Automated CRM Patient Intake Workflow with n8n, Embeddings & RAG
Imagine if every new patient intake just quietly handled itself in the background, organized all the details, made them searchable, and even suggested next steps for your team. No messy copy-paste, no lost context, no “who was supposed to follow up with this person?” moments.
That is exactly what this n8n workflow template does. It ties together form submissions, embeddings, a Weaviate vector store, and a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) agent so you can:
- Ingest patient intake forms automatically
- Split long notes into manageable chunks
- Create embeddings and store them in Weaviate
- Use a RAG agent (powered by a chat model) to process everything intelligently
- Log results into Google Sheets
- Get Slack alerts when something breaks
Let’s walk through how it works, when you should use it, and how to set it up in your own n8n instance.
Why automate CRM patient intake in the first place?
If you are still doing intake manually, you probably know the pain:
- New submissions sit in an inbox waiting for someone to copy them into the CRM
- Details from long notes get summarized inconsistently or missed entirely
- Historical context is scattered across tools and impossible to search properly
By automating CRM patient intake with n8n, embeddings, and RAG, you get:
- Faster triage and routing so new patients are not waiting on manual data entry
- Context-aware responses that use past records and reference data
- Searchable intake history via vector embeddings in Weaviate
- Reliable audit logs and alerts when something fails
In short, you spend less time wrangling data and more time actually helping patients.
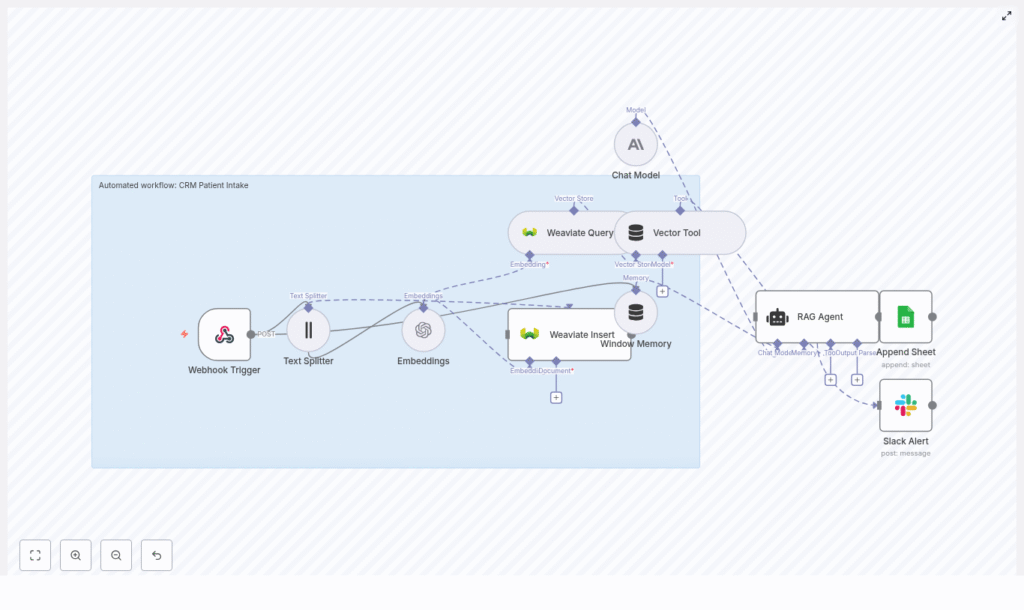
How the workflow fits together: high-level architecture
This template uses a collection of n8n nodes that work together as a pipeline. At a high level, it:
- Listens for incoming form submissions through a webhook
- Splits long text into chunks so embeddings stay meaningful
- Creates embeddings using OpenAI
- Stores and retrieves those embeddings in Weaviate
- Maintains short-term memory for the current intake session
- Runs a RAG agent powered by an Anthropic chat model
- Logs results into Google Sheets
- Sends Slack alerts if anything goes wrong
Here are the key components you will see in the n8n workflow:
- Webhook Trigger – receives POST requests at
/crm-patient-intake - Text Splitter – chunks long text fields (size 400, overlap 40)
- Embeddings (OpenAI) – turns chunks into vectors
- Weaviate Insert & Query – stores and queries vectors in the
crm_patient_intakeindex - Window Memory – keeps short-term session context
- Chat Model (Anthropic) – LLM used by the RAG agent
- Vector Tool & RAG Agent – retrieves context and generates final output
- Append Sheet (Google Sheets) – logs status and audit data
- Slack Alert – notifies a channel when errors occur
When should you use this n8n template?
