Automated AI Code Review with n8n & GitHub
Imagine opening a pull request and getting thoughtful code review comments back in minutes, without waiting for a teammate to be free. That is exactly what this n8n workflow template helps you do.
In this guide, we will walk through how the template listens to GitHub pull request events, grabs the file diffs, builds a smart prompt for an AI reviewer, and then posts contextual comments right back onto the PR. Under the hood, n8n acts as the automation engine, OpenAI (via a LangChain agent) is your “review brain,” and GitHub is the home for your pull requests.
If you are looking to scale lightweight code reviews and save developer time, this setup can quickly become one of your favorite tools.
Why bother automating code reviews at all?
Code review is non‑negotiable if you care about quality, shared understanding, and catching bugs before they hit production. The problem is that a lot of review time gets eaten up by routine stuff: style issues, small edge cases, minor bugs, or missing tests.
That is where an automated AI reviewer shines. Let the AI handle the obvious, repetitive checks so humans can focus on the fun and high‑value conversations: architecture decisions, product trade‑offs, and long‑term maintainability.
With this n8n workflow you can:
- Get fast, consistent feedback on every pull request
- Reduce reviewer fatigue on large or frequent PRs
- Enforce team standards automatically
- Keep humans in charge of final approvals
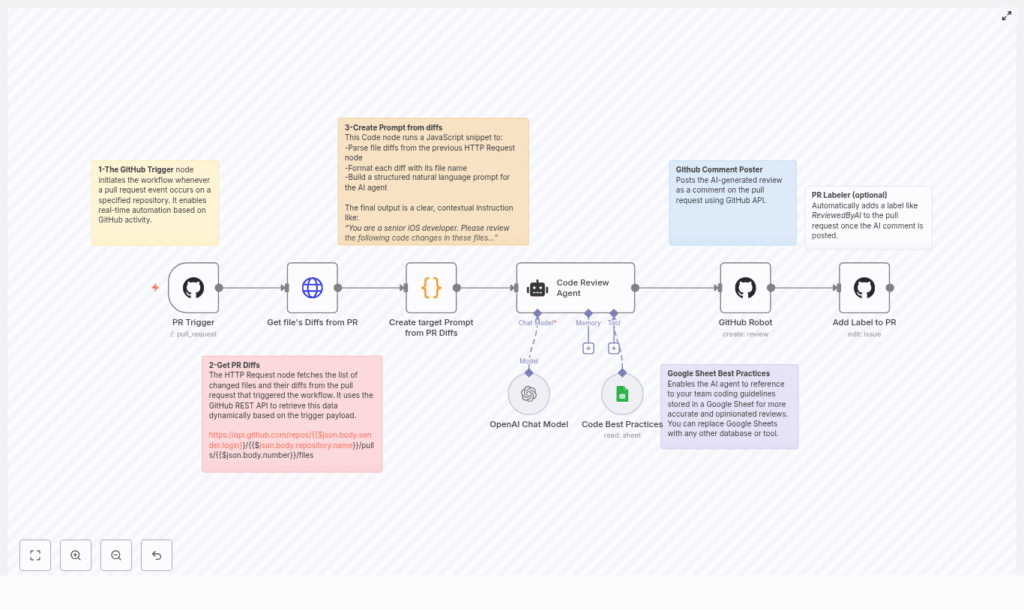
How the n8n AI code review workflow works
Let us zoom out for a second and look at the high‑level flow before diving into each node. The template follows this sequence:
- GitHub PR trigger – n8n listens for
pull_requestevents. - Fetch PR diffs – an HTTP Request node calls the GitHub REST API to get changed files and patches.
- Build the AI prompt – a Code node turns those diffs into a clean, focused prompt for the AI reviewer.
- AI review agent – a LangChain/OpenAI agent analyzes the changes and generates inline‑style comments.
- Post review to GitHub – a GitHub node sends those comments back as a review on the PR.
- Label the PR (optional) – the workflow can tag the PR with something like ReviewedByAI.
- Optional knowledge base – a Google Sheets node (or other source) can feed team guidelines into the AI.
Now let us walk through each part in more detail, and talk about when and why you would use it.
Step-by-step: node-by-node walkthrough
1. GitHub PR trigger – starting the workflow
Everything begins with a GitHub webhook. The first node in the n8n workflow listens for pull_request events on your chosen repository.
