manual intervention.
2. Text Splitter – preparing text for embeddings
Some tickets are short and concise; others are long, with detailed context, logs, or back-and-forth replies. To handle long descriptions effectively, the workflow uses a Text Splitter node.
This node breaks long text into smaller chunks that are easier to embed and search. The template uses example settings such as:
chunkSize = 400chunkOverlap = 40
The overlap helps preserve context between chunks so the model does not lose important details at the boundaries. This step sets the stage for accurate embeddings and better retrieval later on.
3. Embeddings with Cohere – turning text into vectors
Next, the workflow passes each text chunk to a Cohere Embeddings node. Here the text is converted into high-dimensional vectors using the embed-english-v3.0 model.
Each resulting vector is stored along with metadata, such as:
- Ticket ID
- Chunk index or position
This metadata makes it easy to trace any retrieved vector back to the original ticket text, which is crucial for interpretability and debugging.
4. Pinecone Insert – building your vector store
With embeddings created, the workflow inserts them into a Pinecone index. In the template, that index is named ticket_urgency_classification.
This Pinecone index acts as your semantic knowledge base. It allows the workflow to quickly search for similar tickets or relevant context whenever a new ticket needs to be classified. Over time, as you add more examples, this index becomes a powerful source of domain-specific knowledge.
5. Pinecone Query and Vector Tool – retrieving context on demand
When it is time to classify a ticket, the workflow uses a Pinecone Query node to search the index and retrieve the most relevant vectors. These represent tickets or documents that are semantically similar to the one you are currently processing.
A Vector Tool wraps this store so that the RAG agent can call it directly to fetch contextual documents in real time. This is what makes the workflow retrieval-augmented: the model does not rely solely on its pre-trained knowledge, it also consults your own data.
6. Window Memory – keeping short-term context
To support more complex scenarios, the template includes a Window Memory component. This keeps short-term state for the RAG agent, preserving recent interactions or clarifications.
Even if you start with simple one-shot classifications, this memory layer gives you a clear path to expand into multi-turn workflows later, such as chat-based triage or follow-up questions when the model is uncertain.
7. Chat Model and RAG Agent (Anthropic) – deciding urgency
At the heart of the workflow sits a Chat Model + RAG Agent powered by Anthropic. This agent receives:
- The ticket text
- Retrieved context from Pinecone
- A structured classification prompt
Based on this information, the agent decides the ticket’s urgency, typically returning structured output such as JSON with fields like:
urgency: "High" | "Medium" | "Low"rationale– an explanation of the decisionconfidence– a numeric score you can use for routing
This structured output is key. It allows downstream nodes to parse urgency and confidence reliably, without fragile pattern matching or regular expressions.
8. Append Sheet – logging results in Google Sheets
Once the RAG agent has classified the ticket, the workflow uses an Append Sheet node to log the result in a central Google Sheets document.
Typical columns include:
- Ticket ID
- Timestamp
- Urgency level
- Rationale
- Model confidence score
This log becomes your source of truth for tracking, metrics, audits, and continuous improvement. It also makes it simple to build dashboards or share insights with stakeholders.
9. Slack Alert on Error – staying in control
Automation should not be a black box. To keep you informed, the template includes a Slack Alert path that triggers on error.
If any node fails, such as an API timeout or rate limit error, a message is sent to a dedicated #alerts channel. This separation of alerts helps your operations team react quickly to issues without constantly checking logs.
Designing prompts and logic for reliable classification
The power of this workflow comes not only from its architecture but also from how you design the prompts and decision logic. Here are practical tips to help you reach reliable, production-ready performance.
Prompt and data preparation tips
- Use a few-shot prompt in the RAG agent that includes clear examples of High, Medium, and Low urgency tickets. Show both labels and rationales so the model learns how you think.
- Normalize ticket text before embedding. For example, lowercase text, remove noisy HTML, and redact personally identifiable information (PII) where necessary.
- Return structured JSON output from the agent. This makes it easy for downstream nodes to parse fields like urgency and confidence.
- Define a confidence threshold such as 0.7. If the model’s confidence falls below this value, route the ticket to a human review queue or assign a special urgency like “Review”.
These small design decisions help you build trust in the system and make it easier to iterate safely.
Scaling, performance, and cost as you grow
As you move from a pilot to a production deployment, performance and cost become increasingly important. The template is designed to scale, and a few practices can keep your system both fast and cost-effective.
- Batch embedding inserts when importing historical data. Instead of inserting one embedding at a time, group them to reduce overhead.