This workflow is a good fit if:
- You collect patient intake via web forms, portals, or external systems
- You use a CRM or similar system to track patients and follow-ups
- You want a searchable history of patient notes, not just flat text
- You need structured outputs like triage level, recommended follow-up, or formatted CRM entries
Even if your exact tools differ, you can adapt this pattern to your own stack as long as you can hit the webhook and connect to the APIs used here.
Step-by-step: inside the workflow
1. Webhook Trigger – catching new patient submissions
Everything starts with a webhook node. Configure it to accept POST requests at:
/crm-patient-intake
Your form system, middleware, or application should send the patient intake payload to this endpoint whenever a new form is submitted. The payload might look something like this:
Sample webhook payload
{ "patient_id": "12345", "name": "Jane Doe", "submitted_at": "2025-09-01T12:34:56Z", "notes": "Patient reports recurring headaches for 3 months...", "source": "web_form"
}
From here, n8n takes over and moves the data through the rest of the pipeline.
2. Text Splitter – preparing long notes for embeddings
Free-text fields like medical history or notes can get long, and that is where the Text Splitter node comes in. It breaks the text into overlapping chunks so the embeddings stay coherent and token limits are not exceeded.
Recommended settings in the template:
- Chunk size: 400 characters
- Chunk overlap: 40 characters
The overlap helps preserve context across chunks, which makes the later retrieval step much more accurate.
3. Embeddings (OpenAI) – turning text into vectors
Each chunk is then passed to an Embeddings node using a small OpenAI model such as:
text-embedding-3-small
In n8n, store your OpenAI credentials as:
OPENAI_API– your OpenAI API key
These embeddings are what allow you to do semantic similarity search later in Weaviate, which is the backbone of the RAG part of this workflow.
4. Weaviate Insert & Query – building your semantic patient history
Next, the workflow inserts those embedding documents into a Weaviate index named:
crm_patient_intake
The Weaviate Insert node handles storing each chunk along with any useful metadata. Later, a Weaviate Query node searches the same index to retrieve the most relevant context for a given patient or question.
You will configure Weaviate and its credentials in n8n as:
WEAVIATE_API– Weaviate endpoint and API key
This is what makes your intake history actually searchable in a meaningful, semantic way.
5. Window Memory – keeping track of the current session
The Window Memory node stores recent data for the current transaction. Think of it as short-term memory for the RAG agent. It helps the agent keep track of what has already been seen during this specific intake process so responses remain consistent and contextual.
6. Chat Model & RAG Agent – turning context into useful outputs
Now for the “brains” of the operation.
The template uses an Anthropic chat model node as the LLM. You can swap this for another provider if you prefer, as long as you update the credentials and settings.
ANTHROPIC_API– Anthropic API key for the chat model
The RAG agent is configured with a system message like this:
You are an assistant for CRM Patient Intake
Process the following data for task 'CRM Patient Intake':
{{ $json }}
The agent uses:
- Context retrieved from Weaviate via the Vector Tool
- Short-term context from the Window Memory node
With that, it produces a concise output, which could be:
- A recommended follow-up action
- A triage level
- A formatted summary suitable for your CRM
You can customize the prompt to better fit your own intake logic and CRM fields.
7. Append Sheet (Google Sheets) – logging everything for review
Once the RAG agent has done its job, the workflow appends the final status and any key fields to a Google Sheet named:
Log
This gives you:
- An audit trail for each intake
- A simple place to manually review outputs
- A handy data source for downstream teams or reporting
In n8n, store your Google credentials as:
SHEETS_API– Google Sheets OAuth2 credentials
8. Slack Alert – catching errors before they pile up
Things go wrong sometimes. APIs rate limit, vector stores go down, credentials expire. The template already includes a Slack Alert node wired to the onError output of the RAG Agent.