Whenever a PR is opened or updated, GitHub sends a payload to n8n. That payload includes information like the repository, pull request number, and the action that was taken. The workflow then kicks off from there.
A couple of practical tips here:
- Keep authentication secure – use GitHub OAuth credentials or a webhook secret rather than exposing anything sensitive.
- Limit noise – configure the webhook to listen only to the events you actually care about, for example when a PR is opened or synchronized.
2. Fetching file diffs from the PR (HTTP Request node)
Once the workflow is triggered, the next job is to figure out what actually changed. For that, the template uses an HTTP Request node that calls the GitHub REST API endpoint:
/repos/{owner}/{repo}/pulls/{pull_number}/filesThe URL is built dynamically from the webhook payload, so the workflow always hits the right repository and pull request.
The response from GitHub includes:
filename– the path of the changed filestatus– for examplemodified,added, orremovedchanges– how many lines changedpatch– a unified diff with the actual line‑level changes for text files
Those patch values are the raw material for your AI code review. Binary files or files without patch data are handled later so the AI does not get confused.
3. Turning diffs into a focused AI prompt (Code node)
Raw diffs are not something you want to just dump straight into an LLM. The template includes a JavaScript Code node that cleans, structures, and prepares the data for the AI agent.
This node:
- Groups diffs by filename so the AI can reason about each file in context.
- Preserves diff blocks to keep line‑level context intact.
- Skips binary files or anything without a
patchfield. - Sanitizes problematic characters (for example, converting triple backticks) so you do not break the AI’s formatting or downstream parsing.
- Includes clear instructions like:
- Review changes file by file
- Generate inline comments
- Avoid restating the code snippet itself
The result is a structured, readable prompt that tells the AI exactly what its job is and how to format the output so you can easily map it back into GitHub comments.
4. Code review agent with LangChain & OpenAI
Next up is the brain of the operation: a LangChain agent backed by OpenAI. This node receives:
- The prompt generated by the Code node
- Any optional team guidelines from tools like Google Sheets
Some configuration tips for this step:
- Pick a conversational model tuned for reasoning and code, such as a modern OpenAI chat model that handles code snippets well.
- Give the agent a short set of rules that describe:
- How to format comments (for example inline suggestions with file and line references)
- What to focus on (bugs, edge cases, readability, tests, etc.)
- What to avoid (restating large chunks of code, overly verbose explanations)
- Keep response size under control. If the PR is large, you can:
- Process it file by file
- Split diffs into chunks
- Limit the maximum number of comments per run
The agent then analyzes the diffs and outputs review comments in a structure that can be turned into GitHub review entries.
5. Posting AI review comments back to GitHub
Once the AI has done its thing, it is time to send those comments back where they belong: onto the pull request itself.
The GitHub node in the workflow uses the GitHub Reviews API to create a review on the PR. It maps the AI output into the fields GitHub expects, such as:
path– the file path the comment refers topositionorline– the location in the diff or filebody– the actual review comment text
The template is set up to send a single review payload that can contain multiple comments. If your agent returns a structured list of suggestions, you can easily adapt the mapping logic to post several inline comments in one go.
6. Adding an AI review label (optional but handy)
Want an easy way to see which PRs have already gone through the AI reviewer? The workflow can optionally add a label like ReviewedByAI to the pull request.
This uses the GitHub Issues/PR edit endpoint to apply the label. It is a small step, but it makes it much easier to:
- Filter PRs that have had automated coverage
- Track adoption over time
- Quickly distinguish between AI‑reviewed and manually‑only reviewed changes
Feeding in team guidelines with Google Sheets
Out of the box, the AI can already give pretty good feedback. But it gets even better when it understands your team’s specific preferences and standards.
The template supports an optional Google Sheets node that acts as a lightweight knowledge base. You can store things like:
- Coding conventions and style rules
- Architecture decisions and patterns to follow
- Linting rules or security guidelines
The LangChain agent can then use this sheet as a reference when generating comments, so its suggestions are more aligned with how your team actually works. If you prefer, you can swap Sheets for another knowledge source like Notion, an internal KB, or a database.
Crafting effective prompts for AI code review
Good prompts are the difference between “meh” suggestions and genuinely useful reviews. The template includes a prompt pattern designed to keep the agent focused and concise.