- Limit the number of retrieved vectors in Pinecone. Settings such as
top_k = 3-5are often enough to give the RAG agent good context while keeping token usage and latency under control. - Use approximate nearest neighbor settings in Pinecone for faster queries, and tune your index pod size to match your read and write throughput.
- Prune or compress old vectors if you do not need long-term retention for certain tickets. This helps manage storage and keeps your index lean.
By treating performance as part of your design, you can scale confidently without surprises on speed or cost.
Measuring impact and improving over time
Automation is not a set-and-forget effort. The most successful teams treat their workflows as products that evolve. With this template, you have built-in tools for monitoring and evaluation.
Key metrics to track
- Classification accuracy, measured through periodic human audits of a sample of tickets.
- False positives and false negatives for High urgency tickets, since these have the biggest impact on customer experience.
- End-to-end latency, from webhook trigger to logging in Google Sheets.
- Failure rates and error patterns, based on alerts from your Slack channel.
A simple dashboard that shows daily ticket counts by urgency level can help you quickly spot regressions after model updates or prompt changes. Over time, you will see your automation grow more accurate and more aligned with your business needs.
Troubleshooting common issues with confidence
As you experiment and refine, you may encounter a few common challenges. Here is how to approach them without losing momentum.
1. Mismatched embedding dimensions
If you see errors related to vector dimensions, check that the Cohere model you are using matches the vector dimension expected by your Pinecone index. If you change the embedding model, you will need to rebuild or reindex your Pinecone collection so everything aligns.
2. Rate limits and API errors
APIs occasionally fail or throttle requests. Configure exponential backoff and retries in n8n for transient errors. For persistent problems, forward error payloads to Slack so a human can investigate quickly.
3. Noisy or inconsistent predictions
If the RAG agent returns inconsistent urgency labels, consider:
- Refining your prompt with clearer instructions and more examples.
- Adding more labeled examples into your Pinecone index to give the model richer context.
- Layering simple business rules on top, such as “if the ticket contains ‘data breach’, mark as High automatically”.
These adjustments can dramatically stabilize your results without major architectural changes.
Staying secure and compliant
As you automate more of your support operations, it is important to keep security and compliance in focus.
- Redact or remove PII before sending text to third-party APIs, unless you have appropriate data processing agreements in place.
- Use least-privilege credentials for Pinecone, Cohere, Anthropic, and Google Sheets, and rotate keys periodically.
- Audit access to Google Sheets and, where possible, restrict the append sheet to a dedicated service account.
Building these practices into your workflow from the start makes it easier to scale responsibly.
Extending the workflow as your ambitions grow
This n8n template is intentionally modular. Once you have it running smoothly, you can extend it to support richer workflows and deeper automation.
- Auto-assign High urgency tickets to on-call agents using your helpdesk API, reducing response times even further.
- Create feedback loops by allowing agents to correct urgency in Google Sheets, then periodically re-index corrected examples in Pinecone to improve accuracy.
- Support multilingual tickets by detecting language and using language-specific embedding models or routing logic.
Each extension builds on the foundation you already have, so you can expand your automation one step at a time.
Deployment checklist – your launchpad
Before you turn this workflow loose on production traffic, walk through a quick deployment checklist. This keeps your rollout smooth and predictable.
- Verify webhook authentication and confirm the incoming payload schema matches what your nodes expect.
- Confirm Cohere, Pinecone, and Anthropic API keys are configured correctly in n8n.
- Validate the Pinecone index name and ensure the vector dimension matches your embedding model.
- Test the RAG prompt on a set of labeled tickets and tune the
top_kretrieval size for best performance. - Enable Slack alerts for onError paths so issues surface immediately.
Once you have checked these items, you are ready to run a small batch test and observe the results with confidence.
Conclusion – a foundation for smarter support operations
Automating ticket urgency classification with n8n, embeddings, and Pinecone is more than a technical upgrade. It is a shift in how your team spends its time. Instead of manually sorting and guessing which tickets matter most, you let an AI-powered workflow handle the heavy lifting.
The result is faster, more consistent triage and a support team that can focus on high-impact work and meaningful customer conversations. You are not just saving minutes on each ticket, you are building an infrastructure that scales with your growth.
Start with the provided template, run it on a validation set, tune your prompts and confidence thresholds, and add human feedback loops. Each iteration brings you closer to a support operation that is proactive, data-driven, and resilient.
Call to action: Ready to put this into practice? Import the template into your n8n instance, connect