On any error, the workflow sends a message to a Slack channel, for example:
#alerts
The alert includes exception details so your operations team can troubleshoot quickly.
Configure your Slack credentials in n8n as:
SLACK_API– Slack bot token
Configuration checklist: credentials & environment
Before you hit “Execute Workflow”, make sure you have these set up in n8n’s credential manager or as environment variables:
- OPENAI_API – OpenAI API key for embeddings
- WEAVIATE_API – Weaviate endpoint and API key
- ANTHROPIC_API – Anthropic (or your chosen LLM) API key
- SHEETS_API – Google Sheets OAuth2 credentials
- SLACK_API – Slack bot token for error notifications
Once these are in place, you can import the template, hook up the credentials, and start testing.
Security, privacy, and compliance considerations
Because this workflow touches patient data, you need to treat it with care. If your intake forms include PHI, keep in mind:
- Run the workflow in a HIPAA-compliant environment where required
- Enable encryption in transit and at rest for Weaviate and any storage layers
- Use strong access controls and audit logs for all API credentials
- Define data retention policies for both vectorized data and logs
For highly sensitive fields, consider pseudonymization or tokenization before sending anything to third-party APIs, especially LLM providers.
Error handling & observability: going beyond Slack alerts
The template gives you a solid starting point with Slack alerts on errors, but you can expand observability further by:
- Sending logs to an ELK stack, CloudWatch, or your observability platform of choice
- Tracking processing time for each webhook invocation
- Adding retry logic to critical nodes like embeddings and Weaviate insert operations
This helps you catch performance issues and ensure the workflow behaves reliably under load.
Scaling and managing costs
As traffic grows, you will want to keep an eye on both performance and API spend. A few practical tips:
- Batch embeddings when you can, grouping small submissions into a single API call
- Use a smaller embeddings model for storage, and reserve larger or more expensive models for higher value RAG steps if needed
- Scale or shard Weaviate based on query QPS and data volume
That way, you keep the workflow responsive without letting costs get out of control.
Testing & validation before going live
Before you plug this into a real patient intake form, run through a few test cycles:
- Send synthetic test submissions that cover edge cases like:
- Very long notes
- Missing or null fields
- Special characters and unusual formatting
- Validate Weaviate retrieval by querying with known vectors and checking that the right context comes back
- Review the Google Sheets log to confirm formatting, completeness, and correctness of the outputs
This gives you confidence that the pipeline behaves the way you expect before clinicians or coordinators rely on it.
Best practices to get the most from this template
To keep your automated CRM patient intake workflow clean and robust, consider:
- Normalizing text before splitting, such as lowercasing and trimming excessive whitespace
- Adding metadata like submission timestamp, source, or patient ID to each vector document for better filtering
- Limiting PHI sent to external models to only what is absolutely needed
- Documenting your RAG agent system message and updating it as your intake and CRM workflows evolve
These small steps can significantly improve both retrieval quality and compliance posture.
Next steps: getting this running in your n8n instance
Ready to try it out?
- Import the template into your n8n environment (self-hosted or cloud)
- Connect your credentials:
- OpenAI (
OPENAI_API) - Weaviate (
WEAVIATE_API) - Anthropic or your LLM provider (
ANTHROPIC_API) - Google Sheets (
SHEETS_API) - Slack (
SLACK_API)
- OpenAI (
- Send a few test submissions through the webhook
- Tune the RAG agent prompt and outputs to match your CRM fields and triage logic
Once it is tuned, this pipeline can dramatically reduce manual intake work and surface the right patient context exactly when your team needs it.
Call to action: Import this n8n workflow template, hook it up to your tools, and run a few realistic test cases. If you need help adapting it for HIPAA requirements or integrating with a specific CRM, reach out to our team or subscribe for a step-by-step walkthrough.
Want a downloadable JSON of the template or guidance tailored to your stack? Reply with your preferred environment (self-hosted or cloud) and the CRM you are using, and I will send you customized instructions.