The instructions typically ask the agent to:
- Focus on changed code only, not unrelated files
- Return inline comments with exact line context and a short, actionable recommendation
- Avoid repeating the code itself and instead explain what should change and why
Here is an example of the kind of high‑level guidance baked into the Code node:
The agent is a senior iOS developer. Please review the following code changes and generate inline comments per file. Do not repeat the code block or filename; create short, actionable suggestions.
You can adapt the role (“senior backend engineer,” “security reviewer,” “frontend specialist,” etc.) and tweak the expectations to better match your stack and priorities.
Security, privacy, and governance considerations
Sending code to an AI service always raises important security questions, and you should absolutely take them seriously. A few safeguards to keep in mind when running this kind of workflow:
- Limit repository access – only enable the automation on repos or branches that are allowed to use external AI tools.
- Redact secrets – run secret scanning or filtering on diffs before sending them to the LLM. Strip out tokens, passwords, or any credentials that might appear in code or config.
- Keep an audit trail – store AI‑generated comments or logs so maintainers can review the history and spot any problematic suggestions.
With some basic governance in place, you can get the benefits of automation without compromising security or compliance.
Practical setup tips for running this in n8n
Before you hit “activate” on the workflow, here are a few practical things that will save you headaches later:
- Handle secrets correctly Store GitHub OAuth tokens and OpenAI API keys using n8n credentials or your preferred secrets manager. Avoid hardcoding keys directly in nodes or code.
- Respect rate limits Both GitHub and OpenAI have rate limits. For busy repos or large PRs, you may want to:
- Batch API calls
- Pause or queue processing for large pull requests
- Limit how often the workflow runs for the same PR
- Control token usage Large diffs can quickly blow through an LLM’s context window. A simple strategy is to:
- Chunk work per file
- Skip low‑value files (for example generated code)
- Cap the number of lines sent per request
- Test on small PRs first Start with a few small pull requests and iterate on:
- Prompt wording
- Output parsing logic
- How comments are mapped back into GitHub
Once you are happy with the behavior, roll it out to more repositories or branches.
Rolling this out to your team: best practices
Dropping an AI reviewer into an existing workflow can be a big change. Here are some patterns that help adoption go smoothly:
- Start opt‑in Begin with a few repositories or enable the bot only on contributor branches. That way you do not overwhelm teams that are not ready yet.
- Show confidence hints Have the agent include a short confidence note or rationale with each suggestion. It gives reviewers a feel for how strongly the AI “believes” its own advice.
- Keep humans in control Treat the AI as a first‑pass reviewer, not the final authority. Developers should still own approvals and decide which suggestions to accept.
- Continuously refine prompts Watch for false positives or noisy comments and adjust prompts or examples. Over time, you will dial in a tone and level of strictness that fits your team.
Troubleshooting common issues
Things not working quite as expected? Here are a few quick checks that often resolve problems:
- No review is posted on the PR
- Confirm the GitHub webhook is firing and delivering to n8n.
- Verify that the GitHub token has the right scopes (
pulls,issues,repo). - Inspect the Code node’s output format to ensure it matches what the GitHub Reviews API expects.
- AI responses are truncated
- Chunk diffs into smaller pieces.
- Switch to a model with a larger context window if available.
- Reduce the number of files or lines processed in a single run.
- API usage is unexpectedly high
- Add throttling or rate limiting in your workflow.
- Focus only on high‑priority paths such as
srcortests. - Skip trivial or generated files where review adds little value.
When this template is a great fit
You will get the most value from this n8n + OpenAI + GitHub pattern if:
- Your team has frequent PRs and limited reviewer time.
- You want consistent enforcement of style and best practices.
- You are comfortable using an AI assistant for low‑risk, first‑pass checks.
- You are already using n8n or looking for a flexible automation layer around GitHub.
It is especially powerful for:
- Junior onboarding, where the AI can highlight common pitfalls
- Large codebases where humans cannot realistically review every small change in depth
- Teams that want to document and enforce custom guidelines via a simple knowledge base
Wrapping up
This automated AI code review template ties together n8n, OpenAI (through LangChain), and GitHub to create a fast, consistent review layer on top of your existing workflow. It will not replace your senior engineers, but it will absolutely reduce their load by handling routine checks and reinforcing team standards.
With the right