Automate Transcription with n8n, OpenAI & Notion
Convert raw audio into structured, searchable knowledge with a fully automated n8n workflow. This reference guide documents a complete transcription pipeline that uses Google Drive for ingestion, OpenAI for transcription and summarization, Notion for knowledge management, and Slack for notifications.
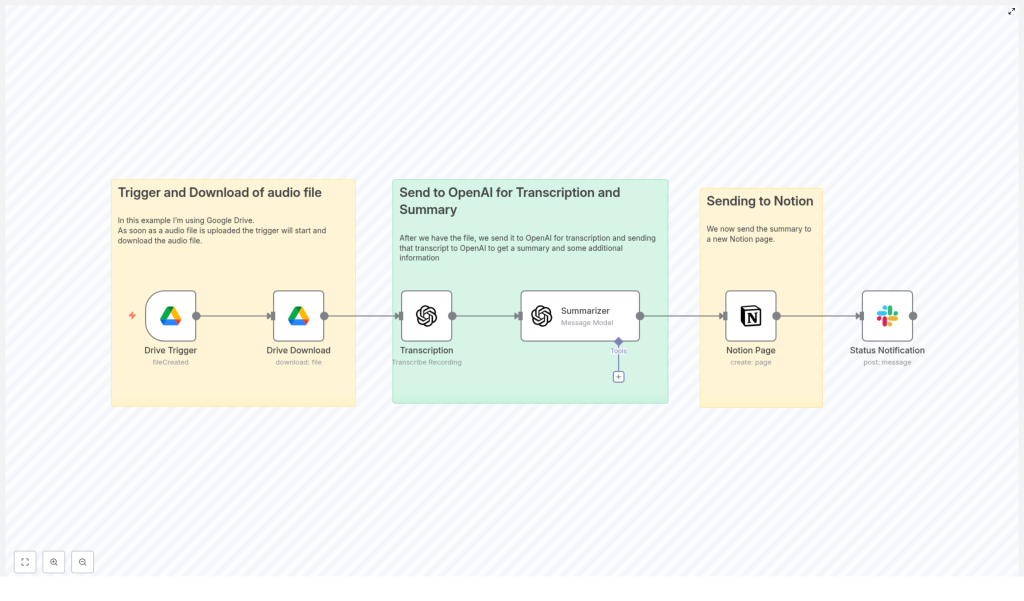
The data flow is:
Google Drive Trigger → Google Drive Download → OpenAI Audio Transcription → GPT JSON Summary → Notion Page Creation → Slack Notification
1. Workflow Overview & Use Cases
1.1 Purpose of the Automation
Manual transcription is slow, inconsistent, and difficult to scale across teams. By using n8n to orchestrate transcription and summarization, you can:
- Reduce manual work for meeting notes, call summaries, and content production.
- Standardize how summaries, action items, and follow-ups are captured.
- Centralize knowledge in Notion so it can be searched, tagged, and shared.
- Ensure every recording automatically produces usable outputs.
1.2 Typical Scenarios
This n8n template is particularly useful for:
- Podcast production – generate episode summaries, notes, and timestamps-ready content.
- Product and engineering teams – document design reviews, architecture discussions, and decisions with action items.
- Customer success and sales – archive customer calls in Notion and track follow-ups from conversations.
2. Architecture & Data Flow
2.1 High-level Architecture
The workflow is built around n8n as the orchestration layer:
- Input: Audio files uploaded to a specific Google Drive folder.
- Processing:
- File download into n8n as binary data.
- Transcription via OpenAI audio API (Whisper-style transcription).
- Summarization via a GPT model with a structured system prompt.
- Output:
- Notion page populated with title, summary, and structured fields.
- Slack message to notify stakeholders that the transcript and summary are ready.
2.2 Node Sequence
- Google Drive Trigger – watches a folder for new audio files.
- Google Drive (Download) – retrieves the file as binary data.
- OpenAI Audio Transcription – converts audio to text.
- GPT Summarizer – transforms raw transcript into structured JSON.
- Notion Page – creates a page or database entry.
- Slack Notification – sends a status update with a link to the Notion page.
3. Node-by-Node Breakdown
3.1 Google Drive Trigger Node
Role: Entry point. Detects when a new audio file is added to a specific Google Drive folder and starts an n8n execution.
3.1.1 Configuration
- Resource: Typically “File” (depending on the node version).
- Event:
fileCreatedso that each new file triggers the workflow. - Folder: Set to the target folder ID where audio files are uploaded.
- Polling frequency: For near real-time, a 1-minute interval is common. Adjust based on API limits and latency requirements.
- Credentials: Google Drive credentials with at least read access to the folder.
3.1.2 Behavior & Edge Cases
- Only files created after the workflow is activated are typically detected.
- Ensure the authenticated account or service account can access the folder, otherwise no events will be received.
- Unsupported file formats will still trigger the workflow, so you may want to filter by extension (e.g.,
.mp3,.wav,.m4a) in later nodes.
3.2 Google Drive Node (Download)
Role: Converts the reference from the trigger into actual binary content for downstream nodes.
3.2.1 Configuration
- Operation:
download(or equivalent “Download file”). - File ID: Mapped from the trigger node output (e.g.,
{{$json["id"]}}). - Binary property: Set to a property name such as
data. This property will contain the binary audio.
3.2.2 Behavior & Edge Cases
- If the file is large, download time may be noticeable. Monitor execution time and consider n8n’s timeout limits.
- Ensure the binary property name is consistent with what the OpenAI node expects.
- If the file is missing or permissions change between trigger and download, the node will fail. Add error handling if this is likely.
3.3 OpenAI Audio Transcription Node
Role: Converts the binary audio into a text transcript using OpenAI’s audio transcription endpoint (Whisper-style models).
3.3.1 Configuration
- Node type: OpenAI or LangChain/OpenAI node configured for audio transcription.
- Operation / Resource:
audio/transcriptionsor “Transcribe” depending on node version. - Binary property: Reference the same property used in the Google Drive node (e.g.,
data). - Model: Use an appropriate audio model. Whisper-style models or the OpenAI audio transcription endpoint are suitable for most use cases.
- Language (optional): If you know the primary language of the recording, set the language parameter to improve accuracy and reduce misdetections.
3.3.2 Behavior & Edge Cases
- Noise and audio quality: Noisy or low-quality audio may reduce accuracy. Consider pre-processing outside n8n if needed.
- Multilingual recordings: If language is unknown, let the model auto-detect. For consistent output, prefer setting the language explicitly when possible.
- File size limits: Very long recordings may approach API limits. For extremely long audio, consider splitting before upload or implementing a chunking strategy.
- Rate limits: Handle rate limit errors with retries in n8n (see the error handling section).
3.4 GPT Summarizer Node
Role: Converts the raw transcript into a structured JSON summary that can be stored and queried easily.
3.4.1 Configuration
- Node type: OpenAI (Chat) or LangChain/OpenAI configured for chat completion.
- Model: The example uses
gpt-4-turbo-preview. You can substitute with a different GPT model depending on cost and quality trade-offs. - Input:
- Map the transcript text from the previous node as the user content.
- Provide a detailed system prompt that instructs the model to output only JSON.
3.4.2 JSON Output Structure
The system prompt should instruct the model to return a JSON object with the following fields:
titlesummarymain_pointsaction_items(date-tagged if relative dates are mentioned)follow_upstories,references,arguments,related_topicssentiment
For consistency, instruct the model to:
- Return JSON-only with no additional commentary.
- Use ISO 8601 format for absolute dates (for example,
2025-10-24). - Apply a clear rule for converting relative phrases such as “next Monday” into absolute dates, if your use case requires it.
- Follow a provided example JSON schema in the prompt.
3.4.3 Handling the Response
- The model’s output may be returned as a string. In that case, parse it to JSON in a subsequent node before mapping to Notion.
- Validation is important. Use a validation or code node to confirm that the response is valid JSON and contains all required keys.
- For very long transcripts, consider chunking the transcript and summarizing each chunk before combining summaries into a final pass to avoid token limits.
3.5 Notion Page Node
Role: Persists the structured summary as a Notion page or database item, making transcripts searchable and organized.
3.5.1 Configuration
- Node type: Notion.
- Operation: Typically “Create Page” or “Create Database Entry”, depending on your workspace setup.
- Credentials: Notion integration with permissions to create pages in the chosen workspace or database.
- Mapping:
- Title: Map from the
titlefield in the GPT JSON output. - Summary content: Use the
summaryfield as the main text block. - Database properties (optional): Map fields such as tags, meeting date, and participants from the JSON structure to Notion properties.
- Title: Map from the
3.5.2 Behavior & Edge Cases
- If the JSON parsing fails or a required field is missing, the Notion node will likely error. Validate JSON before this step.
- Ensure that property types in Notion (e.g., date, multi-select, people) match the data you are sending.
- Notion rate limits are usually forgiving for this use case, but heavy usage may require backoff or batching.
3.6 Slack Notification Node
Role: Notifies stakeholders that processing has completed and provides a direct link to the Notion page.
3.6.1 Configuration
- Node type: Slack.
- Operation: Typically “Post Message”.
- Channel: A team channel or a dedicated notifications channel.
- Message content:
- Include a short one-line summary.
- Include the URL of the newly created Notion page.
- Credentials: Slack app or bot token with permission to post in the chosen channel.
3.6.2 Behavior & Edge Cases
- If Slack is temporarily unavailable, the node can fail. Consider retries or a fallback email notification.
- Check that the bot is invited to the channel where you want to post.
4. Prompt Engineering & Reliability
4.1 Prompt Design Best Practices
- Be explicit: Instruct the model to output only valid JSON, with no extra text.
- Provide an example: Include a complete example JSON object in the system prompt to enforce structure.
- Define constraints: Specify required keys, acceptable value formats, and how to handle missing information.
- Clarify date handling: If you need date-tagged action items, clearly define how to convert relative dates to ISO 8601.
4.2 JSON Validation in n8n
- Use a Code node or dedicated validation node to:
- Parse the string response into JSON.
- Check for required fields like
title,summary, andaction_items.
- If validation fails, send an internal alert or store the raw response for manual inspection instead of writing to Notion.
4.3 Handling Long Transcripts
- Long audio files can produce transcripts that approach model token limits.
- Mitigation strategies:
- Chunk the transcript and summarize each segment separately.
- Combine partial summaries in a final summarization pass.
- Restrict the level of detail requested if only high-level notes are needed.
4.4 Noise and Language Considerations
- For noisy or multilingual recordings:
- Use the language parameter when you know the main language.
- Consider preprocessing audio externally if noise is severe.
5. Security & Access Control
5.1 Credential Management
- Store API keys and OAuth tokens in n8n’s credential storage. Do not hard-code sensitive values directly in nodes.
- Use separate credentials for development, staging, and production environments.
5.2 Principle of Least Privilege
- Google Drive: Limit the integration scope to the folders and files required for the workflow.
- Notion: Restrict the integration to only the databases or pages that need to be created or updated.
- Service accounts: For Google Drive watchers, consider a dedicated service account that centralizes file access rather than relying on individual user accounts.
6. Monitoring, Error Handling & Retries
6.1 Basic Error Handling Patterns
- Transcription retries:
- Configure the OpenAI audio node or a surrounding wrapper to retry on rate limit or transient network errors.
- Administrative alerts:
- If a file fails repeatedly, send a Slack message to an internal admin channel with the file ID and error details.
- Backup logging:
- Optionally log transcripts and summaries to
- Optionally log transcripts and summaries to